Why in the news?
Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved ₹10,700 crore equity infusion for FCI's working capital for 2024-25.
More on news
- FCI started its journey with an authorised capital of ₹100 crores and equity of ₹4 crores. The equity of FCI was increased from time to time.
- The current equity infusion will:
- Strengthens FCI's operational capacity to fulfill its mandate effectively.
- Reduces reliance on short-term borrowings, lowering interest costs and government subsidy.
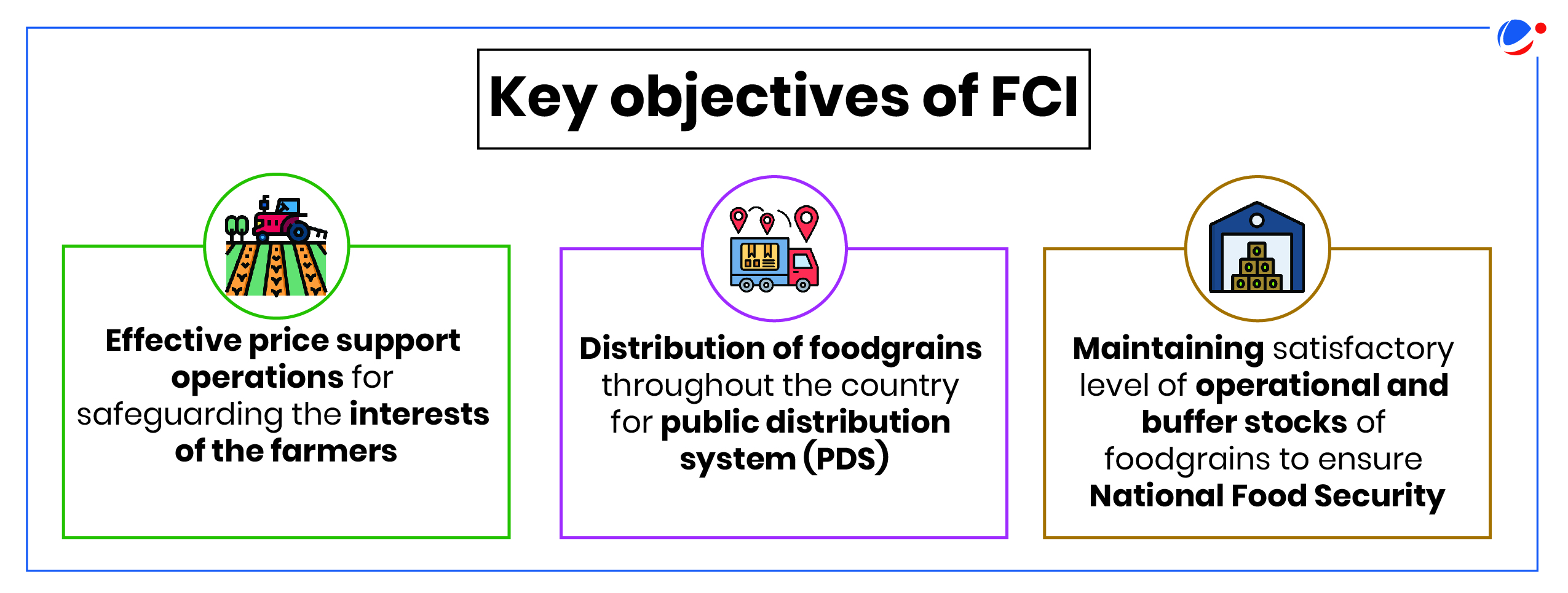
What is Food Corporation of India?
- About: FCI is Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution.
- Genesis: FCI is a statutory body established under the Food Corporation's Act 1964.
- Finance: FCI started its journey with an authorised capital of Rs. 100 Crores and equity of Rs. 4 Crores. The equity of FCI was increased from time to time.
- Key Responsibility: Main agency responsible for execution of food policies of the Gol.
- Functions: It is the nodal central government agency, responsible for the purchase, storage, interstate movement, distribution and sale of food grains.
Working mechanism of Food Corporation of India (FCI
- The FCI, along with state agencies, procures food grains to ensure Minimum Support Price (MSP) for farmers and affordable grains for weaker sections.
- FCI undertakes two types of procurement mechanisms
- Direct Procurement: FCI or State Government Agencies (SGAs) procure food grains, with FCI handling storage and distribution.
- Decentralized Procurement (DCP): States manage procurement, storage, and distribution, handing excess stocks (rice/wheat) to FCI for the Central Pool.
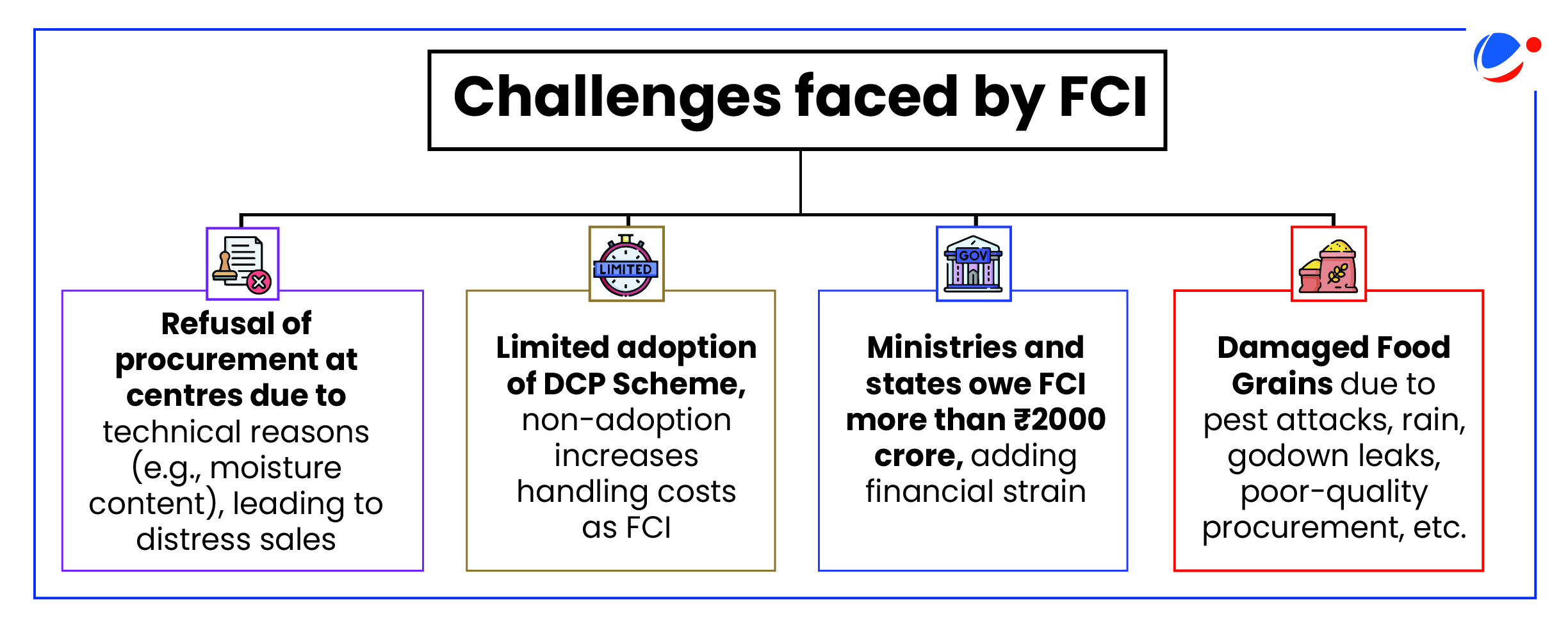
Initiatives taken to improve the functioning of FCI
Structural Reforms
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Initiative: Implemented 'One Nation, One MSP' for direct online payments to farmers.
- Modernized Storage Solutions: The traditional Cover and Plinth storage, which stood at 30.25 LMT in 2014, has been progressively replaced with scientifically managed storage depots and silos.
- Steel Silos: Currently, 22.75 LMT of steel silos are operational, with an additional 41 LMT in development.
- Digital reforms such as AI-Enabled Video Surveillance, ANNA DARPAN portal for seamless end-to-end supply chain management, Vehicle Location Tracking System, Warehouse Inventory Network and Governing System (WINGS) App for mill tagging and warehouse space allocation.



