Report highlighted that reducing black carbon alongside other super pollutants is fastest way to achieve near-immediate climate gains while improving air quality, public health, and the economy.
What is Black Carbon?
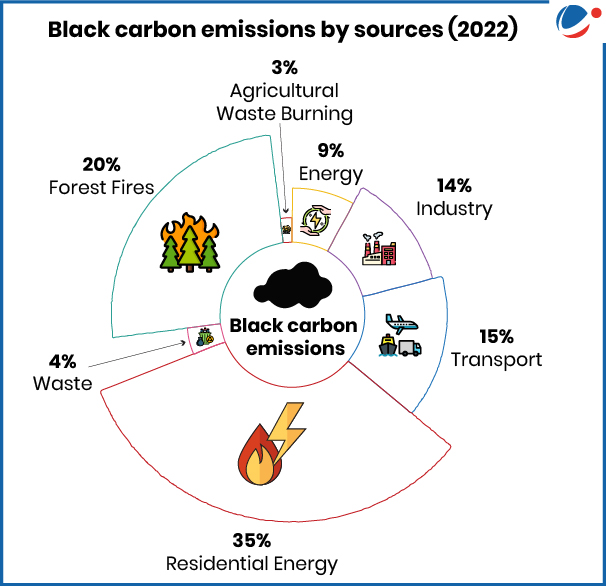
- Black carbon, commonly known as soot, is a component of fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5).
- Black carbon is a Short-Lived Climate Pollutant (SLCP) and lasts only days to weeks in the atmosphere.
- Top emitters: India is second largest black carbon emitter in the world after China.
Impacts of Black Carbon
- Global Warming: One of super pollutants alongside Methane that are responsible for half of global warming.
- Regional Climate Impact: Darkens snow and ice, accelerating ice melting in Arctic and glaciers.
- It is estimated to account for 39% of Yala glacier’s mass loss in Tibetan Plateau.
- Disruption of Hydrological Cycle: Disrupt Asian and West African monsoon precipitation leading to increased flooding and drought risk.
Recommendations
- Tackling black carbon-rich sectors in and around the Arctic (focusing on gas flaring, the shipping sector, and residential heating).
- Integrating black carbon reduction targets into national clean air and energy policies as well as in revisions of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- Implementing coordinated action on super-pollutants such as comprehensive waste management solutions.




