This Mission titled "Fram2" has been launched by Dragon spacecraft of SpaceX. It will carry out a series of experiments, including the first X-ray in space and the cultivation of mushrooms in microgravity.
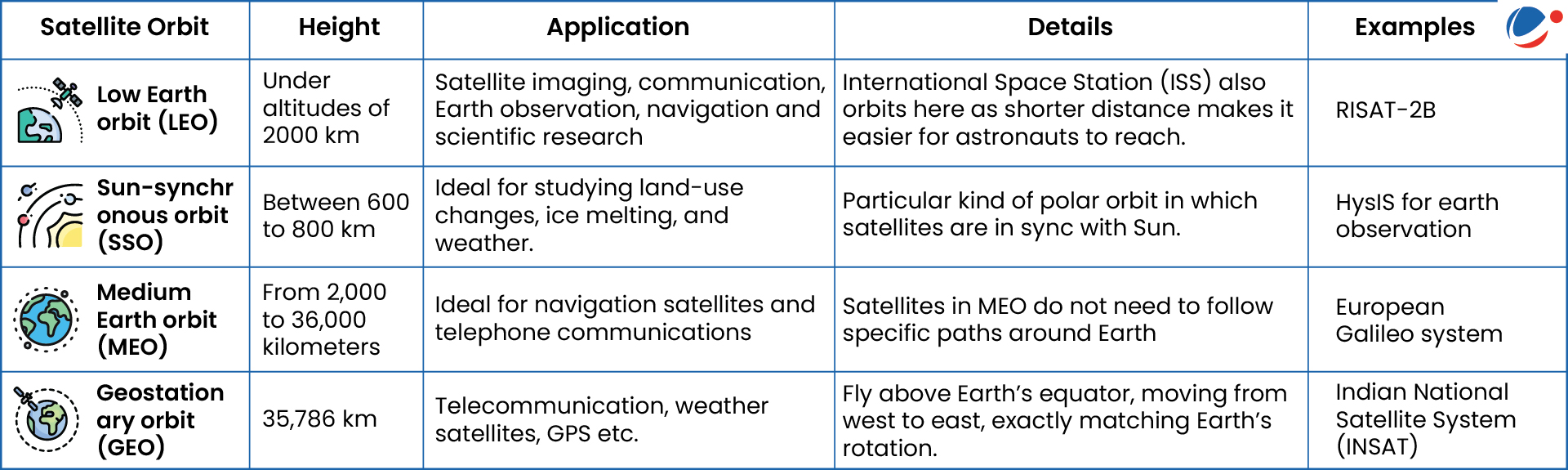
About Earth’s polar orbit:
- A polar orbit is when a satellite orbits Earth by passing over the North and South Poles.
- A deviation of 10 degrees over north and south poles is still classified as a polar orbit.
- Height: Polar orbits are a type of low Earth orbit, typically between 200 to 1000 km in altitude.
- Significance: A spacecraft orbiting over the poles can observe the entire planet as it spins underneath.
- The path is particularly useful for weather, mapping and spy satellites.
- Issue: Launching rocket into polar orbits requires greater fuel since rockets cannot harness Earth’s rotational speed.