Why in the news?
Union Ministry of Agriculture has launched AI-based platform, National Pest Surveillance System (NPSS) that will help farmers connect with agriculture scientists and experts on controlling pests.
About National Pest Surveillance system (NPSS)
- Aim: It aims to reduce the dependence of farmers on pesticide retailers and inculcate a scientific approach among them towards pest management.
- Agencies involved: NPSS is a collaboration of Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage And ICAR-National Research Centre for Integrated Pest Management (ICAR- NCIPM).
- Key Features
- Utilizes cutting-edge technologies: Such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to offer timely and precise pest management advisories.
- Mobile app and web portal: Farmers can take photos of the infested crops or the insect and upload on platform.
- Experts' Advice: Scientists/experts will provide farmers with accurate advice and also suggest pesticides to control the menace.
- Technological applications like NPSS can encourage judicious use of pesticides and promote Integrated Pest Management in India.
About Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
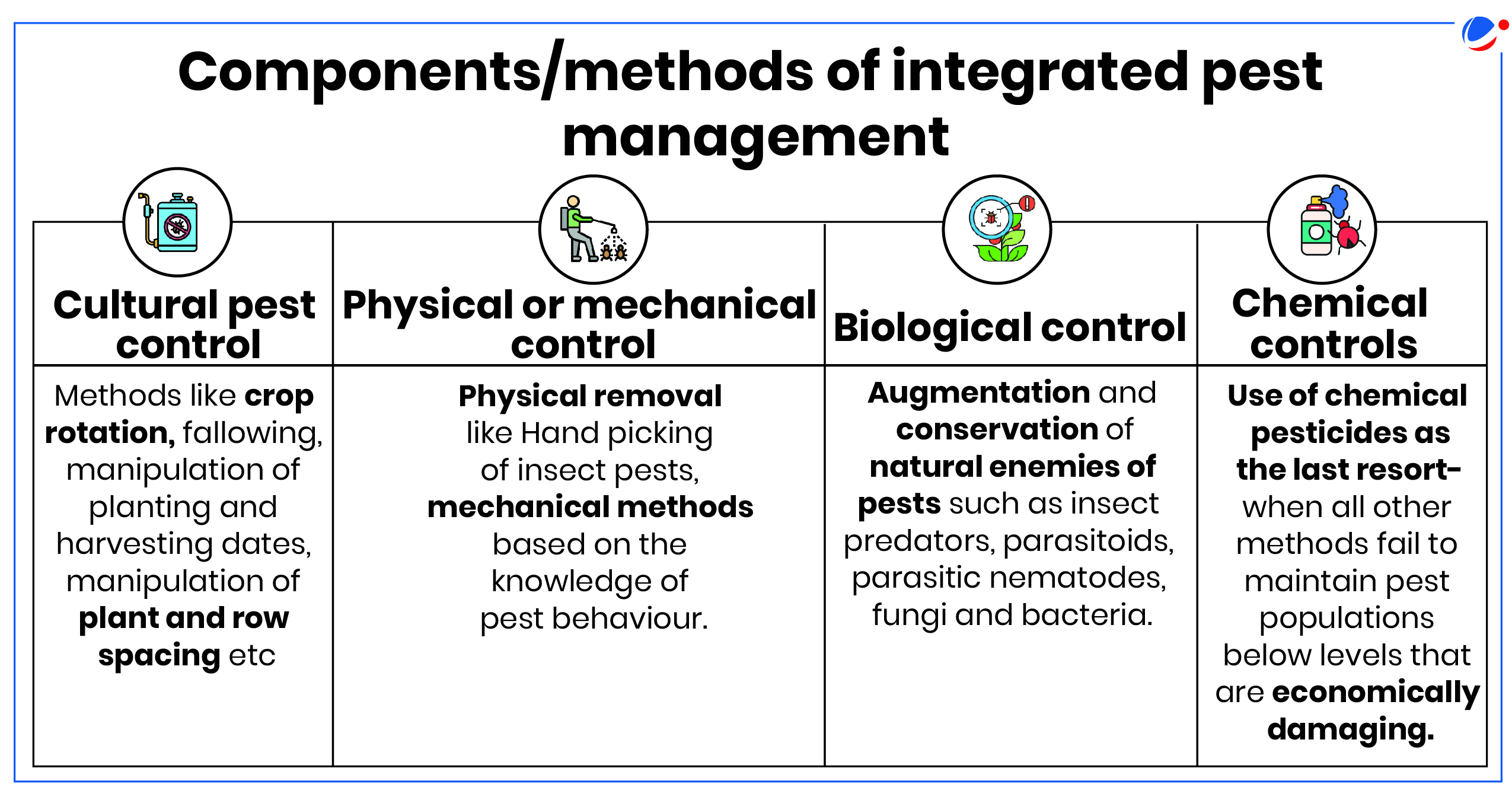
- Definition: It is an eco-friendly approach which aims at keeping pest population below those causing economically damage/loss by employing alternate pest control methods and techniques with emphasis on use of bio-pesticides and pesticides of plant-origin.
Significance of IPM
- Prevents crop yield losses: Crop yield losses due to insect pests, diseases, nematodes, weeds and rodents range from 15-25 % in India, amounting to 0.9 to 1.4 lakh crore rupees a year [Council of Energy, Environment & Water (CEEW)].
- Increases Income Levels: IPM reduces production costs through reduced levels of pesticide use and increased production. Also, higher quality crops (with less residues) can fetch better prices in markets.
- E.g., The implementation of IPM has led to increased pulse production of 15-20 %.
- Prevents Ill-Effects of Excessive Pesticide Use: Such as human and animal health hazards, development of resistance in the pests to pesticides etc.
- Environmental benefits: Due to Reduced Pesticide Residues in the environment-
- Enhances ecosystem services (i.e. pollination, healthy soils, diversity of species).
- Conserve Energy & reduces emissions as Bio-pesticides are derived from animals, plants (neem, tobacco) microorganisms (bacteria, virus, fungus, nematodes) etc.
Concerns
- Possibility of Initial Yield Decline: It can discourage farmers from adopting IPM.
- High Initial Costs: Upfront investment is needed in new equipment, technology, and training.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: About IPM principles or its potential benefits, leading to resistance to change.
- Lack of Monitoring and Data: Effective IPM relies on regular monitoring of pest populations and data collection, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Pest Resurgence: In cases where IPM practices are not implemented correctly or if pests develop resistance to biological control agents.
- Weather and Environmental Factors: It can affect the effectiveness of certain IPM practices
Steps taken for promoting IPM System in India
|
Way forward
- Concentrated effort from government, Farmer Producer Organizations, and researchers to provide education, training, and support to farmers.
- Developing innovative IPM strategies tailored to specific regions and crop systems.
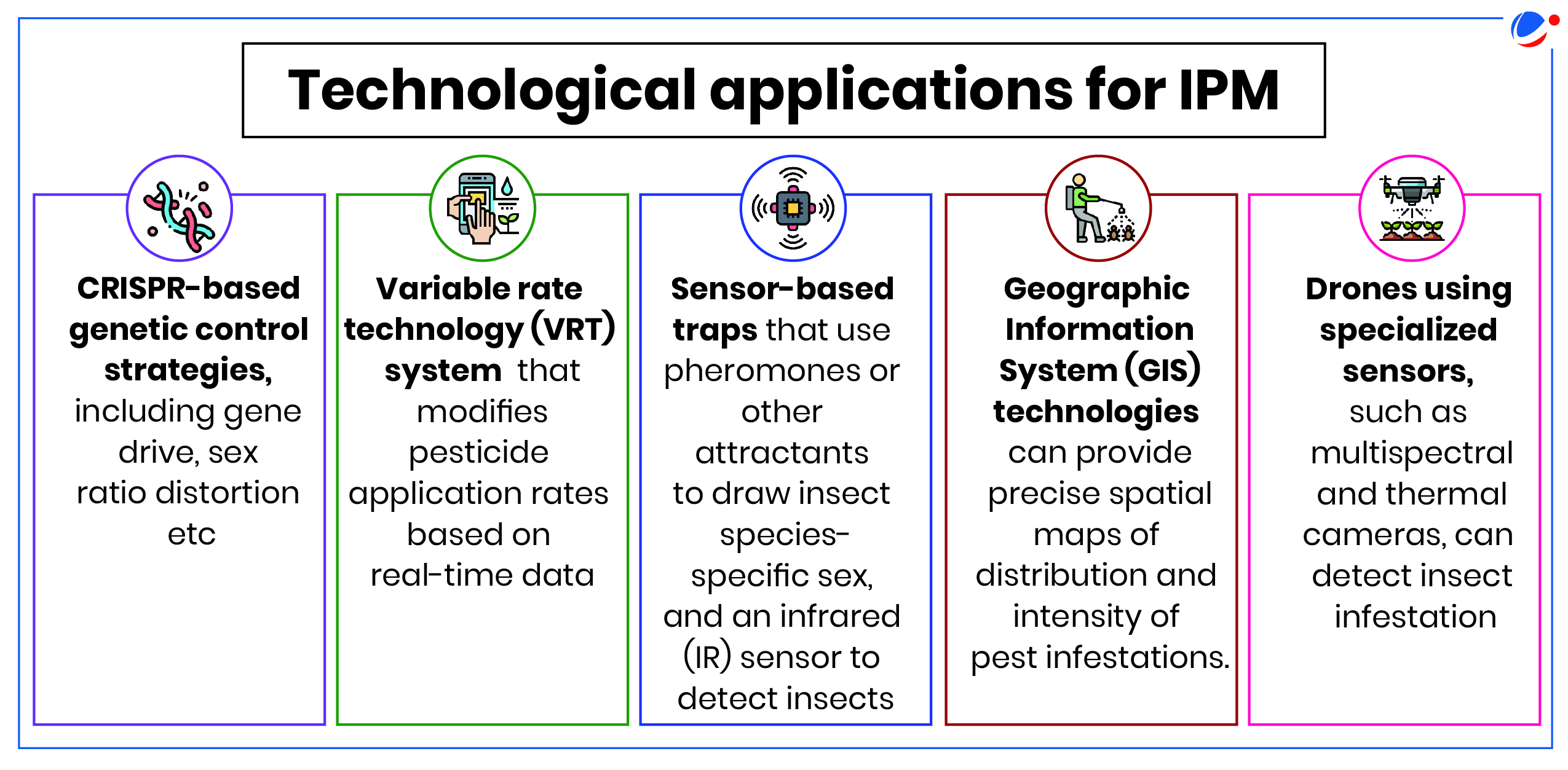
- Invest in developing technological interventions for wider adoption of IPM.