Why in the News?
Recently, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) withdraw its direction to Food Business Operators (FBOs) to not market their milk and milk products in the name of A1 and A2.
More about the News
- Earlier, FSSAI stated that standards of milk as specified in Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011 do not mention/ recognize any differentiation of milk on the basis of A1 and A2 types.
- Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011 has been enacted under the Food Safety and Standards Act 2006.
Basis of the Classification
- A1 and A2 are genetic variants of Beta (β)-casein protein. Casein (make 80 % of milk protein) is one of the two types of protein found in milk. The other one is Whey.
- Differentiation in both is linked to difference in structure of amino acid sequence.
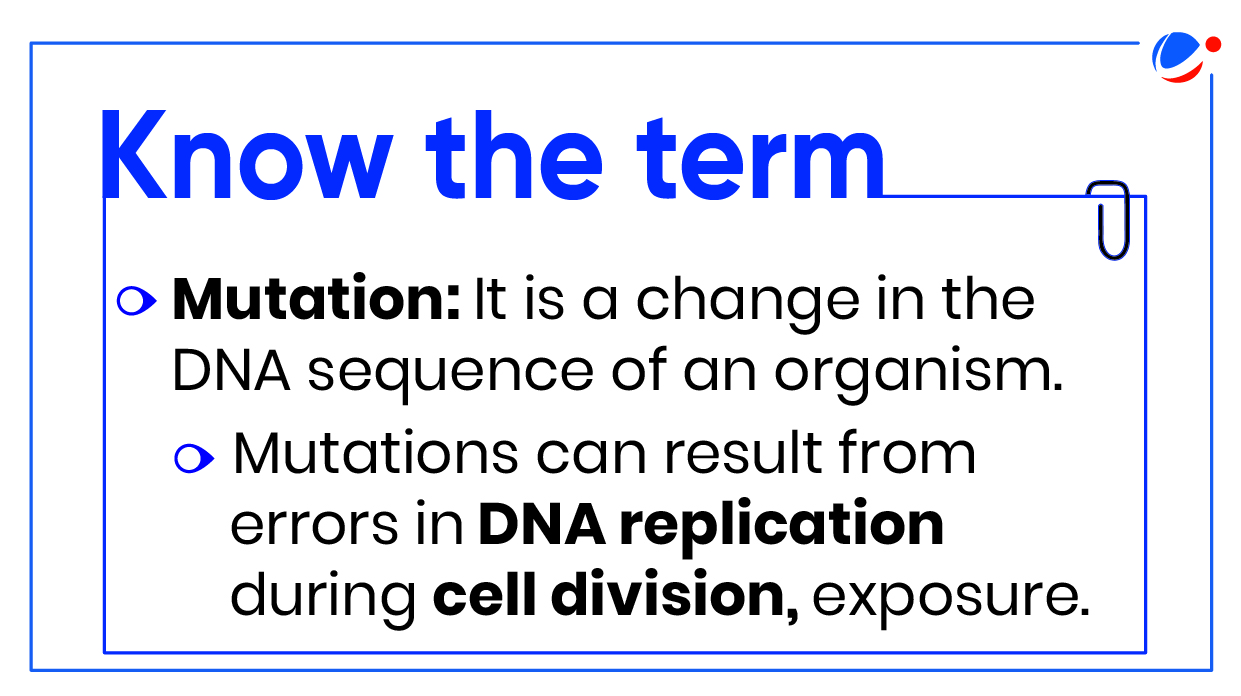
- Also, A1 evolved from A2 through natural mutation.
- Regular milk contains both A1 and A2 beta-casein, while A2 milk is unique in that it contains only the A2 variant.
- Studies of the National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR) have confirmed that indigenous cows and buffaloes produce A2 milk.
Comparison between A1 and A2 Milk | ||
Parameters | A1 Milk | A2 Milk |
Nutrition |
|
|
Health benefits |
|
|
Source |
|
|
About Proteins
|



