Commitment to Reducing Inequality (CRI) Index 2024 released
CRI is released by Oxfam and Development Finance International.
- CRI assessed the commitment of 164 countries and regions to fight inequality.
- SDG 10 aims to reduce inequality.
- It assessed the performance on the basis of three parameters: Public Services Spending, Progressive taxation and Labour rights and wages.
Key Highlights of the Index
- Ranking:
- Top performers: Norway, Canada, and Australia
- Worst performers: South Sudan, Nigeria, etc.
- India’s rank: 127
- Other South Asian countries such as Nepal (115) and Sri Lanka (118) have performed better than India.
- Rising Inequality:
- Gap between the Global South and the Global North has suddenly grown more rapidly than at any time since World War II.
- Billions of people face the terrible hardship of high and rising food prices and hunger, while the number of billionaires has doubled in the last decade.
- Key Deriving Factor: Conflict, debt crisis, and climate shocks, these are constraining spending in low- and lower middle-income countries.
- 84% of countries have reduced their spending on education, health and/or social protection.
Key Recommendations to Reduce Inequality
Measure taken to reduce inequality in India
|
- Tags :
- Inequality
- Commitment to Reducing Inequality (CRI) Index
- Oxfam
Hand-in-Hand (HIH) Initiative
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) opened the 2024 Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum.
About HIH
- Launched in 2019 by FAO
- It supports the implementation of nationally led, ambitious programmes to accelerate agrifood systems transformations by eradicating poverty (SDG1), ending hunger and malnutrition (SDG2), and reducing inequalities (SDG10).
- It uses advanced geospatial modeling and analytics, as well as a robust partnership-building approach.
- Areas of intervention: Developing value chains for priority commodities, building agro-industries, etc.
- Members:72 countries (India is not a member)
- Tags :
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Agri-food Systems
- Hand-in-Hand (HIH) Initiative
CareEdge Released Its Inaugural Sovereign Credit Ratings
CareEdge released its inaugural report on Sovereign Ratings, covering 39 Global Economies.
- Thus, CareEdge became the first Indian credit rating agency to enter the global scale ratings space, including sovereign ratings.
Key Highlight
- Assigned an AAA rating to Germany, Netherlands, Singapore, and Sweden.
- India was assigned BBB+, citing its resilient post-pandemic recovery and its focus on infrastructure investment.
- India's general government debt-to-GDP ratio is projected to reduce from 80% (currently) to 78 % by FY30.
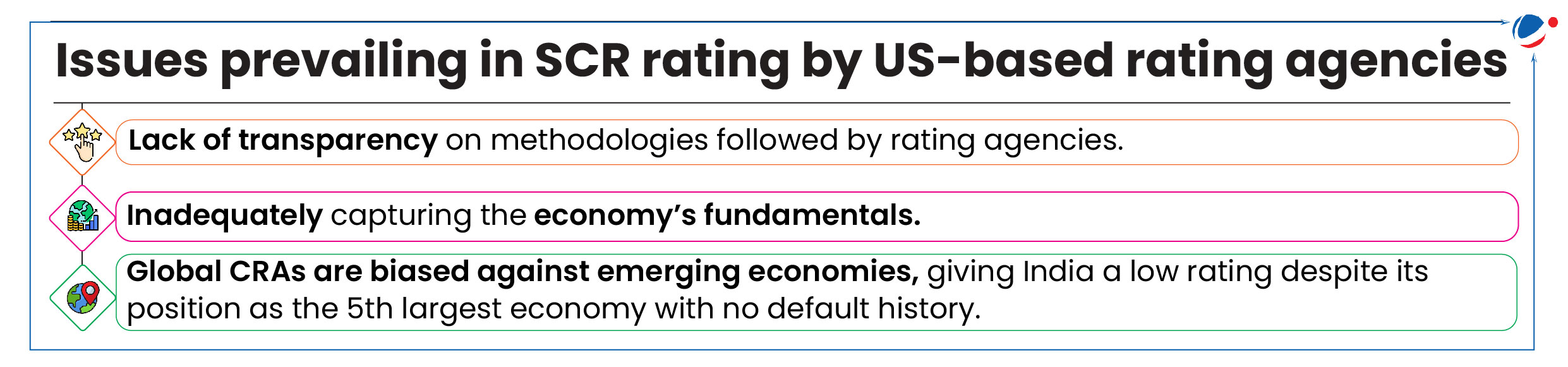
About Sovereign Credit Rating (SCR)
- Credit ratings are forward-looking opinions on the relative ability of an entity to meet its financial commitments, i.e., credit risk or relative creditworthiness of a borrower.
- SEBI regulates domestic credit rating agencies (CRISIL, ICRA, CARE etc.).
- SCR represent an assessment of a country's or sovereign entity's ability to meet debt obligations, including both capability and willingness to repay debt.
- SCR facilitates borrowing from global capital markets at low cost, boosts investors’ confidence, attracts foreign investment, etc.
- Currently, SCRs are dominated by 3 US-based rating agencies – S&P, Moody’s, and Fitch.
- Tags :
- CareEdge
- Sovereign Ratings
Global Family Farming Forum (GFFF) launched
Global Family Farming Forum (GFFF) was launched at Food and Agriculture Organization’s World Food Forum (WFF).
- GFFF celebrates essential role of family farmers in building sustainable agrifood systems and tackling the impacts of the climate crisis.
- GFFF also marked the halfway completion of the United Nations Decade of Family Farming 2019-28 (UNDFF).
- UNDFF was declared by United Nations General Assembly and it serves as a framework for countries to develop public policies and investments to support family farming.
About Family farming
- Family Farming: Is a means of organizing agricultural, forestry, fisheries, pastoral and aquaculture production that is managed and operated by a family, and is predominantly reliant on the family labour of both women and men.
- Significance of Family farming
- Food security: With over 550 million farms worldwide, it is the backbone of food production.
- It produces 70 to 80%of the world’s food in value terms.
- Nutritional diversity: Family farming, in low- and middle-income countries, grow diverse, nutritious food and support crop biodiversity.
- Sustainable stewardship: Family farmers use traditional methods, minimal external inputs to maintain soil health and build climate resilience naturally.
- Food security: With over 550 million farms worldwide, it is the backbone of food production.
- Challenges faced by Family farming: Financial barriers, limited access to assistance, genetics and knowledge., fragmentation of land, market access difficulties, climate threats, lack of generational succession support, etc.
In a related news
|
- Tags :
- Global Family Farming Forum



