Introduction
Recently, in Arvind Kejriwal vs CBI case, Supreme Court said that Arvind Kejriwal's continued incarceration would infringe upon the right to personal liberty under Article 21. With this and similar other decisions, Supreme Court has upheld the principle of bail as rule and jail as exception, while underlining the sacrosanct nature of the individual's right to personal liberty guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Concept of Liberty
- Liberty refers to the state or condition in which an individual has the freedom to act according to their will, without undue restraint or coercion from external forces.
- There are two aspects to the concept of Liberty (see infographic).
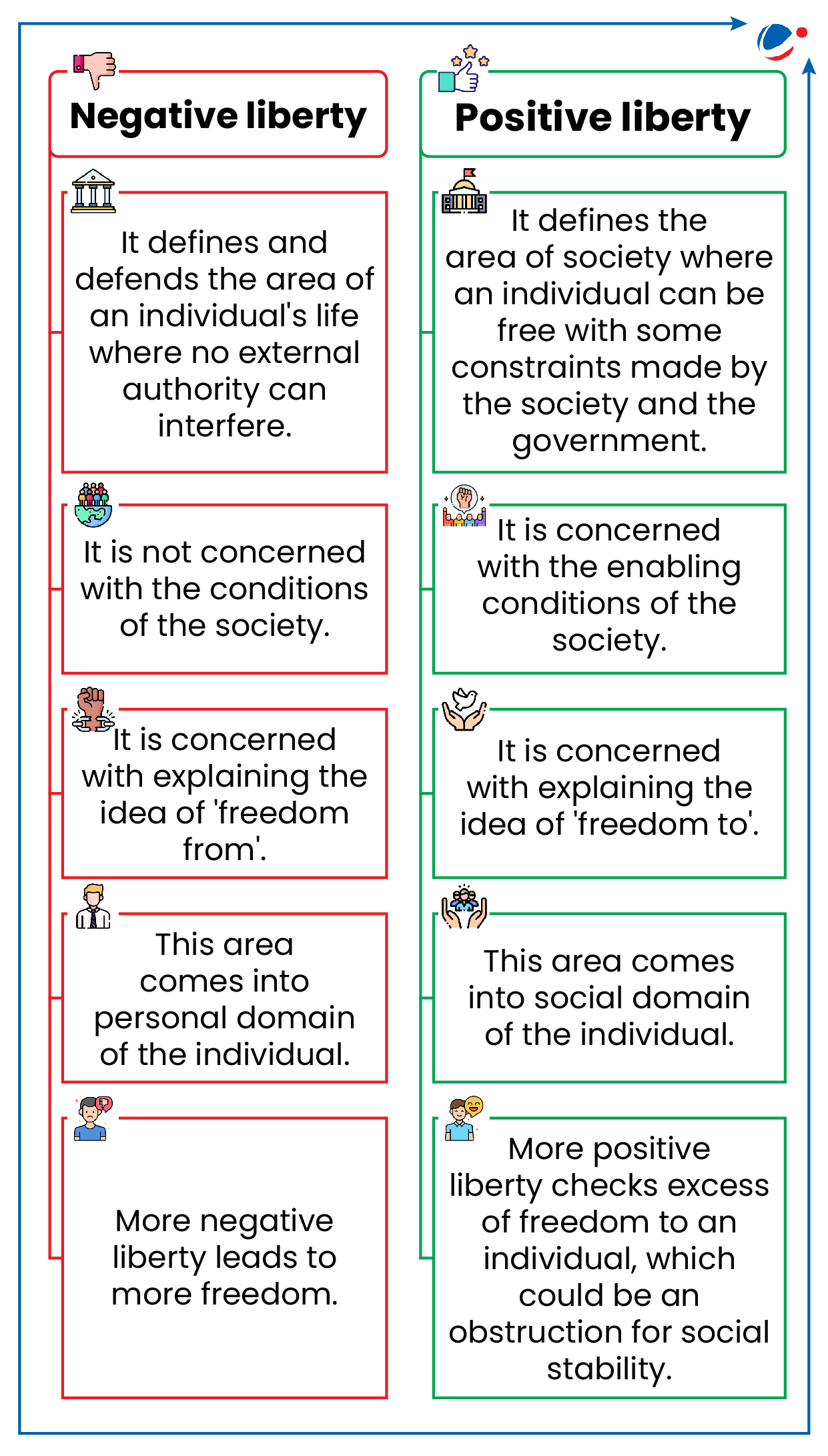
- Constraints on Liberty: Restrictions on liberty may be imposed by force or government through laws and can also result from social inequality and economic inequality.
- Need for Constraints: Differences exist between people regarding their ideas and opinions, and there are conflicting ambitions and competition to control scarce resources.
- Therefore, every society needs some restraints to ensure that differences may be discussed and debated without one group coercively imposing its views on the other. However, such restraints must be reasonable and justified.
- Need for Constraints: Differences exist between people regarding their ideas and opinions, and there are conflicting ambitions and competition to control scarce resources.
Ethical Frameworks surrounding Liberty
- John Stuart Mill's Harm Principle: Mill urged for minimal state intervention in the exercise of liberties, arguing that "the only power that can be rightfully exercised over any member of a civilised community, against his will, is to prevent harm to others". This is called the 'harm principle'.
- Constraints: Mill believed that that the state or society do not have any justification in restricting self-regarding actions (actions having consequences only for individual actors and nobody else).
- However, the state or society can control other-regarding actions (actions having consequences for others).
- For instance, in Navtej Singh Johar vs. Union of India case, the Supreme Court buttressed its conclusion that the state cannot criminalise homosexuality (self-regarding action) by recalling Mill's theory.
- Constraints: Mill believed that that the state or society do not have any justification in restricting self-regarding actions (actions having consequences only for individual actors and nobody else).
- Liberty and Rights: Liberty is integrally linked to the rights as the due enforcement of the rights ensures the availability of legitimate freedom to the subjects of the state.
- Principle-based Framework: Rights framework emphasizes on liberty based on moral principles and human rights, which sometimes are in conflict with one another.
- According to it, civil liberty depends upon positive laws such as legal rights.
- Principle-based Framework: Rights framework emphasizes on liberty based on moral principles and human rights, which sometimes are in conflict with one another.
- Isaiah Berlin's Ethical Pluralism: It is a political and philosophical theory that there are multiple objective values and principles that are part of humanity's essence.
- Berlin's value pluralism emphasizes on both positive liberty and negative liberty as fundamental human value.
Constitutional Framework surrounding Liberty
|
Key Stakeholders | ||
Stakeholders | Roles/Interests | Ethical Considerations |
Individual |
|
|
Society |
|
|
Government |
|
|
Judiciary |
|
|
Civil Society |
|
|
Ethical Issues associated with Liberty
- Liberty vs Security: Striking the right balance between protecting individual liberty and ensuring national security is an ethical challenge.
- Laws like the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) and the National Security Act (NSA) have been criticized for their misuse in curtailing individual liberties but are deemed necessary for national security.
- Recently, Supreme Court emphasized that depriving a person of their liberty, even for a single day, is a day too many.
- Freedom of Speech vs Hate Speech: Rise of social media has led to an increase in hate speech and misinformation but what exactly constitute hate speech is undefined in law.
- Thus, it is dependent upon the interpretation of implementing authorities resulting in curtailment of freedom of speech in some cases while non-punishment to actual hate speeches in some other cases.
- Cultural traditions vs women's rights: Women and Transgender often face restrictions, social stigma, and non-realization of their fundamental rights due to patriarchal structure of society.
- Ethical challenge is navigating between respecting cultural traditions and advancing women's rights and freedom.
- Right to Privacy vs Surveillance: Supreme Court has declared the Right to Privacy as a fundamental right but there are concerns on how data of citizens is collected, stored and used by government entities and private sector.
- Ethical dilemma for government is to ensure public safety and deliver good governance without violating individual's privacy.
- Economic Inequality vs Liberty: Liberty is often linked to economic freedom as it also means opportunity to explore one's full potential in an enabling society.
- However, economic inequality hinders that opportunity by limited access to quality education, healthcare, basic infrastructure services like water, sanitation, and electricity etc.
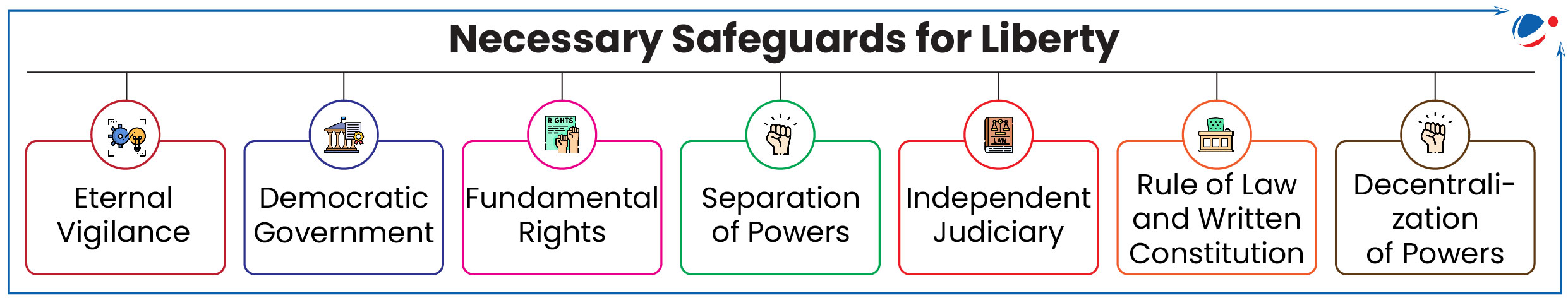
Conclusion
The concept of liberty is multidimensional, encompassing both personal autonomy and the ethical responsibility to prevent harm to others. Supreme Court has consistently reinforced the idea that personal liberty is paramount. Philosophically, John Stuart Mill's harm principle offers a critical framework for understanding when and why liberty may be legitimately restricted. Together, these perspectives remind us that liberty, while fundamental, must be balanced with justice and fairness in any democratic society.
Check your Ethical AptitudeAs a district magistrate, you are approached by the police requesting approval to detain a prominent political activist under preventive detention laws. The activist has been organizing large protests against certain government policies, which the police argue could lead to unrest and disruption of public order. However, the activist has not been involved in any violence, and the protests have been largely peaceful so far. At the same time, the activist's legal team submits a petition emphasizing their right to freedom of speech and expression under Article 19 and personal liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution. They argue that any preventive detention would be an unjust violation of these constitutional rights and that the protests are a legitimate expression of public dissent in a democracy. On the basis of the case study answer the following questions:
|



