The images were captured by remote sensing payloads i.e. Solar Ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), aboard Aditya-L1 spacecraft.
- These images will help in studying solar flares, energy distribution, sun spot, understanding and predicting space weather, monitoring solar activity and UV radiation over a wide wavelength range.
About SUIT and VLEC
- SUIT: To image Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultra-violet (UV) and, to measure solar irradiance variations in near UV.
- VELC: To study solar corona and dynamics of coronal mass ejections.
About Aditya L-1
- Launched in 2023, it is India’s first space mission to observe Sun from a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from Earth.
- It was launched by Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) XL (PSLV-C57) with 7 payloads on board.
Significance of Aditya L1
- To understand Coronal heating and solar wind acceleration.
- Observe in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for study of particle dynamics from Sun.
Other solar missions
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe; European Space Agency’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory; China’s Kuafu-1 solar probe etc.
About Lagrange point (L1)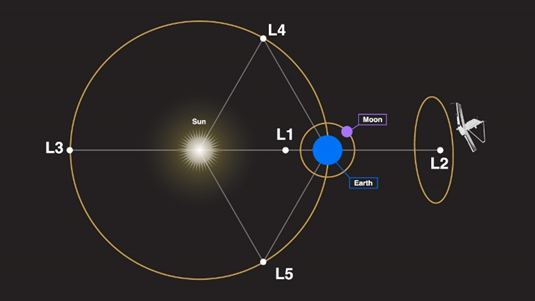
|




