The Ministry of Power has identified 47 dams, including 38 commissioned and nine under-construction dams, as potentially affected by GLOFs from glacial lakes.
- Subsequent to the Teesta-III dam collapse last year, the Central Water Commission (CWC) has decided to review the design flood of all the existing and under-construction dams vulnerable to GLOFs.
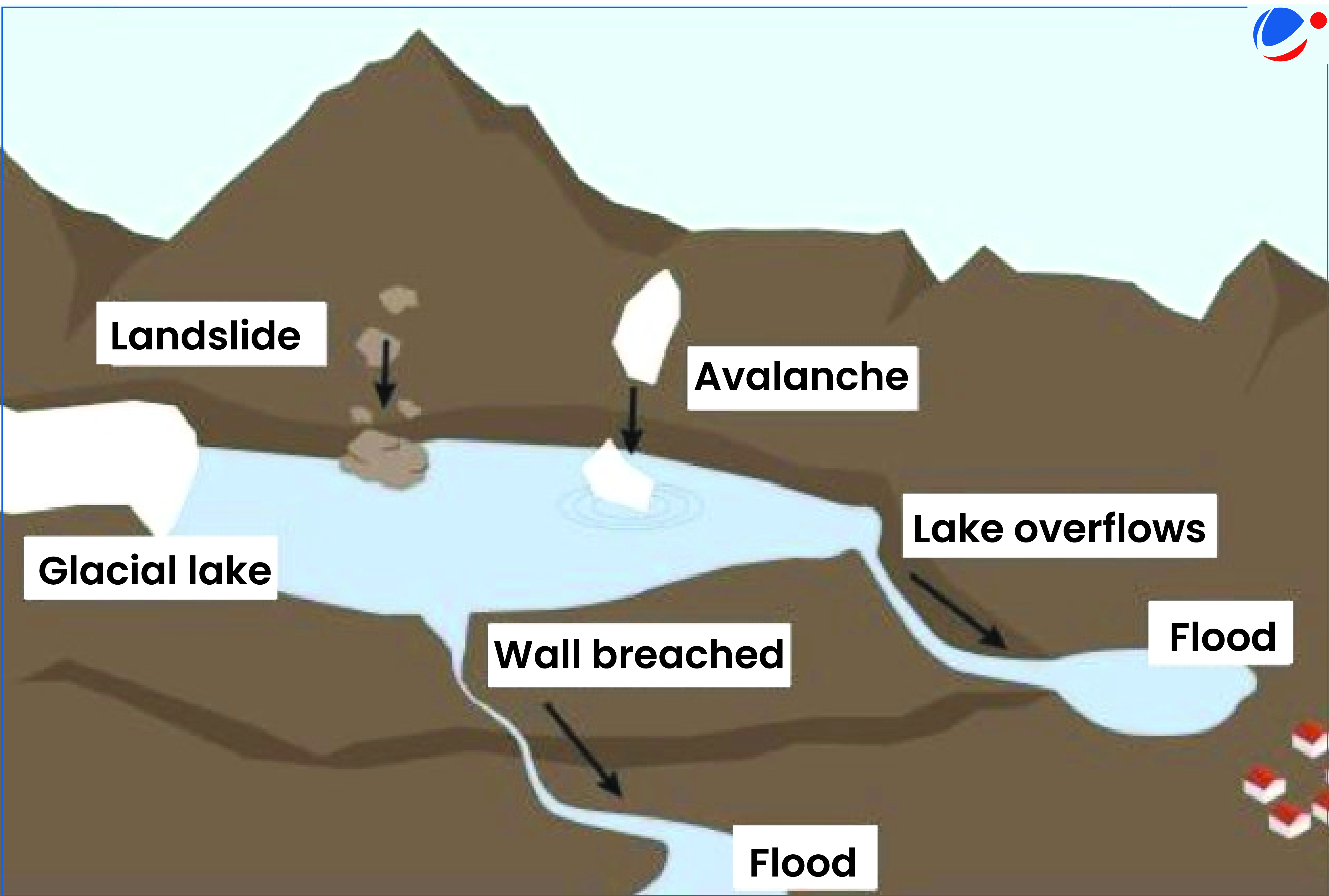
About Glacial Lake Outburst Flooding (GLOFs)
- It occurs when the water levels of glacial lakes breach their boundaries causing large amounts of water to flow into nearby streams and rivers (See image).
Reasons for GLOFs
- Geological: Earthquake, breach of moraine dams, etc.
- Morphological: Mass movement into glacial lakes, water seepage through glacial structures, etc.
- Physical: Excessive precipitation, Cryoseism (non-tectonic seismic event of the glacial cryosphere), etc.
- Anthropogenic: Climate Change and global warming, etc.
Challenges of GLOFs
- Unpredictable: can occur suddenly with little warning.
- Loss of lifes: E.g-Lake outburst in Kedarnath valley in 2013 led to around 6,000 deaths.
- Remote areas: like Chamoli’s Rishighanga valley GLOFs in 2021.
Strategies to manage GLOFs risks:
- Hazard risk zonation and mapping, monitoring of glacial lakes using technology, restrictions and regulations of construction activities in hazard-prone areas, etc.




