Released by the NASA and European space Agency, composite images of plume of gas and dust streaming from a star are from about 625 light-years from Earth in one of the closest star-forming regions of our Milky Way galaxy.
- Considered as successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, JWST is an advanced space-based observatory launched in 2021 to study universe, primarily in the infrared spectrum.
Life Cycle of a Star
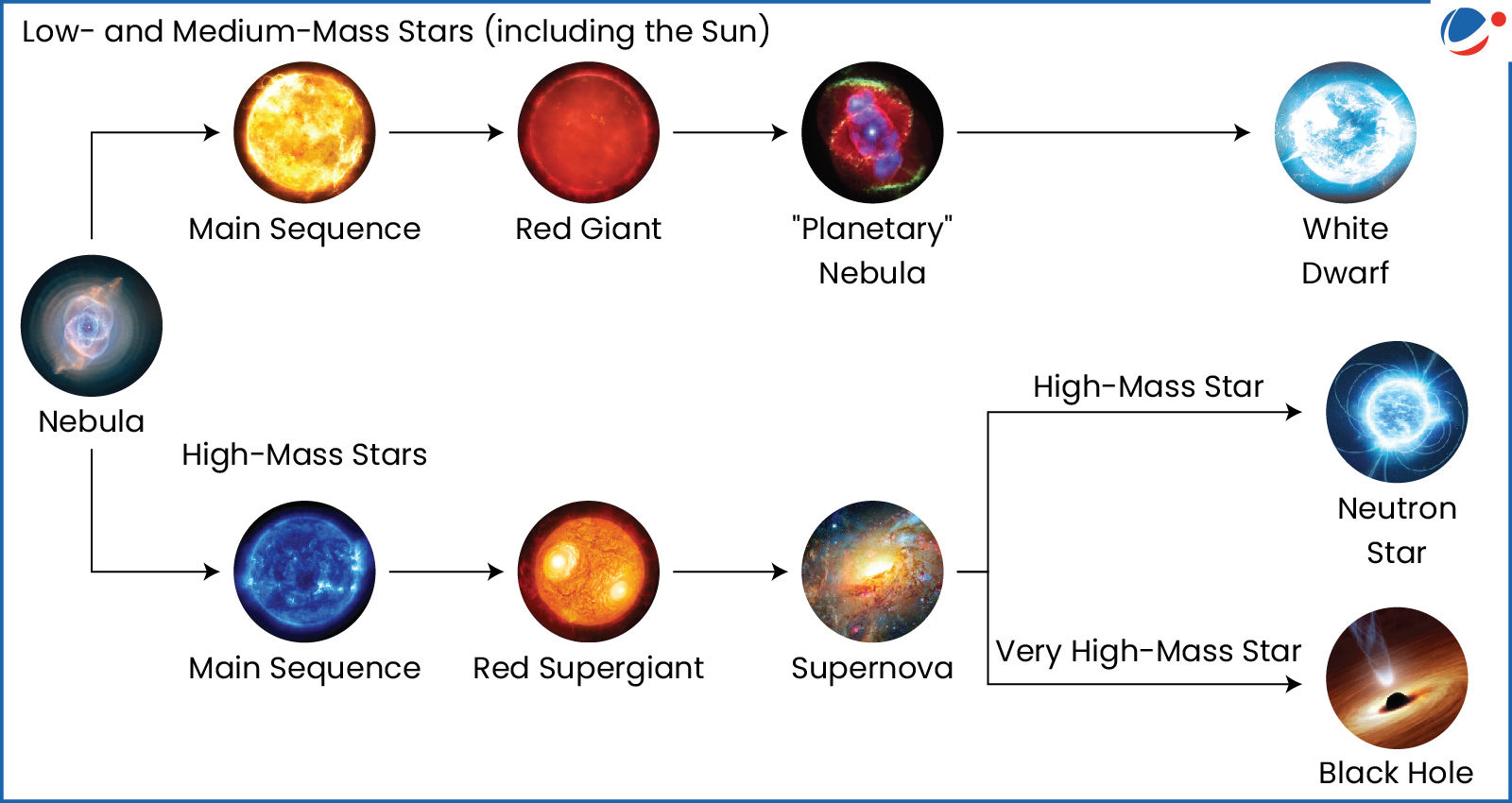
- Nebula (Birth): A star starts as a nebula, a large cloud of gas (mainly hydrogen and helium) and dust.
- Protostar: Gravity collapses nebula into dense, heating, spinning regions that form a protostellar disk.
- Main Sequence: It is the star's longest phase, steadily fusing hydrogen into helium in its core.
- Our Sun is about halfway through its main sequence.
- Red Giant or Supergiant: When hydrogen in the core is depleted, the star evolves based on its mass.
- Low to Medium Mass Stars (e.g., the Sun): Core contracts, outer layers expand, and star becomes a red giant.
- Massive Stars: Expand into supergiants, fusing heavier elements (e.g., carbon, oxygen, up to iron) in successive stages.
- End Stage
- Low to Medium Mass Stars: Outer layers eject as a planetary nebula and core becomes a dense, non-fusing white dwarf.
- If its mass stays below the Chandrasekhar Limit (1.4 solar masses), it remains stable.
- High Mass Stars (10 solar masses or more): When the core accumulates iron, it collapses under gravity and rebounds in a catastrophic explosion called supernova.
- If the core remnant is 1.4–3 solar masses, it becomes an incredibly dense neutron star.
- If the remnant exceeds ~3 solar masses, it collapses into a black hole, with gravity so strong that not even light escapes.
- Low to Medium Mass Stars: Outer layers eject as a planetary nebula and core becomes a dense, non-fusing white dwarf.







