Colossal Biosciences used both cloning and gene-editing based on 2 ancient samples of dire wolf DNA to birth three pups.
- Instead of traditional cloning, scientists used a less invasive method involving endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) from gray wolves, the dire wolf's closest living relatives.
- These cells were gene-edited to match dire wolf DNA, leading to the first successful de-extinction of Dire wolf, extinct for over 10,000-13,000 years.
- Colossal Biosciences is also working to bring back the extinct pink pigeon (native to Mauritius) by tapping into the fertilized egg of a pink pigeon to extract primordial germ cells (PGCs).
- PGCs are embryonic precursors of sperm and egg that pass on genetic and epigenetic information from one generation to the next.
- Colossal Biosciences is also working to bring back the extinct pink pigeon (native to Mauritius) by tapping into the fertilized egg of a pink pigeon to extract primordial germ cells (PGCs).
What is Cloning?
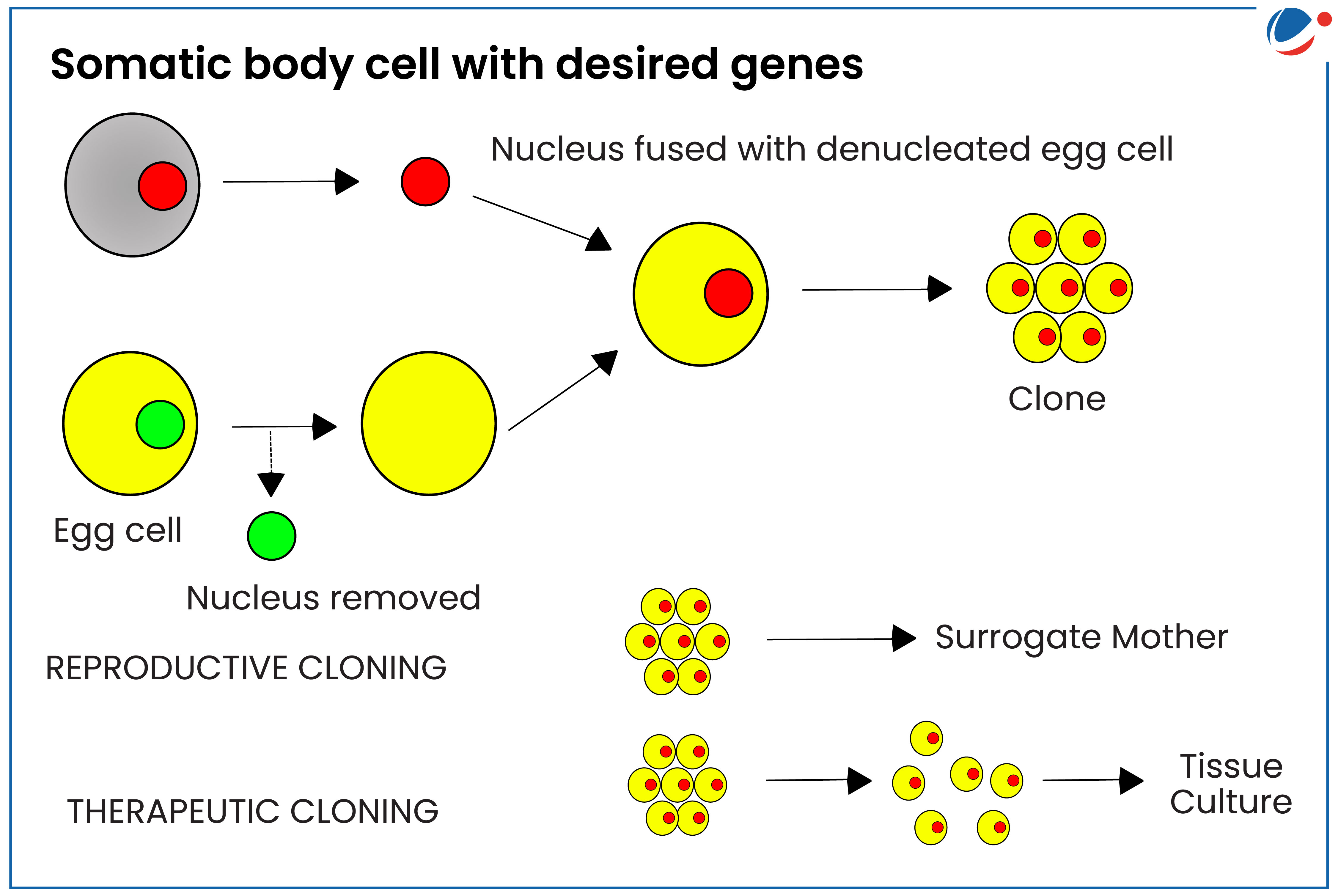
- Cloning means making an identical copy. There are 2 types of cloning:
- Reproductive cloning: The deliberate production of genetically identical individuals. E.g. 1st cloned animal, Dolly, the sheep (1996)
- Therapeutic cloning (embryonic cloning): It involves cloning of embryos for research purposes.
- Methods: Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), embryo splitting.
Ethical issues in cloning
- Commodification of animals: Violation of principle of consent and treating them as commodities for human use.
- Violation of bioethics: Cloning can be seen as interference in the natural process of procreation. E.g. Production of designer babies with ‘desirable’ characteristics.
- Kantian ethics: The principles of end-in-itself and “Act others as you desire to be acted” consider cloning as unethical.




