Why in the News?
Recently, in a High- Level Meeting was held between the EU Trade Commissioner, the Indian Commerce and Industry Minister.
More on the news
- During the meeting a roadmap based on six broad principles for building a mutually beneficial partnership between India and the European Union (EU) was outlined. (see infographic)
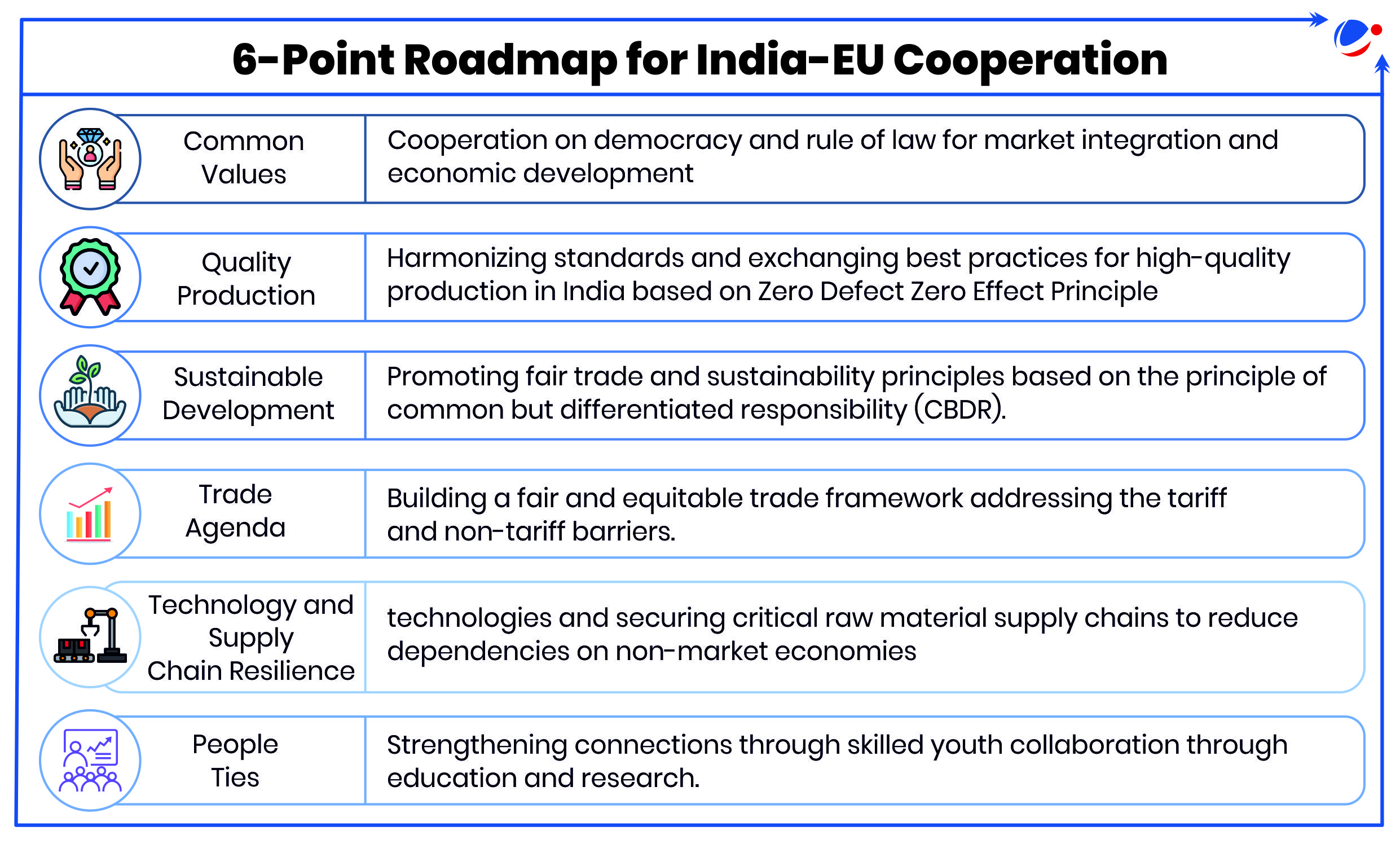

Significance of India-EU Relations
Mutual
- Historical Relations: India was amongst the first countries to establish diplomatic relations with the European Economic Community in 1962.
- During the 5th India-EU Summit held (2004) in Hague, their relationship was upgraded to a Strategic Partnership.
- Trade Partnership:
- EU: India's largest trading partner
- India: EU's 9th-largest trading partner with India maintaining trade surplus (2023)
- Strategic Alignment: Common interests in security, renewable energy, climate action, and multilateralism. Examples-
- India-EU Bilateral Dialogues exist on Counter-Terrorism, Cyber Security, Migration and Mobility, Maritime Security, Human Rights, Non-Proliferation and Disarmament.
- EU's Indo-Pacific Strategy provides strategic convergence on India's role in the Indo-Pacific.
- Both are committed to reforming multilateral institutions like the World Trade. Organization (WTO) is an essential priority for both.
- India-EU Clean Energy and Climate Partnership launched in 2016 aims at reinforcing cooperation on clean energy and implementation of the Paris Agreement.
- Connectivity: Connectivity Partnership (2021) between both focused on enhancing digital, energy, transport and people-to-people connectivity.
- Projects like India Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) hopes to strengthen connectivity between the EU-India.
For India
- Investment: Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows from the EU to India, one of the largest sources, is valued at USD 107.27 Bn. (Apr 2000-December 2023).
- E.g. Business 20 (B20) platform under G20 promotes trade and investment promotion between India and the EU.
- Export promotion: The EU provides an avenue for tapping India's export potential, particularly in IT, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and agriculture.
- E.g. EU-India Bilateral Trade in Services increased by 48% between 2019 and 2022.
- Security & Defence: European defence companies can contribute to India's defence modernisation under the 'Make in India' campaign. E.g. manufacturing of Airbus C-295 aircrafts in India.
- Technology & Innovation: Collaboration in AI and digital transformation accelerates India's technological progress.
- E.g. India-EU Trade and Technology Council (2022) is a strategic coordination mechanism to tackle challenges related to the nexus of trade, technology, and security.
For the European Union (EU)
- Access to market: India can be the EU's valuable trade partner and provide access to India's large and growing market.
- E.g. In 2024, India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) signed a Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) with 4 European states- Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- Cultural & Educational Ties: India's young, skilled workforce contributes to Europe's talent pool and strengthens academic collaborations.
- Geopolitical cooperation: The EU can leverage India's centrality in the Indo-Pacific and growth potential to improve its geopolitical position in the Global South.
- Security and Stability: India can provide security and stability in the Indian Ocean through which critical European sea lines of communications (SLOCs) carrying 35% of its trade with Asia pass.
Challenges
- Lack of Trade diversification: Due to restrictive trade regime and regulatory with non-tariff barriers like Technical barriers to trade (TBT), sanitary and phyto-sanitary (SPS) measures.
- Only 20 product categories make up 90% of total EU goods exports to India.
- EU's import dependence on China: Since 2010, India's share in the EU's import basket has stagnated, compared to the growing share from China.
- Delayed FTA negotiations: Due to Divergent perspectives: On issues like digital regulation, bilateral investment treaties, dispute settlement process and investor protection, etc.
- Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) negotiations were held between 2007 and 2013 but remained dormant till 2021.
- Carbon border adjustment mechanism (CBAM): India has concerns that it could create new trade barriers for its exports to the EU.
- The EU's CBAM will impose additional 25% tax on energy-intensive goods exported from India to the EU, impacting 0.05% of India's GDP (Centre for Science and Environment).
- Lack of consensus: on some aspects of labour laws, human rights, environmental standards etc. which hinders investments in India by EU companies.
- The role and opinions of European civil society may be seen as contentious with India's strategic autonomy principle. E.g. ban on activities of Amnesty International in India.
Way Forward
- Fastrack FTA: Formal re-negotiations for the India - EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA), an Investment Protection Agreement and a Geographical Indications Agreement were launched in 2022.
- Trade Reforms: Predictable tariffs and harmonised rules, liberalizing imports through diversification of supply chains would further increase business confidence and investment.
- E.g. Liberalisation of public procurement would create opportunities for European firms and address India's infrastructure deficit.
- Green cooperation: Focus on sustainability and energy transition can be capitalized through closer cooperation for trade and innovation in green transition goods.
- Labour policy: India has been reforming its labour codes based on international standards.
- Provisions of occupational safety and labour sustainability need to be upheld to enable the India-EU FTA negotiations.



