Why in the News?
In the context of the 75th Anniversary of India-Indonesia Diplomatic Relations, the Indonesian President visited India.
Key Developments during the visit
- The two countries signed MoUs on Health Cooperation, Traditional Medicine, Maritime Safety and Security, Digital Development and Cultural Exchange Programme (2025-2028).
- A joint report was presented by the co-chairs at the 3rd India- Indonesia CEOs Forum.
- He was also the chief guest at India's 76th Republic Day celebrations.
- A joint statement was released by the 2 countries highlighting the areas of cooperation.

Significance of India-Indonesia Relations
Mutual Benefits
- Economic engagement: India–Indonesia Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD Dialogue) (2023) aims to enhance collaboration and foster a shared understanding of global issues.
- Maritime Security: Enhancing cooperation through engagement with regional mechanisms to ensure the safety and security of sea lanes of communication.
- E.g. Safety of Navigation in the Straits of Malacca and Singapore (SOMS)
- Defence and Security:
- Strategic and operational interaction between the defence forces: E.g. India–Indonesia Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT), bilateral exercises Garuda Shakti (Army) and Samudra Shakti (Navy), and participation in other multilateral exercises- Milan, Komodo, Tarang Shakti and Super Garuda Shield.
- Developing defence indigenization and modernization capacities: E.g. talks on technology transfer of Brahmos missile are in progress.
- Multilateral reforms: Close coordination in the multilateral fora including UN and the G20 and focus on reformed multilateralism.
- Regional partners: Indonesia recently became a full member of the BRICS and both are part of other forums Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), Indo-Pacific Oceans' Initiative (IPOI), Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), Pacific Islands Forum (PIF), etc.
- Infrastructure & Connectivity: E.g. India's Development Partnership with the Indonesia-Malaysia-Thailand Growth Triangle (IMT-GT)
- Cultural and Heritage Cooperation: E.g. Cultural Exchange Programme (2025-2028), Annual festival 'Bali Jatra' commemorates the maritime trade and cultural exchange between India (Odisha) and Bali (Indonesia).
- Other areas of common interests: Condemning all forms of terrorism, Collaboration in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), cybersecurity etc.
For India
- Trade: Indonesia is the second largest trading partner of India in the ASEAN region (after Singapore).
- Bilateral trade increased from $4.3 billion in 2005-06 to $29.40 billion in 2023-24.
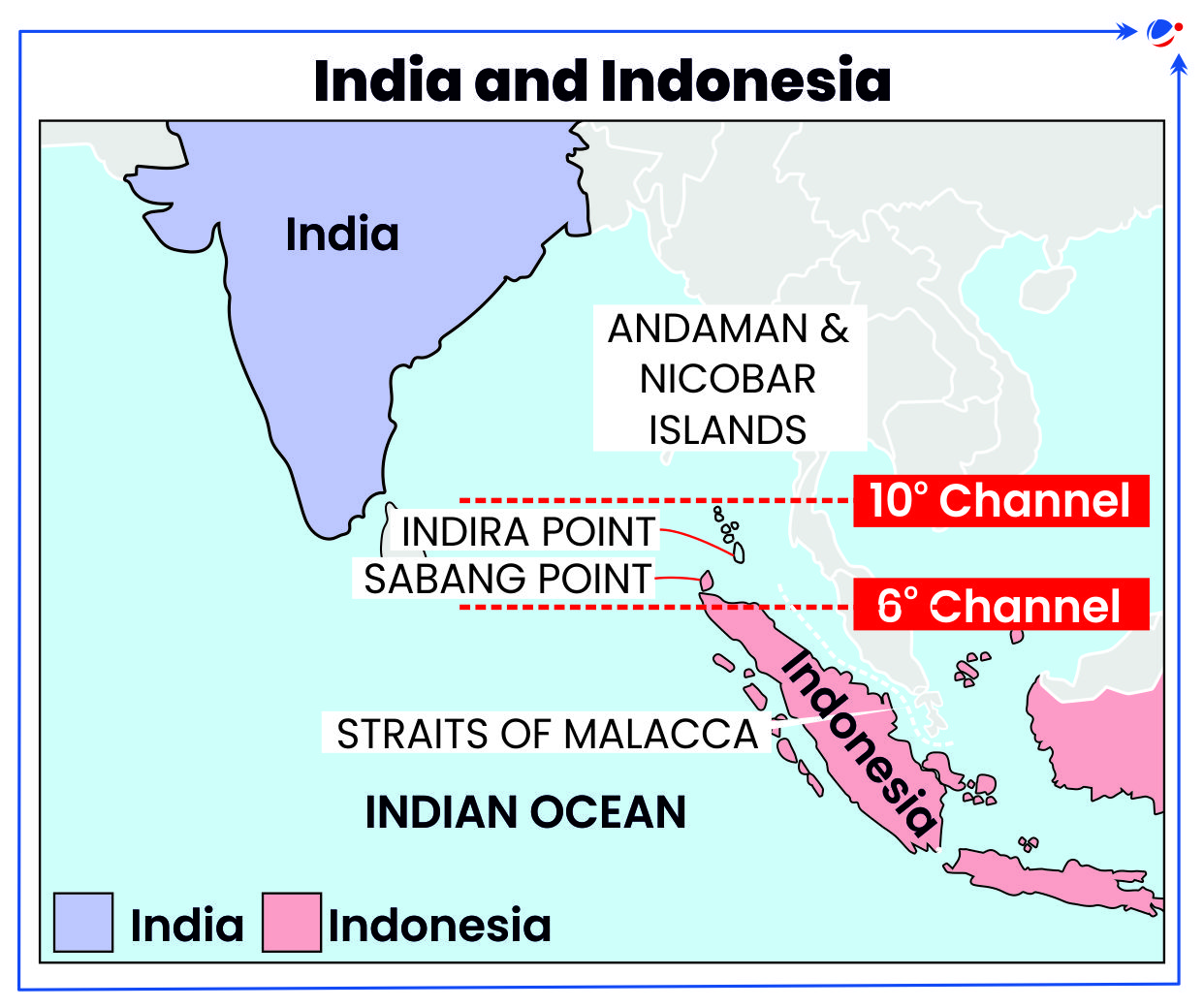
- Geostrategic significance: India, in line of its Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, is aiding development of Sabang port in Aceh, Indonesia.
- It enhances maritime connectivity and provides a geostrategic leverage in the Indo-Pacific region to counter China's influence.
- Sabang port would allow India easier access to the Malacca Strait and there is a proposal to establish connectivity to Andaman and Nicobar.
- Internationalization of rupee: MoU on Local Currency Settlement Systems (LCSS) for financial integration through usage of local currency for bilateral transactions (2024).
- Health and Pharmaceuticals: Sharing best practices on Digital Health initiatives increase capacity building programmes for healthcare professionals etc.
For Indonesia
- Market Access: India is an important export destination for Indonesia as it is the 2nd largest buyer of coal and crude palm oil from Indonesia.
- Investment: Indian companies have made significant investments in Indonesia in infrastructure, power, textiles, steel, automotive, etc.
- E.g. India's GMR Airports Limited will be developing and operating Kualanamu International Airport in Medan, Indonesia.
- Climate Change and Disaster Resilience: Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) activities by India have aided Indonesia which is prone to earthquakes, tsunamis etc.
- Indonesia joined the India-led Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Food Security: India's support in Indonesia's new mid-day meal scheme through the sharing of knowledge and experience.
- Space Cooperation: Cooperation between ISRO and its Indonesian counterpart (BRIN) on Integrated Biak Telemetry, Tracking and Command (TTC) Facilities for Satellites and Launch Vehicles (2024).
- Education and Skill Development: Capacity building training for Indonesian professionals under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Programme, cooperation under the ASEAN-India Network of Universities (AINU).
Challenges
- Unrealized Trade Potential: The bilateral trade potential between India and Indonesia stands at US$ 61 billion which around 33% higher than the actual current trade volume.
- High tariff, non-tariff barriers along with low FTA (India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement) utilisation are major constraints to trade.
- The bilateral trade of $29.40 billion (2023-24) is low compared to the set target of US$ 50 billion in trade by 2025.
- China's influence: China plays a dominant role in the development of Indonesia. Indonesia has accepted huge investments from China under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) which raises concerns for India.
- Slow Progress of strategic projects: Progress on strategic projects like Indonesia's purchase of Brahmos missiles, development of Sabang Port etc. has been slow with impact of various economic and geopolitical factors.
- Lack of connectivity: Limited direct air connectivity, visa issues have hindered greater people-to-people interactions.
Way Forward
- Identifying areas of collaboration: India and Indonesia must also identify areas of collaboration for convergence beyond the China factor by creating an "ASEAN Plus" policy.
- E.g. Aligning ASEAN's Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) with India's Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)- Indonesia has committed to supporting the maritime resources pillar under the IPOI.
- Trade Reforms: Rationalizing FTAs, accelerating consensus on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) etc. be encouraged to improve economic integration.
- Capitalizing on Regional cooperation: Engaging more actively in fora like ASEAN, East Asia Summit (EAS), BRICS, IPOI etc.
- Indonesia can be invited to join the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) for realizing the goal of Act East Policy.
- Cooperation in the Global South: Work together on issues of importance to the Global South through South-South Cooperation.
- E.g. Indonesia acts as a bridge connecting India to the Pacific Island countries.
- Developing Minilaterals: Minilaterals like the trilateral partnerships like India-Indonesia-Australia can be promoted to act on focussed sectors of cooperation.
- People-to-people Ties: Promoting cultural exchanges, opportunities for education and employment and tourism.
- E.g. Capitalizing on 2025 being declared as the ASEAN-India Year of Tourism.



