Why in the News?
Genome India Project (GIP) has achieved a significant milestone by making the genomic data of 10,000 individuals publicly accessible.
More about News
- Whole genome sequencing data for 10,000 individuals have been archived at Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC).
- IBDC, Faridabad is India's first national life science data repository, mandated to archive publicly funded research data. It is supported by Department of Biotechnology.
- Framework for Exchange of Data Protocols (FeED)' and the IBDC Portals were also launched at Genome India Data Conclave.
- 'Framework for Exchange of Data (FeED)' Protocols is under Biotech-PRIDE Guidelines and it ensures high-quality, nation-specific data sharing in a transparent, fair, and responsible manner.
Genome India Project
- It was initiated in 2020 by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India with collaborations of 20 institutions to map India's genetic diversity.
- Primary objective: Build a comprehensive catalogue of genetic variations that reflect unique diversity of Indian population.
- Key Achievements:
- 20,000 samples collected from 83 diverse populations, establishing a bio bank.
- 10,000 genomes sequenced in first phase, creating a reference genome for India.
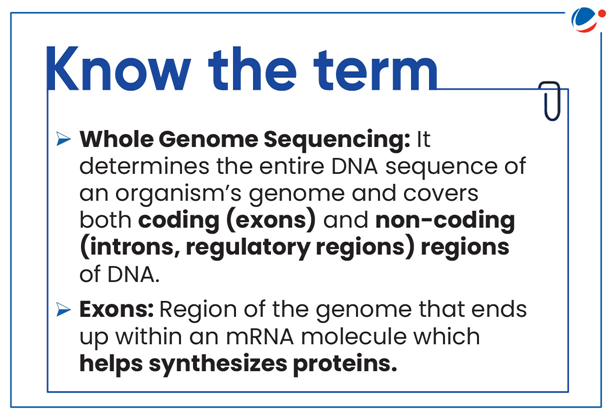
What is Genome Sequencing?
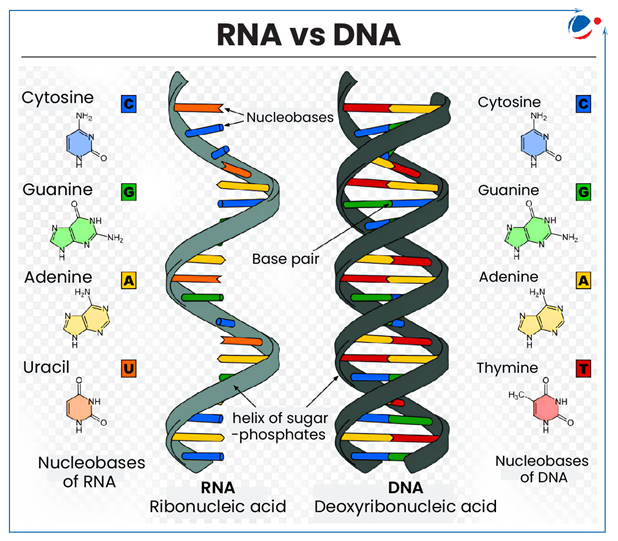
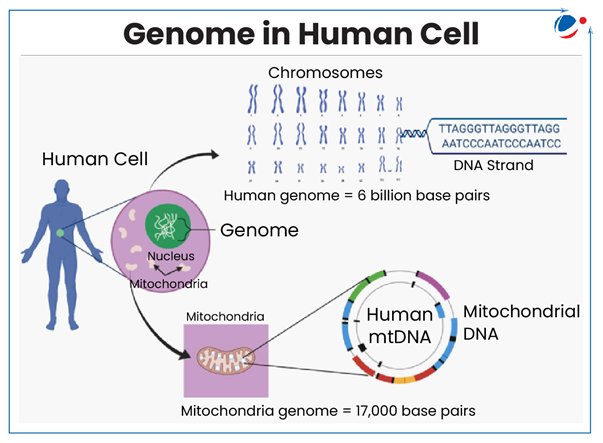
- What is Genome: It is entire set of genetic material i.e. DNA/RNA (DNA in most organisms) present in an individual or species.
- It contains all information necessary for development, functioning, and maintenance of that organism.
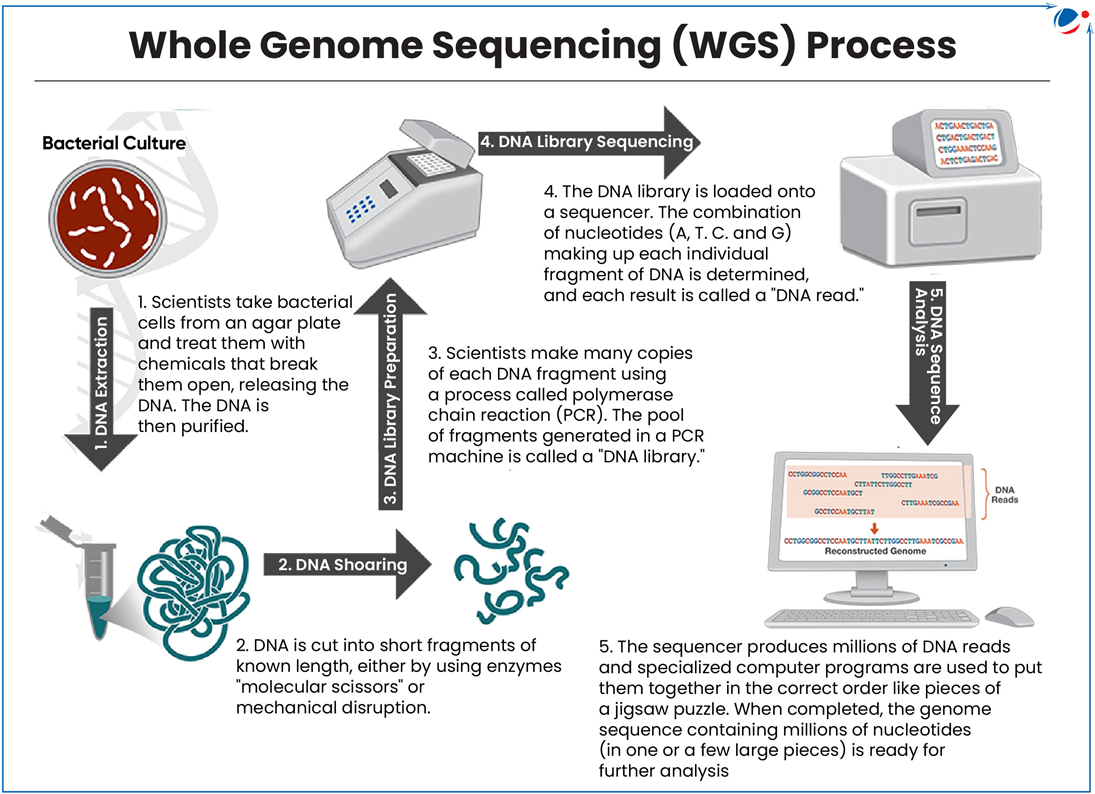
- Genome Sequencing: It is process of determining complete genetic material sequence of an organism's genome.
- It determines the precise sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA/RNA strand.
- Sequence of bases (often referred to by first letters of their chemical names: A, T, C, G and U) encodes biological information that cells use to develop and operate.
- Applications:
- Healthcare and Medicine:
- Medical Research: Genome sequencing aids in identifying genetic disorders and Enhances disease research by linking genetic variations to prevalent health conditions.
- Other Applications: Facilitates precision medicine, early detection of diseases, aids in cancer research etc.
- Public Health & Epidemic Control:
- Epidemiology: Tracking pathogens during outbreaks allows for better public health responses.
- Vaccine Development: Helps in designing vaccines against infectious diseases.
- Agricultural Science: It helps in improving crop varieties and livestock through genetic insights.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Helps in cataloging species and understanding evolutionary links.
- Healthcare and Medicine:
Other Projects on Genome Sequencing
|
Challenges related to Genome Sequencing
- Data Accuracy and Error Correction: Despite advancements, sequencing technologies still grapple with errors, particularly in long-read sequencing.
- Lack of Data Protection and Regulation: Many Indian genomic samples are sent abroad for sequencing, as existing regulations allow commercial export of biological samples. This raises concerns about data security and privacy.
- Ethical Issues: Raises ethical concerns like potential for genetic discrimination, question of Informed Consent, issues of eugenics etc.
- Inequity and low diversity: Unregulated market forces may create barriers to better healthcare access, especially for the poor and ethnic minorities.
- Cost and Accessibility: While sequencing costs have dropped significantly, large-scale projects remain expensive, limiting accessibility in low-resource settings.
- Fragmentation of genetic data: With a number of organizations providing genetic testing services, the data remain in silos.
- Without a framework for collecting well aggregated summary data, the data remains inaccessible for public health decision-making.
Way Forward
- Advancements in Sequencing Technologies: Continued innovation in sequencing platforms e.g. improvements in long-read accuracy to detect complex genomic rearrangements, using next generation sequencing (NGS) etc.
- NGS is a high-throughput DNA sequencing technology that allows for rapid and parallel sequencing of millions of small DNA fragments simultaneously.
- NGS enables sequencing entire genomes much faster and at a lower cost compared to traditional sequencing methods like Sanger sequencing.
- NGS is a high-throughput DNA sequencing technology that allows for rapid and parallel sequencing of millions of small DNA fragments simultaneously.
- Ethical Frameworks and Policy Development: Establishing clear ethical guidelines and policies for genome sequencing applications, particularly in population screening, is essential.
- Global best practices can be followed for curbing various ethical and privacy related issues e.g. Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act (GINA) of US.
- Cost Reduction and Global Accessibility: Efforts to further reduce sequencing costs and simplify workflows will make genomic technologies more accessible worldwide.






