Key suggestions included focus on improving business performance, upgrading digital technology services and tapping business growth potential in MSME clusters.
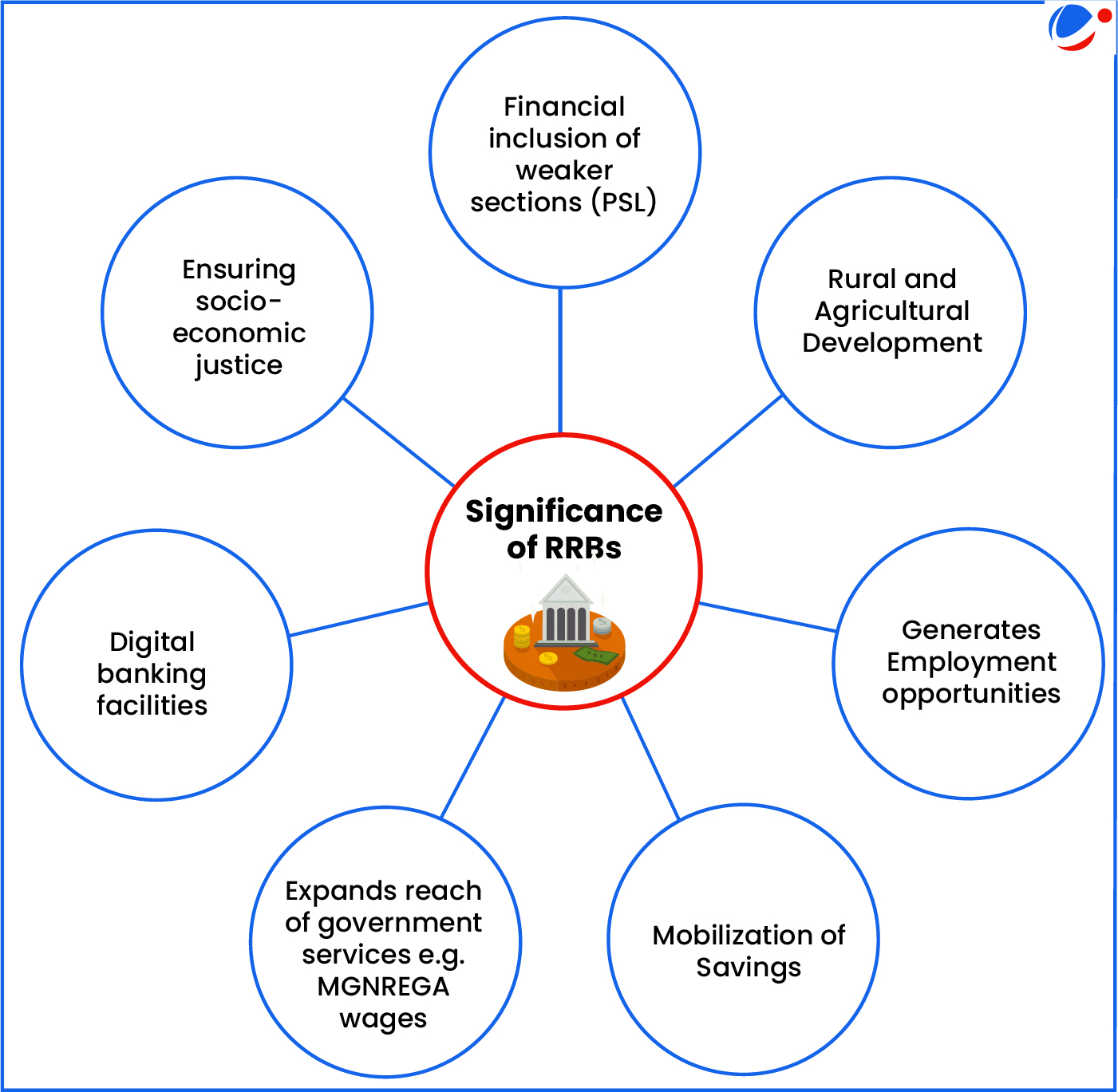
About RRBs
- They are established under the RRB Act, 1987 based on the recommendation of Narasimham Working Group (1975).
- Aim: To provide banking and credit facilities for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- There are 43 RRBs presently in India.
- They are jointly owned by Government of India, State Governments and Sponsoring Commercial Banks (50:15:35).
- They are Scheduled Commercial Banks (Government Banks) regulated by RBI and supervised by NABARD.
- Created primarily for rural areas, however, may also set up branches in urban areas.
Issues with RRBs
- Lack of coordination in Branch expansion: Results in inequitable distribution.
- Difficulties in Deposit mobilization: Practical exclusion of the richer rural population restricts deposit mobilization.
- Issues with human resource: High attrition rate due to availability of more attractive jobs. (urban orientation)
- Loans by Commercial Banks are more attractive due to lower interest rates for weaker sections.
Way Forward
- Structural consolidation to improve efficiency.
- Recapitalization of RRBs for capital augmentation.
- Periodic review and capacity building of human resources.




