Why in the news?
In 2024, India and Indonesia commemorated 75 years of the establishment of diplomatic relations.
More about the news
- Several activities were undertaken to mark 75 years of Track 1.5 Diplomacy in India-Indonesia bilateral ties.

- Indonesian embassy organised e-sports show match at the India Gaming Show 2024 in Pune, underscoring the immense potential of esports as a platform for cultural exchange and international cooperation.
- Embassy of India in Jakarta, in partnership with Observer Research Foundation hosted the inaugural Jakarta Futures Forum (JFF) in 2024.
- JFF is a vision and a commitment from both countries to build a meaningful and inclusive future together.
- First-ever "India-Indonesia defence industry exhibition-cum-seminar" organised in Jakarta.
Significance of India-Indonesia bilateral relations
For both countries
- Maritime security in the Indian Ocean region: Joint Exercises like Samudra Shakti (Navy), and India-Indonesia Coordinated Patrol (IND-INDO CORPAT) enhance interoperability between the two navies and facilitate the prevention drug trafficking, maritime terrorism, armed robbery, piracy etc. in the Indian Ocean region.
- Synergy in the vision for the Indo-pacific region: Both countries agreed on the "Shared Vision of India-Indonesia Maritime Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific" and share a similar vision for a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region which respects ASEAN centrality.
- India's Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) and Indonesia's Global Maritime Fulcrum vision synergize, enhancing geopolitical engagement.
- Strategic partnership: Both countries established Strategic Partnership in 2005, later elevated to a New Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2018 ,allowing for new collaboration in field of defence industry, science and technology etc.
- Cooperation in multilateral forums: Both nations cooperate on matters like maritime security, digital transformation, etc., on multilateral platforms like the G20, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), East Asia Summit, and the United Nations.
- Sharing of best practices: India–Indonesia Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD Dialogue) was launched in July 2023 to provide a distinctive platform for mutual learning and policy coordination.
- Expanding military-to-military engagements: E.g., INS Sindhukesari docked in Jakarta, as part of military-to-military engagements, for the first time in February 2023 for operational turnaround.
- Shared history and Cultural values
- Both countries participated in the Bandung Conference in 1955, which led to the establishment of the Non-Aligned Movement (1961).
- Stories from great epics of Ramayana and Mahabharata form source of Indonesian folk art and dramas.
- Bali Yatra is celebrated with a great deal of fervour in both India and Indonesia.
- Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre promotes bilateral cultural linkages between India and Indonesia.
For India
- Enhancing India's Defence exports: Indonesia has expressed interest in the BrahMos missile and Light Combat Aircraft among others.
- Important trade partner: Indonesia is India's largest trade partner in ASEAN region.
- Total Bilateral Trade between both countries stands at around USD 38.85 Billion (during fiscal year 2022-23)
- Internationalization of Indian rupee: MoU to promote the use of local currencies for cross-border transactions were signed by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Bank Indonesia (BI) in 2024.
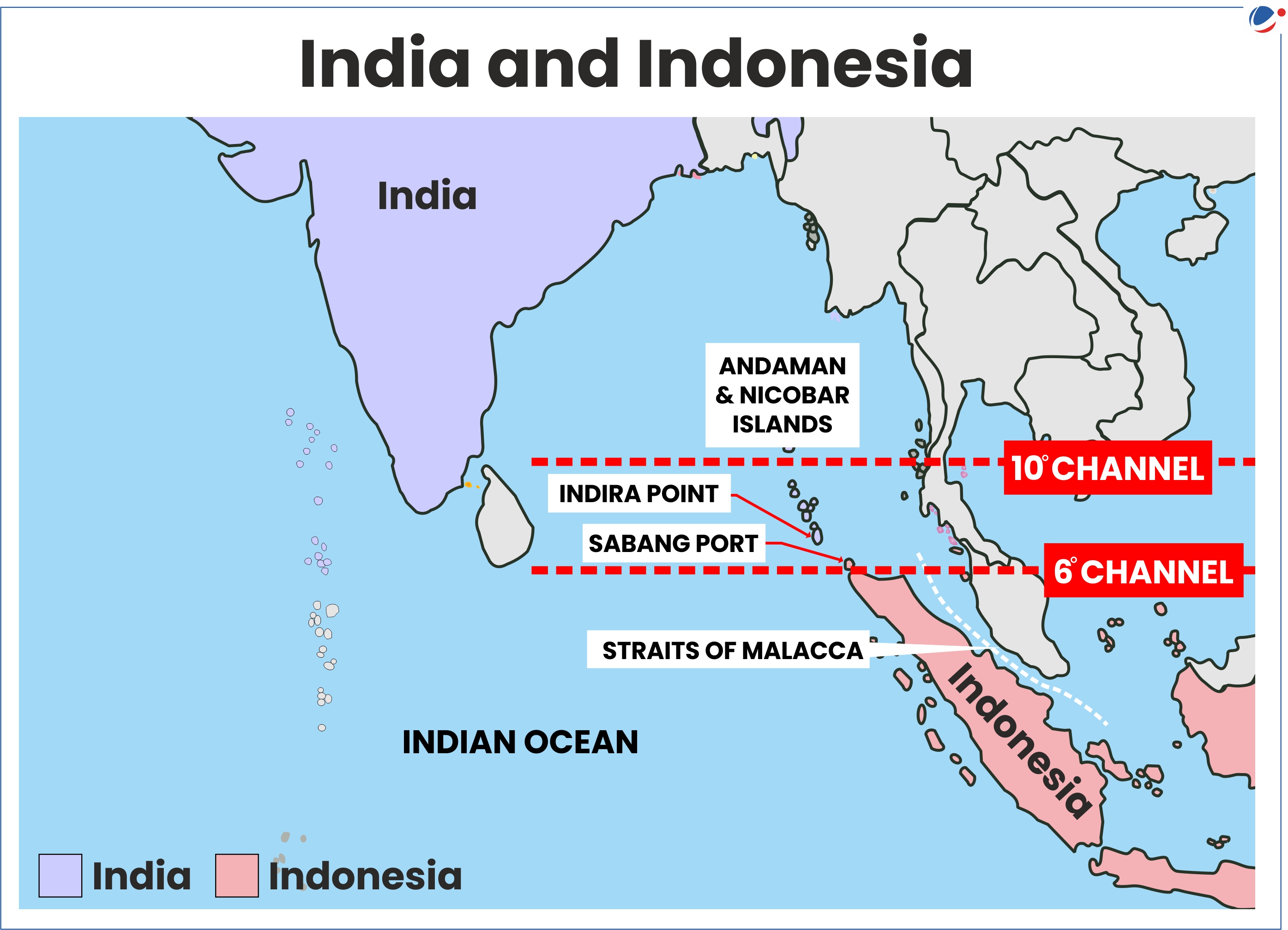
- Enhancing maritime Connectivity: Under Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, India is helping in development of port infrastructure especially Sabang port in Aceh, Indonesia.
- Sabang port is a deep seaport that would allow India easier access to the Malacca Strait and there is a proposal to establish connectivity to Andaman and Nicobar.
For Indonesia
- Important export destination: India is the 2nd largest buyer of coal and crude palm oil from Indonesia.
- Humanitarian Assistance: India launched Operation Samudra Maitri to provide humanitarian assistance to Indonesia, post-earthquake and tsunami in 2018.
- Development Partnership: Indonesia is a major recipient of capacity-building platforms like ITEC (Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation Programme), and Technical Cooperation Scheme (TCS) of the Colombo Plan.
Challenges in the relationship
- Trade Imbalance: The balance of trade favours Indonesia due to India's large imports of palm oil and coal.
- Unrealized trade potential: As per some estimates bilateral trade potential is US$ 61 billion, 33% higher than current trade.
- Dominance of China: Indonesia has accepted substantial Chinese investment under the Belt and Road, which has raised concerns.
- Regulatory and procedural Challenges:
- Joint production and defense supplies have failed due to differing acquisition processes.
- A special window for addressing Indian investors' concerns has been dysfunctional.
- Lack of connectivity: Limited direct air connectivity and visa issues have hindered greater people-to-people interactions.
Way Forward
- Tourism Diplomacy: India-Indonesia should establish 'RICH'- Religious, Cultural & History, theme-based tourism plan to strengthen the sector and people to people exchanges.
- Enhancing Trade: Need for greater economic cooperation, including accelarating of a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to address trade and investment barriers.
- Enhance strategic Interfaces: Indonesia, as a neighbour, should consider joining International Solar Alliance, Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure, and Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Substantive Cooperation through Engagement: Both countries shall utilize regional multilateral forums such as the ASEAN Regional Forum, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), and Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).



