SC in Kolkata Municipal Corporation & Anr Vs Bimal Kumar Shah & Ors has stated that Article 300A has been characterised both as a constitutional and also a human right.
- Article 300A states that “no person shall be deprived of his property save by authority of law”.
Key highlights of the judgment
- Deprivation of any person’s immovable property must follow a fair procedure of law.
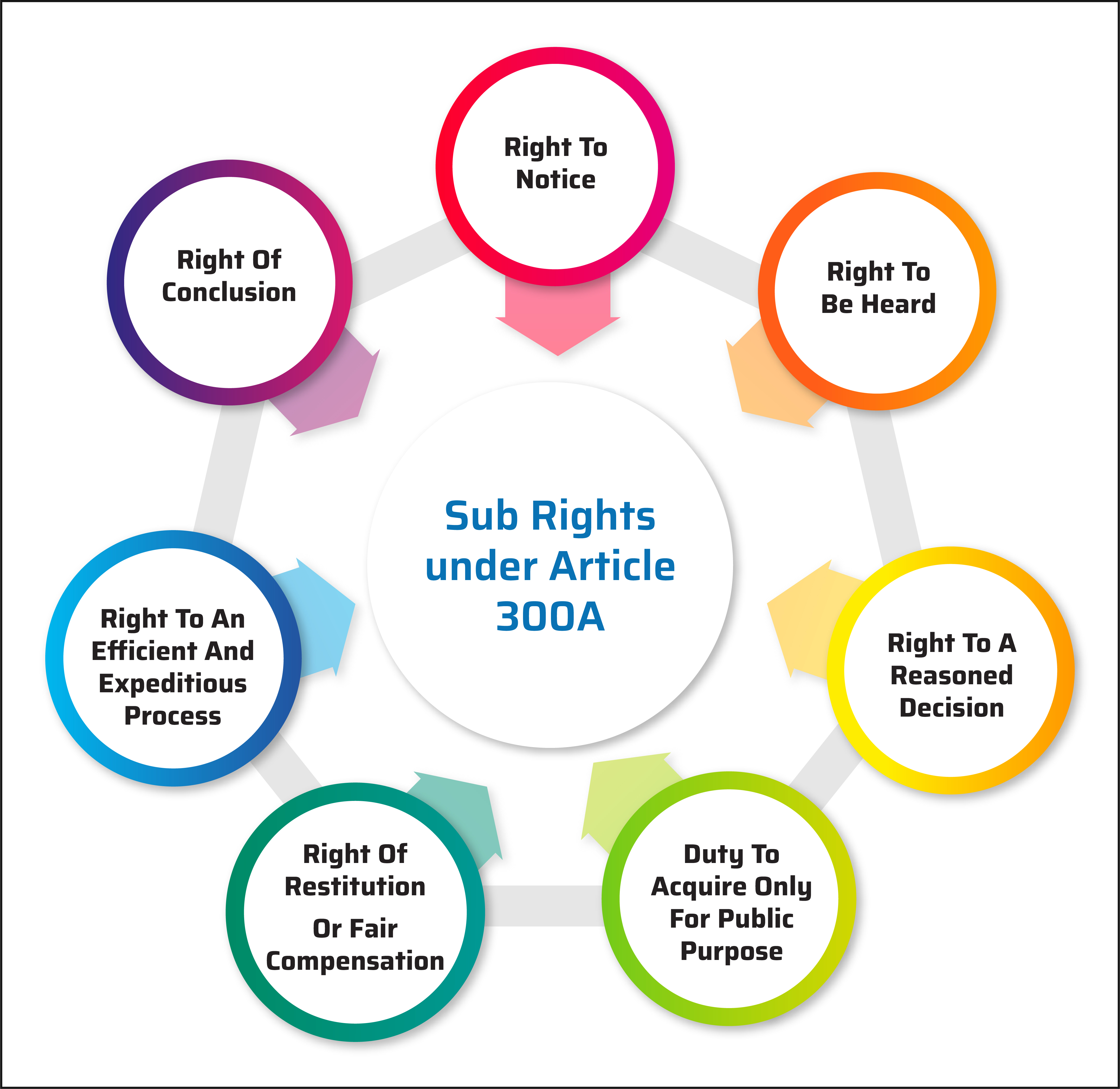
- Minimum content of constitutional right to property comprises of seven sub-rights or procedures (non-exhaustive). (refer to the Infographic)
- Compulsory acquisition will be unconstitutional if proper procedure is not established or followed before depriving a person of their right to property.
Status of Right to Property in India
- Right to property was explicitly held as a fundamental right under Article 19(1)(f) and Article 31, at the inception of the Constitution in 1950.
- 1st Constitutional Amendment (1951): Added Article 31A to provide for acquisition of any estate as against the provisions enshrined under Articles 14 and 19.
- 44th Constitutional Amendment (1978): Removed right to property as a fundamental right by repealing Articles 19(1)(f) and Article 31 and made it a constitutional right under Article 300A.




