A recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters shows that excessive groundwater extraction has shifted Earth's rotational pole, highlighting the impact of human activities on the planet.
Key Findings of the Study
- Between 1993 and 2010, excessive groundwater extraction caused Earth's rotational pole to shift 80 cm eastward, which contributed to a 0.24-inch rise in sea levels by altering planet's mass distribution.
- Shift in Earth's rotational axis is driven by movement of groundwater from aquifers to oceans.
- This shift occurred at a rate of 4.36 cm per year, challenging previous climate models that primarily focused on ice sheet melting.
- Most of the world's oceans experience an increase of near 10 mm, but there was a sea level drop observed over the Indian and the Pacific Ocean adjacent to regions of groundwater depletion in Northwestern India and western North America.
About Motion of Earth
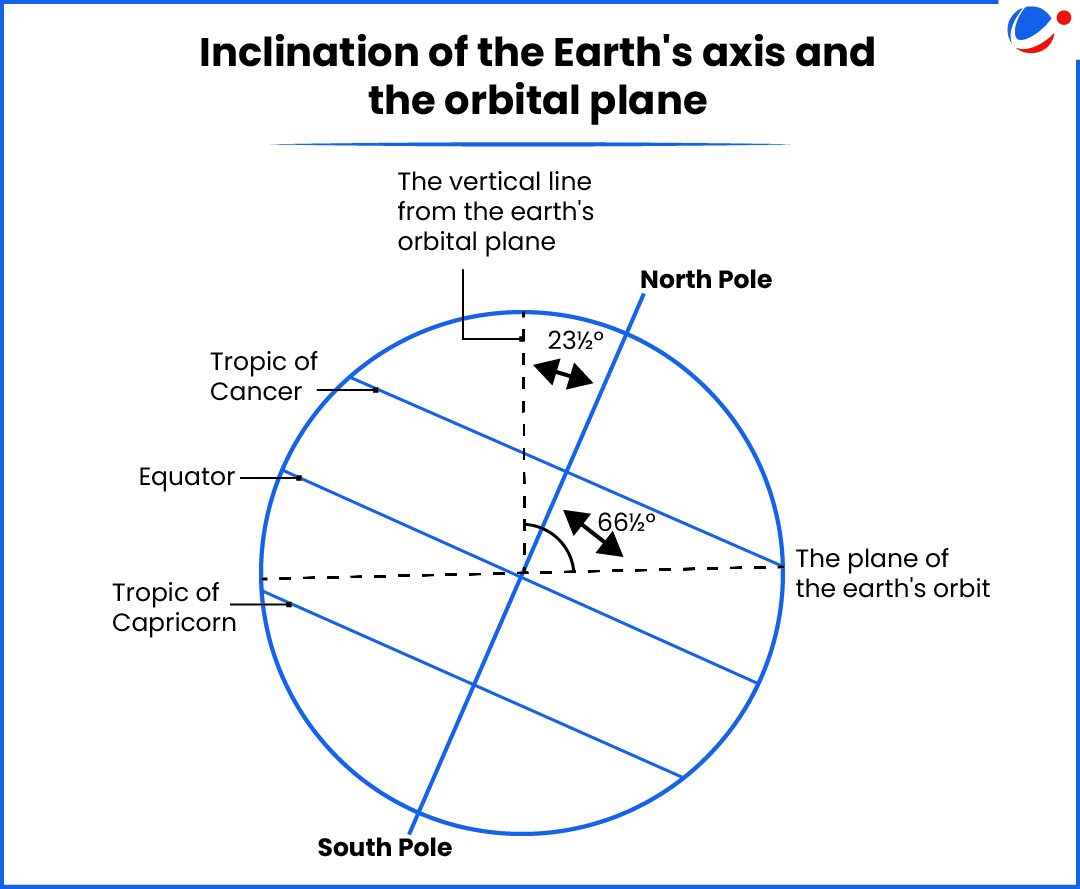
- Earth has two types of motions: rotation and revolution.
- Rotation is the movement of Earth around its axis, while revolution is the movement of Earth around the sun in a fixed orbit.
- Earth's axis is an imaginary line that is tilted at an angle of 66½° to its orbit.
- Effects of the Earth’s Inclination
- Day and night occur due to Earth's rotation, while seasons change because of its revolution.
- It also causes variations in heat distribution, creating seasons and climate zones.
- Effects of the Earth’s Inclination





