Election Commission Introduces Home Voting
Election Commission of India for the first time provides facilities of home voting in coming 2024 election.
- The step is in line with Election Commission (EC) motto ‘No voter is left behind’.
Home Voting Facility:
- Under this, voting from home takes place with involvement of a full contingent of polling staff and security personnel with secrecy of voting diligently maintained.

Beneficiaries:
- Persons with disabilities (PwDs) meeting 40% benchmark disability.
- Senior citizens aged above 85 years.
Other Steps by EC to make voting inclusive:
- Ease of voting by abolishing Form-M for kashmiri migrants residing at Jammu and Udhampur.
- SVEEP (Systematic Voter’s Education and Electoral Participation) to engage PwDs and also sensitise their friends, families, polling officials, etc.
- Proposed Multi-Constituency Remote Electronic Voting Machine (RVM): It would enable migrant voters to exercise their vote from their current place of residence.
- Postal ballot: It allows votes being sent by post. following Persons are entitled to vote by post:
- special voters.
- service voters.
- voters on election duty and.
- electors subjected to preventive detention
- Proxy voting: It allows registered elector to delegate his voting rights to a representative he nominates. Available for service voters.
- Tags :
- Election Commission of India
- Home Voting Facility
- Elections
- Service Voters
- Systematic Voter’s Education and Electoral Participation
Criminalization of Politics
44% of sitting Member of Parliament (MPs) face criminal charges, 5% are billionaires according to the Association of Democratic Reforms (ADR) report.
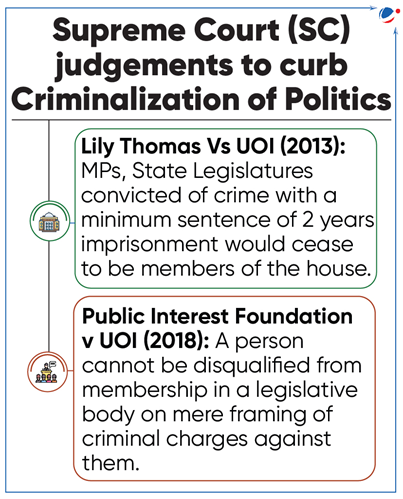
- ADR report also highlights that:
- 50% of MPs facing criminal charge from Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Himachal Pradesh.
- Among sitting MPs with criminal charges, 29% face serious criminal cases including allegations of murder, attempt to murder, crime against women etc.
About Criminalisation of Politics
- Refers to infiltration of criminals, lawbreakers, and corrupt individuals into political system, who then use their influence to further their own interests at cost of country and its citizens.
- Reasons
- Growing nexus between political parties and criminals.
- Lack of laws and rules for governing elections procedure
- Money power i.e. Buying votes for another illegitimate purpose.
- Impact
- Against free and fair elections.
- Affects good governance and integrity of public servants.
- Corrupt activities like taking bribes, embezzling public funds etc. damages social fabric of society.
- Tags :
- Criminalization of Politics
- Free and Fair Elections
- Association of Democratic Reforms
Disclosure Of Assets By Election Candidates
Supreme Court, while hearing an appeal on election petition, held that election candidates have right to privacy as regards to matters which are of no concern to voters or are irrelevant to candidature of public life.
- Statutory provisions regarding declarations by Election candidates
- Section 33 of the Representation of People’s Act (RPA), 1951: Deals with nominations for election of candidates and presentation of valid information.
- Section 36 of RPA, 1951: Provides for scrutiny of nomination and empowers returning officer to reject nominations on grounds of any defect of ‘substantial character’.
- Tags :
- Election
- Right to Privacy
- Representation of People’s Act
SC Asks Government To Act on Misleading Advertisements
Supreme Court (SC) asked the Government to act on FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) firms using misleading advertisements.
- Court also requested Union Ministries to detail the actions taken to combat deceptive advertising practices, which negatively impact public lives.
Misleading Advertisements
- Misleading advertising is any published claim that gives a consumer an incorrect understanding of the product or service.
- Under Consumer Protection Act 2019, an advertisement is misleading if it
- Falsely describes a product/service,
- Gives a false guarantee to nature, quantity or quality of product/service,
- Represents unfair trade practice, or
- Deliberately conceals important information.
Impact of misleading advertisements
- Violates consumers’ right to information and choice
- Potential to cause consumer financial loss and mental agony
- Severe repercussions on consumer health and safety, especially with advertisements of drugs or medical devices of questionable efficiency.
Initiatives Taken to combat misleading advertisements.
- ‘Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022’ issued by Central Consumer Protection authority (CCPA).
- Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954: It prohibits advertisement for remedies alleged to possess magic qualities.
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: Establishes CCPA to regulate matters relating to misleading advertisements.
- Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006: Penalty for misleading advertisements pertaining to food.
Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act of 1954
|
- Tags :
- Misleading ads
- Consumer Protection Act 2019
- Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 1954
- Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- Central Consumer Protection authority



