Why in the news?
Recently, on occasion of Civil Services Day, Prime Minister highlighted that civil servants play a pivotal role in furthering governance and public welfare.
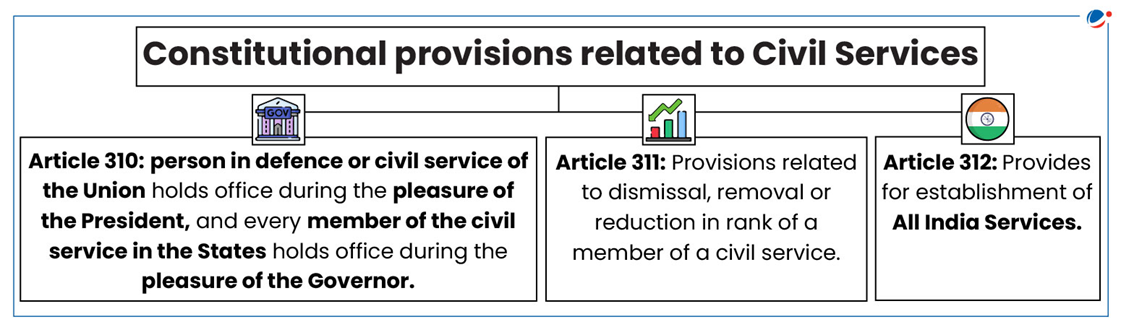
About Civil Services
- Civil servants are permanent officials in the executive wing of governance.
- Genesis: The concept of a merit-based modern Civil Service in India was introduced in 1854 following Lord Macaulay's Report,
- Post-independence: Civil Services, after Independence, have been categorised into three types:
- All India Services (common to both Centre & States): recruited and trained by the Central Government, but, for work, they are assigned to different States.
- Central Services (for purely Central subjects) and
- State Services (for administration of subjects under State jurisdiction).
Role of Civil Servants in Governance
- Continuity of governance: Being part of permanent executive Civil servants ensure continuity in governance even when elected governments change.
- Interface between government and people: Civil servants act as the main channel for communicating people's needs to the government and implementing government policies on the ground.
- Policy formulation: They provide necessary inputs, identify policy areas, analyse alternatives, solutions to societal issues etc. and advice to the ministers.
- Cementing Indian democracy:
- Free and fair elections: Election Commission has played a pivotal role in ensuring elections in India are free and fair. Reforms introduced by former CEC T.N.Seshan is considered to be critical in reducing the influence of money and muscle in election.
- Participative democracy: Example, in 1976, A.M. Gokhale introduced the Village Development Board (VDB) in Nagaland for decentralised grassroots planning and development.
- Inclusive democracy: Many civil servants have played critical role in giving voice to voiceless. For example, in 2020, the Balangir district administration launched 'Sweekruti' to integrate the transgender community into mainstream activities and social security schemes.
- Growth and development:
- Enforcing law and order: Peace is crucial for socio-economic development of the country. Civil servants work towards addressing social tensions, conflicts and thus create social unity and harmony.
- For instance, Sanjukta Parashar (IPS officer), also known as Iron Lady of Assam played a critical role on in tackling northeast insurgency.
- Overcoming resource constraints: For example,
- IAS officer Armstrong Pame, known as the Miracle Man of Manipur, crowdfunded through social media to construct a 100 km road in 2012 without state financial aid. Now this road is also known as "people's road".
- Operation Sulaimani, pioneered by Prasanth Nair (former District Collector of Kozhikode in Kerala), uses nameless donations from the public to provide food with dignity. This facilitates in ensuring Right to Food.
- Enforcing law and order: Peace is crucial for socio-economic development of the country. Civil servants work towards addressing social tensions, conflicts and thus create social unity and harmony.
- Career Diplomats: Civil servants represent their country in international forums and play an important role in negotiating agreements, promoting national interest, protecting friendly relations with other countries, etc.
- Quasi- Judicial role: Civil servants serves on tribunals, like Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal, Cyber Appellate Tribunal etc.,
- Delegated Legislation: The civil servants frame departmental legislation. The legislature gives a broad outline of legislation and delegates to the civil servants the power to make details of that legislation.
Challenges associated with the functioning of civil services
- Autonomy: Frequent transfer, political pressure and interference, and need for approval from higher authorities, etc. compromises the autonomy of civil servants.
- Infrastructure: Many Indian cities, particularly rural areas, lack proper infrastructure and resources, impacting effective implementation of government programs and service delivery.
- Red-tapism: Complex bureaucratic procedures, hierarchical system in civil services, make the decision process time-consuming, slowing down the progress and make it difficult to implement change in society.
- Security: Civil servants and their family members are often exposed to risk of violence, and threats from criminals or extremists.
- For example, Death threats to IAS officer, Tukaram Mundhe for raiding illegal bars, demolishing encroachments and action against land and water mafia.
Initiatives taken to improve the functioning of Civil Servants
|
Conclusion
Each step taken by a civil servant towards transparency, efficiency, and integrity, brings our nation closer to its goals of inclusive development and good governance. In recent years, government undertook multiple steps to enhance civil servants work efficiency, capacity building etc. However, a careful restructuring of civil services is further required to address issues faced by citizens in 21st century, and enhance delivery of services.



