Why in the news?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Asset Reconstruction Companies) Directions, 2024.
More on the news
- Issued Under: The powers conferred by Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- Applicable for every ARC registered with the Reserve Bank under Section 3 of the SARFAESI Act, 2002.
- Aim: To streamline and regulate the functioning of ARCs in India, ensuring transparency, accountability, and integrity in the financial system.
About ARCs
- Definition: ARC is a financial institution that buys the Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) or bad assets from banks and financial institutions so that the latter can clean up their balance sheets.
- ARCs are required to resolve the assets within a maximum of 8 years of acquisition of financial assets and redeem the SRs representing the assets.
- Genesis: SARFAESI Act in 2002 envisaged that ARCs would be registered and regulated by RBI. There are 29 ARCs in operation in India (2022).
- Narsimham Committee – II (1998) proposed asset reconstruction companies, on the similar lines of asset management companies' prevalent globally.
- Types: Based on ownership, ARCs could be public, private or public-private partnership.
- Examples: National Asset Reconstruction Company Limited (NARCL), India Debt Resolution Company Ltd etc.
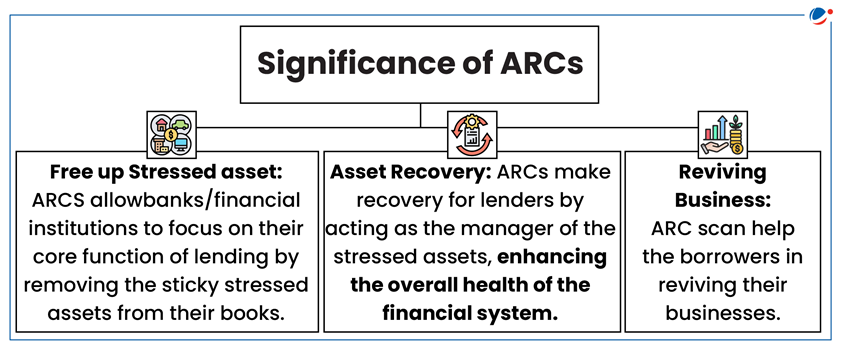
How ARCs Work?
- Asset Acquisition: ARCs acquire financial assets from banks/ FIs either on their own books or in the books of a trust set up for the purpose of securitisation and/ or reconstruction.
- Security Receipts: Lenders sell stressed loans to ARCs at a discount. Unless the transaction is entirely in cash, ARC issues security receipts that are redeemable as and when it recovers the specific loan.
- Management Fee: ARCs also charge bad-loan sellers a management fee of 1.5% to 2% of the value of the asset every year.
Need of Reforms in ARCs
- Sub-optimal performance of the ARCs: Banks and FIs could recover only about 14.29% of the amount owed by borrowers in stressed assets sold to ARCs from FY04 to FY13.
- Sales of stressed assets to ARCs Decreased: It has gradually decreased over the years. In 2021-22, only 3.2% of the previous year's gross NPAs were sold to ARCs.
- Other: Vintage NPAs being passed on to ARCs, lack of debt aggregation, Lack of skill for holistic resolution of distressed borrowers, emergence of IBC as alternative resolution mechanism etc.
Key Provisions of Master RBI (ARCs) Directions, 2024
- Net Own Fund (NOF): To commence the business of securitisation or asset reconstruction, an ARC is required to have a minimum NOF of Rs300 crore and thereafter, on an ongoing basis.
- Registration: Before commencing the business of securitisation or asset reconstruction, an ARC shall apply for registration and obtain a certificate of registration (CoR) from the RBI.
- Leadership Positions: It set age limit of 70 for MD/CEO or Whole-time Director and tenure of 5 years at a time, with a maximum tenure of 15 years continuously.
- ARCs shall report to IBA: Details of CAs, advocates and valuers (who committed serious irregularities in professional services) for including in Indian Banks' Association (IBA) database.
- Internal audit: ARCs shall put in place an effective internal control system providing for periodical checks and review of the asset acquisition procedures and asset reconstruction measures.
- Other Provisions:
- ARCs are prohibited from raising money by way of deposit.
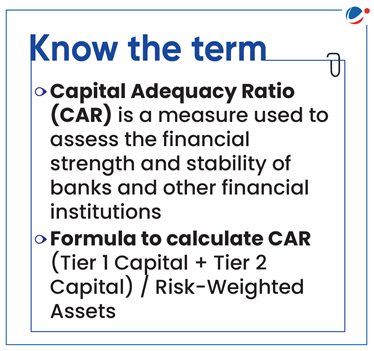
- They are also mandated to maintain a capital adequacy ratio of a minimum of 15% of its total risk-weighted assets.
Other recent changes by RBI in ARCs Regulations
- Strengthened corporate governance of ARCs: RBI mandated that the chair of the board and at least half the directors in a board meeting must be independent directors.
- Increased Transparency: ARCsmust disclose their track record on returns generated for the security receipt investors, and engagement with ratings agencies of schemes floated in the last eight years.
- Fair Practices Code (FPC): In order to achieve the highest standards of transparency and fairness in dealing with stakeholders, ARCs are advised to put in place a Board-approved FPC.
- Member of CIC: Every ARC shall become a member of at least one credit information company (CIC) which has obtained certificate of registration from the RBI.
Way Forward
- Broaden scope of ARCs: Consider permitting ARCs to acquire financial assets from all regulated entities, including FPIs, and all NBFCs irrespective of asset size and from retail investors.
- Regulatory Disincentives: For delay by lenders in internally resolving the NPA assets to ensure disposal of NPAs in time.
- List of NPAs (intend to sell/auction): This should be prepared by all regulated lenders and disclosed to ARCs after entering into a confidentiality agreement for increasing predictability of stressed assets.
- Fraud Accounts: Sale of fraud accounts to ARCs may be permitted with appropriate safeguards, without diluting the fixing of accountability at banks/FIs level or affecting criminal proceedings against the responsible persons by competent authorities.
- Asset Acquisition from Foreign: For debt aggregation, ARCs may be allowed to acquire stressed loans to domestic borrowers from regulated overseas banks and FIs.




