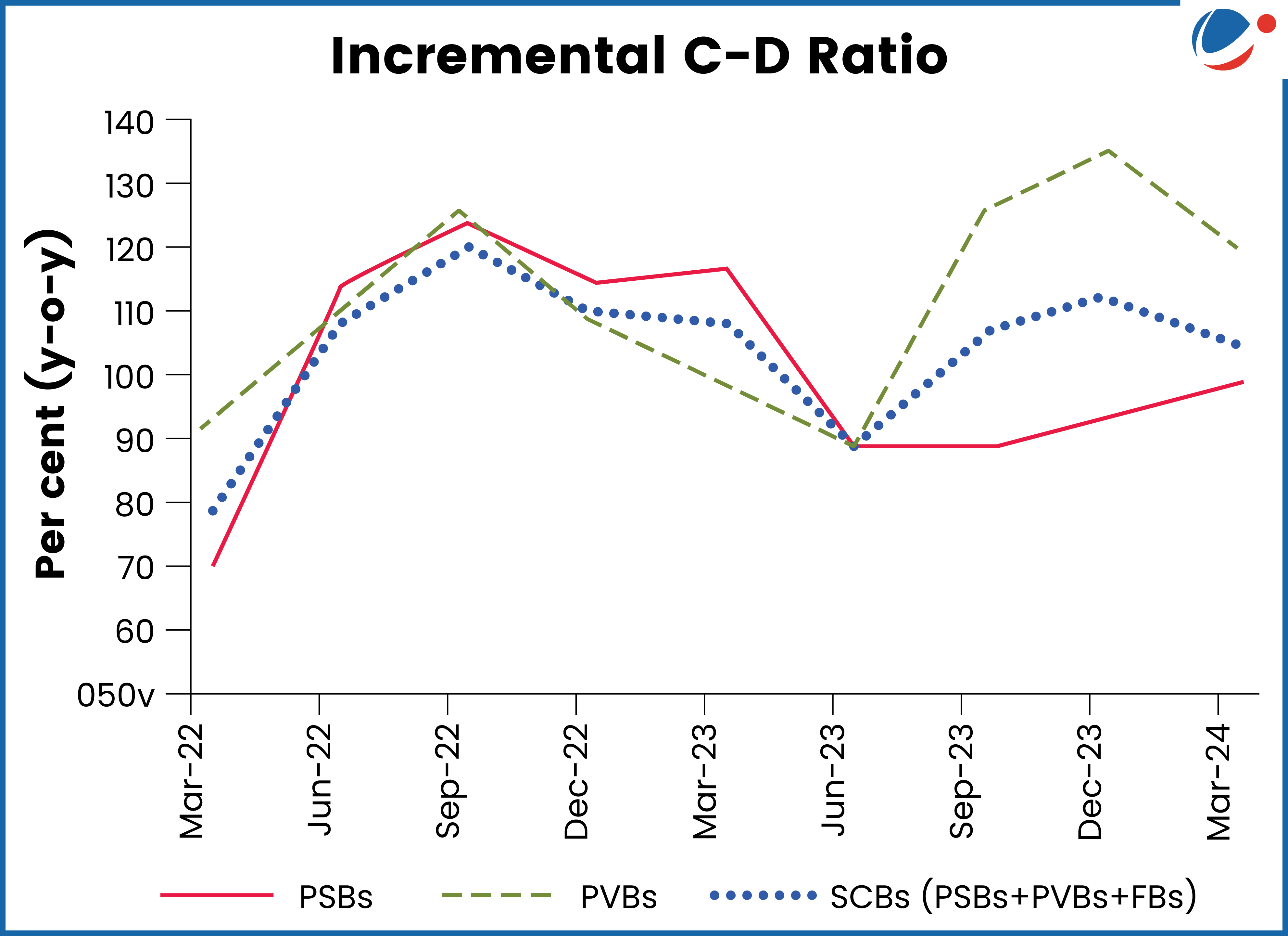
Reserve Bank of India has told banks to bridge the gap between credit and deposit growth and reduce CD ratio.
- CD Ratio is a financial metric representing the percentage of loans a bank has issued relative to its total deposits.
- According to the RBI’s Financial Stability Report (refer to the graph):
- CD ratio has been rising since September 2021 and peaked at 78.8% in December 2023.
- Over 75% of the banks with C-D ratios above 75% are private sector banks. a
Key Reasons for high CD ratio
- Higher credit growth
- Rising retail credit (includes vehicle loans, personal loans, etc.).
- From April 2022 and March 2024, bank lending to the retail sector grew at a CAGR of 25.2%.
- Increasing loans to businesses and MSMEs.
- Rising retail credit (includes vehicle loans, personal loans, etc.).
- Slower deposit growth:
- Banks are facing stiff competition with each other.
- Additionally, customers are transitioning from savers to investors and diverting funds to capital markets, slowing deposit growth.
Impact of High CD Ratio
Bank may face:
- Pressure on Net Interest Margins (NIM): NIM is a measure of the net return on the bank’s earning assets like investment securities, loans, etc.
- Liquidity risk: Banks' may be unable to timely meet payment obligations.
- Credit risk: Borrowers could default on their contractual obligations




