Why in the News?
Pandavula Gutta and Ramgarh Crater were recognised as Geo-Heritage Sites
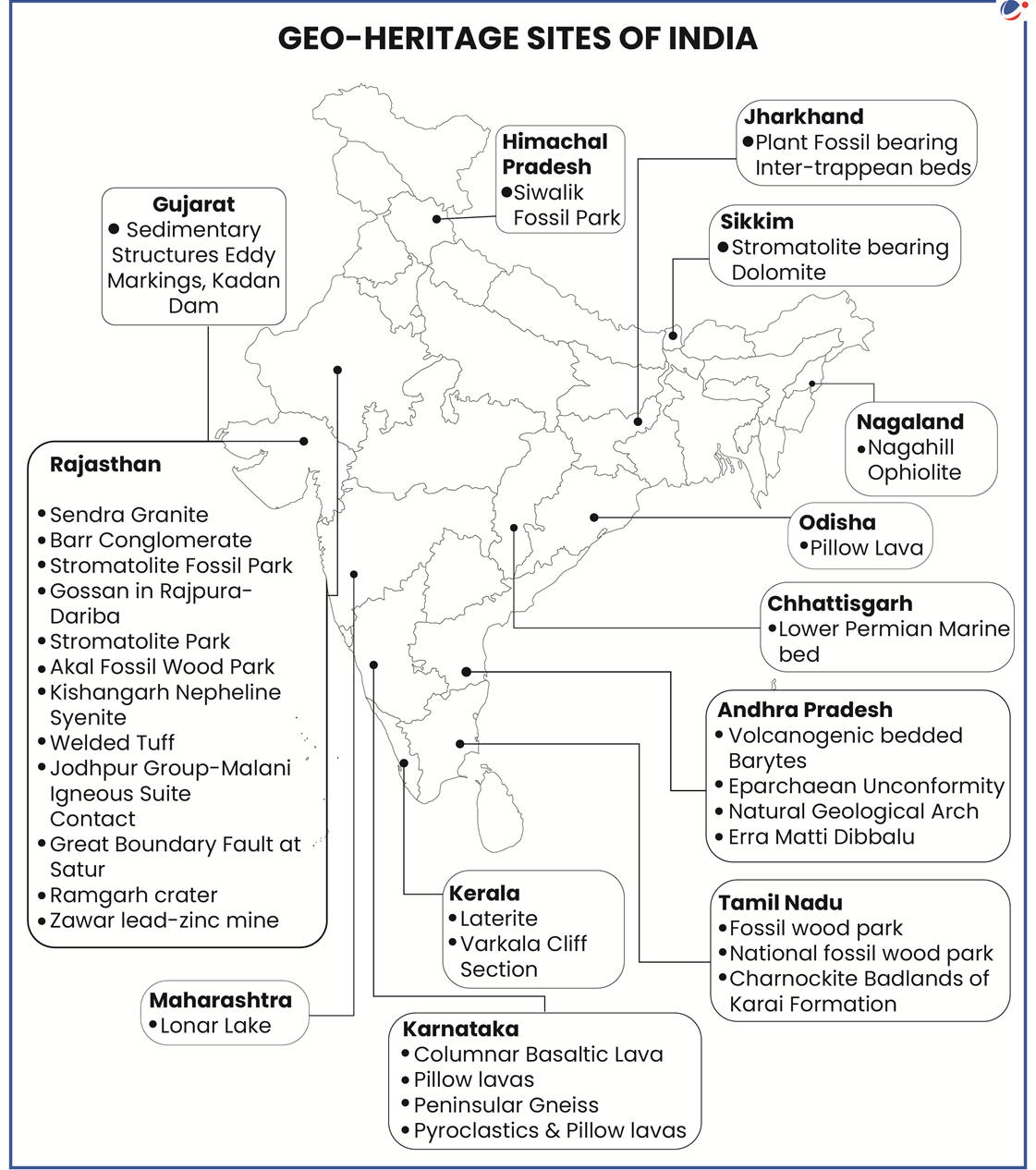
About Geo-Heritage Sites
- Geo-heritage sites are sites of rare and unique geological, geomorphological, paleontological, and stratigraphic significance.
- These includes caves, natural rock-sculptures, sediments, rocks, minerals, meteorites or fossils
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) recognizes, declares and maintains the Geo-heritage sites in India (refer map)
About Pandavula Gutta

- Located in Telangana (Jayashankar Bhupalpally district) is considered to be older than Himalayas.
- Discovered in the year 1990.
- It houses Palaeolithic Paintings which depict:
- Wild life (Bison, Antelope, Tiger, and Leopard etc.),
- Geometric shapes (swastika symbol, circles and squares) and
- Weapons (bows, arrows, sword and lancer etc.)
- These cave paintings offer a rare glimpse into the prehistoric man's rock art identified on walls and ceilings of caves, rock shelters and isolated boulders.
About Ramgarh Crater (Ramgarh Astrobleme)

- "Astrobleme" is used to describe a geological feature formed by the impact of a meteorite.
- Located in Rajasthan (Baran district), situated on the old course of river Parbati.
- First discovered by the Geological Survey of India in 1869 and was recognised as a 'Crater' by the Geological Society of London.
- The now eroded crater in the Vindhyan Supergroup of sedimentary rocks dates back to the Mesoproterozoic age (roughly 1600 to 1000 million years ago)
- One of the three Meteorite Impact Craters of India
- The other two being Lonar in Maharashtra and Dhala in Madhya Pradesh.
- The presence of coesite, a high-pressure polymorph of Silicon dioxide (SiO2) indicates that the site has an impact origin and confirms the meteorite strike.
- Diameter of around 3.2 kilometres and has an elevation of more than 200 metre.
- The middle of the crater consists of a 10th Century temple dedicated to lord Shiva 'Bhand Devara Temple" (built in the style of Khajuraho).
- Crater hill also comprises of cave temples dedicated to a local goddess Kisnai and Annapurna.
- Currently protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 and its Crater Lake (Pushkar Talab) is notified under "wetland" under Wetland (Conservation & Management) rules, 2017.
- The Crater was recognised and added to the "Earth Impact Database" by the Planetary and Space Science Centre (PASSC) in Canada.
- The PASSC was established in Canada (2001) and the "Earth Impact Database" provides information about confirmed meteoroid impact structures in the world.