Introduction
UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) in partnership with Gallup, and Oxford Wellbeing Research Centre released the World Happiness Report (WHR) 2024. Finland topped in the rank for the seventh successive year whereas India was ranked 126th out of 143 nations.
What is the Happiness?
There is no universally accepted definition of happiness, however, Ananda, or pure bliss, is an idea deeply rooted in Indian culture. It represents a profound and transcendent state of happiness and well-being that goes beyond fleeting pleasures and is considered the ultimate goal of human existence
How does money affect happiness?
|
Different philosophical theories explaining happiness
|
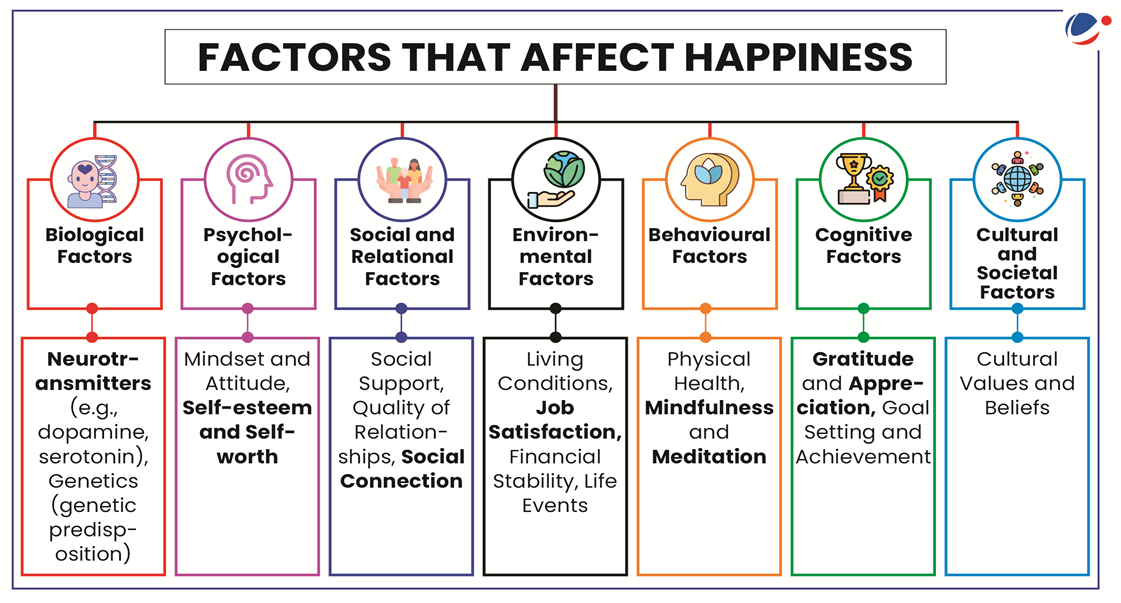
Happiness: A Multifaceted Pursuit with Far-Reaching Impacts

Happiness is a fundamental human pursuit and plays a crucial role at various levels of human existence.
- Individual-Level Benefits of Happiness: Happiness is closely linked to improved mental health, increased productivity, and stronger, more satisfying relationships.
- Studies show that happiness can lead to a 12% boost in productivity and is positively correlated with marital satisfaction.
- Social-Level Impacts: At the societal level, happiness fosters a sense of belonging and social cohesion, contributing to lower crime rates.
- Happier communities also tend to exhibit higher levels of civic engagement and trust in political institutions.
- National-Level Implications: Happiness is associated with political stability, the adoption of sustainable practices, and economic growth.
- Countries that have integrated "Gross National Happiness" schemes into their development plans have seen a boost in their economic performance.
- Global Ramifications: On an international scale, happiness is linked to greater global peace and cooperation, as well as more equitable distribution of resources and reduced deprivation.
- The Global Peace Index suggests that countries with higher levels of happiness tend to score higher on measures of peacefulness and international collaboration.

Instant Gratification vs. Lasting Happiness
|
How do Ethical Values Cultivate Happiness?
- Altruism and Compassion: Ethical values that promote concern for others, such as altruism and compassion, have been shown to increase feelings of meaning, purpose, and overall well-being.
- Integrity and Authenticity: Living with integrity, by aligning our actions with our values, can foster self-respect, confidence, and a sense of authenticity. This tends to promote happiness and life satisfaction.
- Fairness and Justice: Upholding ethical principles of fairness, justice, and equality helps create a more harmonious and stable society, reducing sources of conflict, resentment, and unhappiness.
- Self-Regulation and Discipline: Ethical values that encourage self-discipline, impulse control, and emotional regulation can help people make healthier choices and manage stress more effectively.
- Positive Relationships: Ethical values that prioritize honesty, trust, and respect in our relationships tend to foster more meaningful, supportive, and mutually fulfilling connections.
Check your Ethical AptitudeIn pursuing economic growth and development, many nations prioritize material prosperity over human well-being and sustainable practices. This approach often overlooks the broader determinants of happiness at individual, societal, and global levels. In the context of above idea, answer the following questions
|



