World Bank Group Guarantee Platform (WBG GP)
The WBG GP went live for business.
- Initiated in 2024, WBG Guarantees consolidates all guarantee products and experts from across the WBG institutions at Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA).
- WB guarantees are provided to private lenders, for infrastructure financing, where the demand for debt funding is large, political and sovereign risks are significant, and long-dated financing critical to a project’s viability.
- Previous to the launch of the platform, the WBG offered 20 guarantee solutions each with different processes, rules, and standards that impeded clients access.
![An infographic titled "WB Group [Global partnership of five institutions]" lists five entities: IBRD, IDA, IFC, MIGA, and ICSID, with brief descriptions. A note states IBRD and IDA form the WB, and India is part of all except ICSID.](https://d2av8kbir6lh9m.cloudfront.net/uploads/5om3HATsRs7eVFpVPvzDPKnpkId54AWpjldIh42v.jpg)
WBG GP
- Aims to boost WBG annual guarantee issuance to $20 billion by 2030.
- The WBG issued approximately $10.3 billion in new guarantees using products from the platform in 2024.
- Provides three types of coverages:
- Credit guarantees for loans to the public or private sector;
- Trade finance guarantees;
- Political risk insurance against non-commercial risks for private sector projects or public-private partnerships.
Significance
- Simplified market-friendly menu of guarantee options offering multiple options to WB clients.
- Streamlines processes, removes redundancies, and provides greater accessibility by de-risking investments in developing countries.
- Prioritizing high-impact projects and facilitating growth.
- Drive sustainable development and inclusive growth through innovative financing.
- Tags :
- WBG GP
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- Credit guarantees
- Trade finance guarantees
- Political risk insurance
- World Bank Group
SAARC Currency Swap Arrangement
RBI announced SAARC currency swap framework for 2024-2027.
- RBI in concurrence with Union Government revised the Framework under which RBI would enter into bilateral swap agreements with SAARC central banks, who want to avail of swap facility.
- Currency Swap Arrangement (CSA) is a contract under which two counterparties agree to exchange two currencies at a set rate and then to re-exchange those currencies at an agreed upon rate at a fixed date in future.
- Previously, in 2012, SAARC countries set up Framework on Currency Swap mechanism to meet the short-term forex liquidity requirement.

Key Highlights of the revised Framework
- Under the Framework for 2024-27, a separate INR Swap Window has been introduced with various concessions for swap support in Indian Rupee (Total corpus of the Rupee support is ₹250 billion).
- RBI will continue to offer swap arrangement in USD and Euro under a separate US Dollar/ Euro Swap Window with an overall corpus of US$ 2 billion.
Significance of CSAs
- Helps maintain financial stability during a crisis by providing a backstop line of funding for forex liquidity requirements.
- Helps in addressing short-term balance of payments stress.
- Tags :
- SAARC Currency Swap Framework
- Currency Swap Arrangement
Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio
Reserve Bank of India raised concerns over bank’s high CD Ratio and asked them to bridge the gap between credit and deposit growth and reduce CD ratio.
- CD Ratio is a financial metric representing the percentage of loans a bank has issued relative to its total deposits.
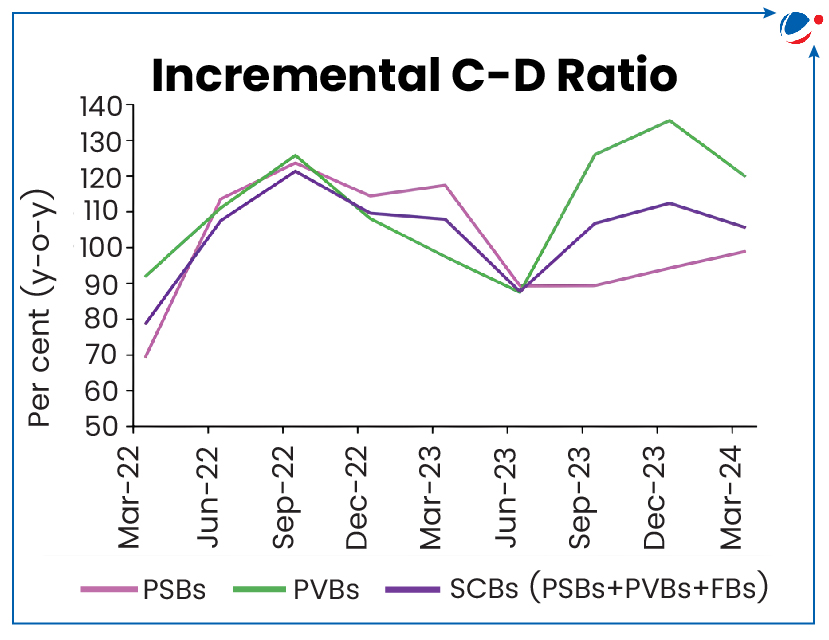
- According to the RBI’s Financial Stability Report (refer to the graph):
- CD ratio has been rising since September 2021 and peaked at 78.8% in December 2023.
- Over 75% of the banks with C-D ratios above 75% are private sector banks.
Key Reasons for high CD ratio
Higher credit growth
- Rising retail credit (includes vehicle loans, personal loans, etc.).
- From April 2022 and March 2024, bank lending to the retail sector grew at a CAGR of 25.2%.
- Increasing loans to businesses and MSMEs.
Slower deposit growth
- Banks are facing stiff competition with each other.
- Additionally, customers are transitioning from savers to investors and diverting funds to capital markets, slowing deposit growth.
Impact of High CD Ratio
Bank may face
- Pressure on Net Interest Margins (NIM): NIM is a measure of the net return on the bank’s earning assets like investment securities, loans, etc.
- Liquidity risk: Banks' may be unable to timely meet payment obligations.
- Credit risk: Borrowers could default on their contractual obligations
- Tags :
- RBI
- Financial Stability Report
- Credit-Deposit (CD) Ratio
RBI Directions on Fraud Risk Management
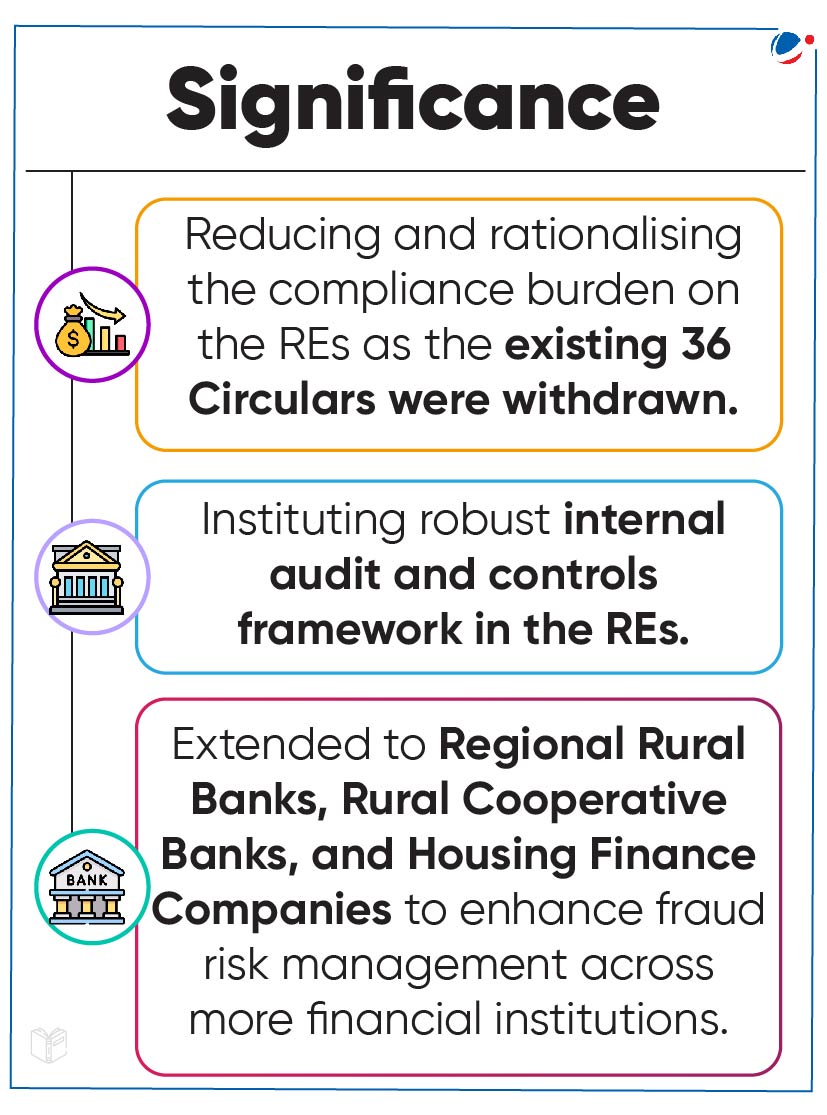
RBI has issued three revised master directions on fraud risk management for Regulated Entities.
Regulated Entities under RBI
- Commercial Banks (including Regional Rural Banks) and All India Financial Institutions;
- Cooperative Banks (Urban Cooperative Banks / State Cooperative Banks / Central Cooperative Banks);
- Non-Banking Finance Companies (including Housing Finance Companies).
Major Points of Master Directions
- In compliance with the Supreme Court judgement in State Bank of India & Ors. Vs. Rajesh Agarwal & Ors of 2023 REs shall ensure compliance with the principles of natural justice in a time-bound manner before classifying Persons / Entities as fraud.
- The requirement for Data Analytics and Market Intelligence Unit is mandated to strengthen risk management systems.
- Framework on Early Warning Signals and Red Flagging of Accounts has been strengthened for early detection and prevention of frauds in the REs.
- Also, timely reporting to law enforcement agencies and supervisors.
- Tags :
- RBI
- Regulated Entities
- Fraud Risk Management
Ways And Means Advances (WMA) Scheme
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased the Ways and Means Advance (WMA) limit of States/UT to Rs 60,118 crore from existing Rs 47,010 crore.
- This will enable Sates/UTs to better manage their fiscal situation.
- Apart from WMA, Special Drawing Facility (SDF), and Overdraft (OD) facility are important financial accommodation instruments availed by States/UTs.
- These instruments are governed by under the RBI Act, 1934.
About Ways and Means Advance (WMA)
- Advances to States/UTs provided by RBI to meet temporary mismatches in the cash flows of receipts and payments.
- Facility is also available for the Union Government.
- Types: Normal WMA and Special WMA (now known as Special Drawing Facility (SDF))
- First, a state/UT is provided with a special WMA and after its exhaustion, it gets a normal WMA.
- Special WMA has lower interest rate than Normal WMA
- Interest rates are linked to Repo rate.
- Availed by State against the collateral of Consolidated Sinking Fund (CSF), Guarantee Redemption Fund (GRF), Auction Treasury Bills (ATBs), etc.
- CSF and GRF are reserve funds maintained by some State with the RBI.
- Availed by State against the collateral of Consolidated Sinking Fund (CSF), Guarantee Redemption Fund (GRF), Auction Treasury Bills (ATBs), etc.
About Special Drawing Facility (SDF)
- Availed by State against the collateral of Consolidated Sinking Fund (CSF), Guarantee Redemption Fund (GRF), Auction Treasury Bills (ATBs), etc.
- CSF and GRF are reserve funds maintained by some State with the RBI.
About Overdraft Facility
- Facility is provided whenever financial accommodation to a State exceeds its SDF and WMA limits.
- Generally, State Governments/UTs can avail overdraft on 14 consecutive days (relaxation can be provided by RBI).
- Tags :
- Special Drawing Facility
- Ways and Means Advance (WMA)
- Overdraft Facility
- RBI Act, 1934
Domestic Money Transfer (DMT)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in a review revised framework for domestic money transfer
- 'Framework aims to regulate money transfer services offered by regulated entities in India.'
- The framework for Domestic Money Transfer (DMT) was introduced in 2011.
- The framework is revised by RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Review was done as there has been significant increase in the availability of banking outlets, developments in payment systems for funds transfers, etc.
- Revised framework shall come into effect from November 01, 2024.
- Tags :
- RBI
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Domestic Money Transfer (DMT)
Financial Inclusion Index
RBI released Financial Inclusion Index for March 2024
- The value of the Index for March 2024 stands at 64.2 vis-à-vis 60.1 in March 2023
About Financial Inclusion Index
- It is a comprehensive index incorporating details of banking, investments, insurance, postal as well as the pension sector.
- It captures the extent of financial inclusion across the country.
- Single value index (0 to 100), where 0 is complete exclusion and 100 is full inclusion.
- It includes three broad parameters viz., Access (35%), Usage (45%), and Quality (20%).
- It is published annually in July.
- Tags :
- RBI
- Financial Inclusion Index
New SEBI Guidelines for Credit Rating Agencies (CRAS)
Guidelines, issued under SEBI Act (1992) and Regulation 20 of CRA Regulations, will enhance the Ease of Doing business for CRAs and protect investor interests.
Key guidelines
- Communicating rating to companies: By CRAs and within one working day of the rating committee meeting.
- Appeal against rating: Companies can request a review or appeal of the rating decision have three working days of the rating committee meeting.
- Public disclosure: CRAs must publish a press release on their website and inform the stock exchange/debenture trustee within seven working days of the rating committee meeting
- Record maintenance: CRAs must keep records of these disclosures for 10 years.
About Credit rating in India
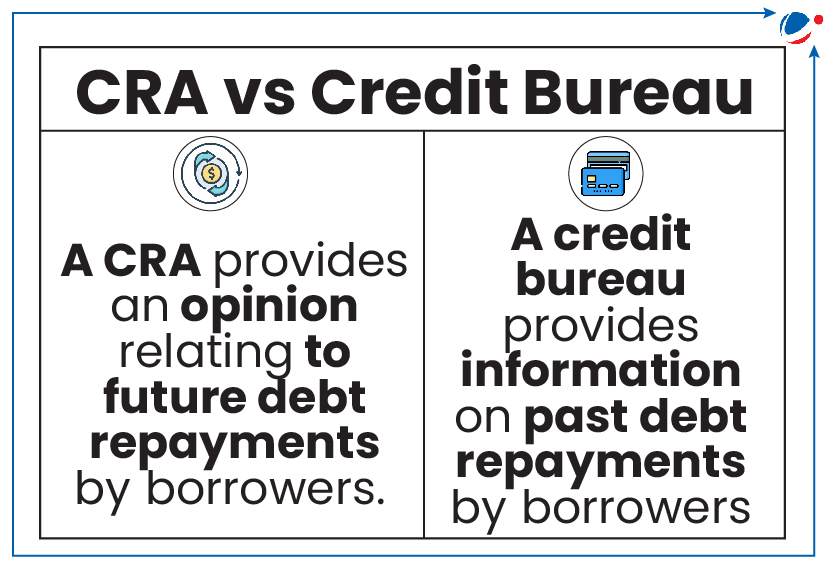
- Credit ratings: It represents a CRA’s opinion on the probability of timely repayment of debt and the likelihood of default on interest and principal payments.
- CRA: SEBI (Credit Rating Agencies) Regulations, 1999 defines CRA.
- A CRA is a corporate body involved (or proposes to be engaged) in rating securities (either listed or to be listed on a SEBI-recognized stock exchange).
- 7 CRA’s registered with SEBI: CRISIL, CARE, ICRA, Acuité, Brickwork Rating, India Ratings (Ind-Ra) And Research Pvt. Ltd, Infomerics Valuation And Rating Pvt. Ltd.
- Tags :
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- Credit Rating Agencies
- Credit Bureau
- CRA Regulations
Inverse ETF
SEBI proposed to introduce a new asset class for investors which can offer investment strategies including long-short equity funds and inverse ETFs.
About Inverse ETF (‘Short ETF’ or ‘Bear ETF’)
- It is an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) constructed by using various derivatives to profit from a decline in the value of an underlying benchmark.
- ETFs are marketable securities that track an index, a commodity, bonds, or a basket of assets like an Index Fund.
- It gains from a drop in the value of an underlying benchmark.
- Only intended for short holding periods.
- Tags :
- SEBI
- Inverse ETF
- Marketable Securities
- Bear ETF
- Short ETF
SEHER Program
Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) and TransUnion CIBIL has launched SEHER Program.
- WEP is a public-private partnership platform incubated at NITI Aayog aiming at empowering women entrepreneurs.
About SEHER Program
- It is a credit education program which will help women entrepreneurs to access financial tools for business growth with financial literacy content and business skills.
- Program is part of WEP’s Financing Women Collaborative (FWC), a first-of-its-kind initiative aimed at accelerating access to finance for women entrepreneurs.
- Presently, only 7% of overall outstanding loans to MSMEs are to women-led businesses, signifying the need for improving credit access to women entrepreneurs.
- Tags :
- NITI Aayog
- Women Entrepreneurship Platform
- Credit Education
- SEHER Program
Survey of Unincorporated Enterprises in India
Annual Survey of Unincorporated Sector Enterprises (ASUSE) results for 2021-22 and 2022-23 was released,
- ASUSE was conducted by National Sample Survey Office, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It covered unincorporated non-agricultural establishments pertaining to proprietorship, partnership (excluding Limited Liability Partnerships), Self-Help Groups (SHG), co-operatives, societies/trusts etc.
About Unincorporated Enterprise
- It is a producer unit which is not incorporated as a legal entity separate from the owner.
- The fixed and other assets used in unincorporated enterprises do not belong to the enterprises but to their owners.
- Enterprises as such cannot engage in transactions or contractual relationships with other economic units nor incur liabilities on their own behalf.
Key highlights of Survey (2022-23)
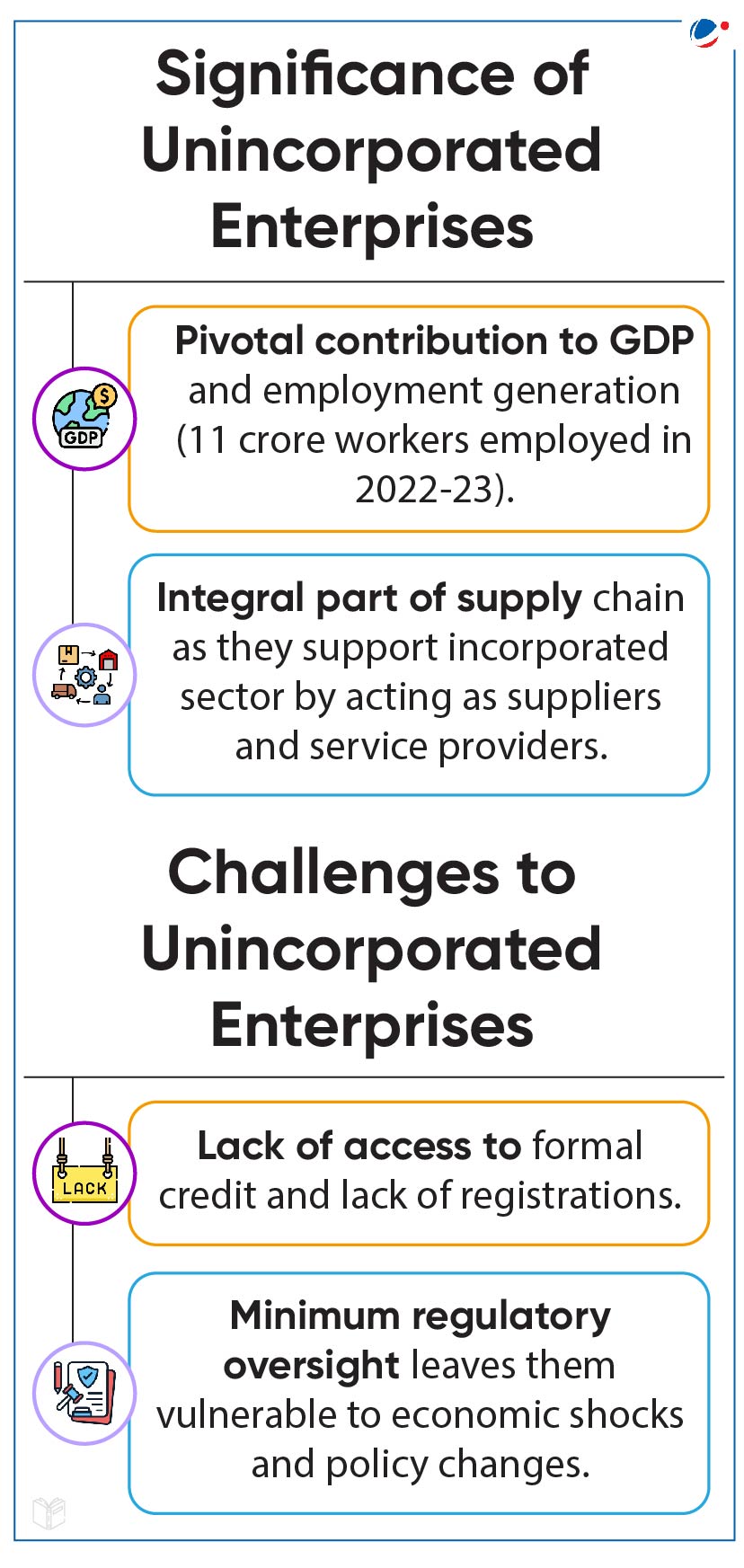
- Establishments in the sector grew by 5.88% (from 2021-22) to 6.50 crore, out of which about 55% belong to rural areas.
- Highest number of establishments are in Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal and Maharashtra.
- Gross Value Added (GVA) showed a 9.83% increase from 2021-22.
- Women entrepreneur led 54% of proprietary establishments in the Manufacturing sector.
- Rapid rate of digitization with a 7.2% increase in use of internet for entrepreneurial purpose.
- Improvement in credit availability showcased by increase in outstanding loan per establishment to Rs. 50,138 in 2022-23.
- Tags :
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- National Sample Survey Office (NSSO)
- Unincorporated Enterprise



