FAO released State of the World's Forests 2024 Report
Theme for this year: “Accelerating Forest solutions through innovation”.
Key highlights
- Deforestation Rate declined to 10.2 million hectare (ha) per year in 2015–2020 from 15.8 million ha per year in 1990–2000.
- Non-Timber Forest Products support livelihoods of about 275 million people in India.
- India ranked 3rd for average annual net gain in forest area from 2010- 2020.
Need for Innovation in Forest Sector

- Climate change related stress (wildfire, pest): Innovative forest and land management strategies needed for resilience.
- Shift towards bioeconomy: Zero-carbon bioeconomy needs innovation for diverse, efficient wood-based product uses.
- Opportunity from non-wood forest product: Many wild forest-based foods, including fish, are rich in micronutrients and have high nutritional content.
Barriers to development of innovations in forest sector
- Lack of innovation culture discouraging curiosity, creativity and risk-taking.
- Capital limitations like human (deficient skill); natural (limited access to forest); social (restricted tenure rights), etc.
- Lack of policy support impacting technology adoption.
Recommendations to scale up innovation
- Recognizing and rewarding innovation can help foster conducive culture.
- Boost skills, capabilities and knowledge to ensure that forest-sector stakeholders have capacity to manage innovation creation and adoption.
- Provide opportunities for knowledge and technology transfer, and build appropriate safeguards.
- Ensure universally accessible financial resources.
- Tags :
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- State of the World's Forests 2024 Report
United Nations Water Convention
Ivory Coast joined the United Nations Water Convention (Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes).
United Nations Water Convention
- Genesis: Adopted in Helsinki (Finland) in 1992 and entered into force in 1996.
- Legally binding: Requires Parties to use transboundary waters reasonably and equitably and ensure their sustainable management.
- Members: India is not a party
NOTE: UN Watercourses Convention (UN Convention on the Law of the Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses) was adopted in 1997. Indus Waters Treaty (1960) aligns with it.
- Tags :
- Indus Waters Treaty
- UNITED NATIONS WATER CONVENTION
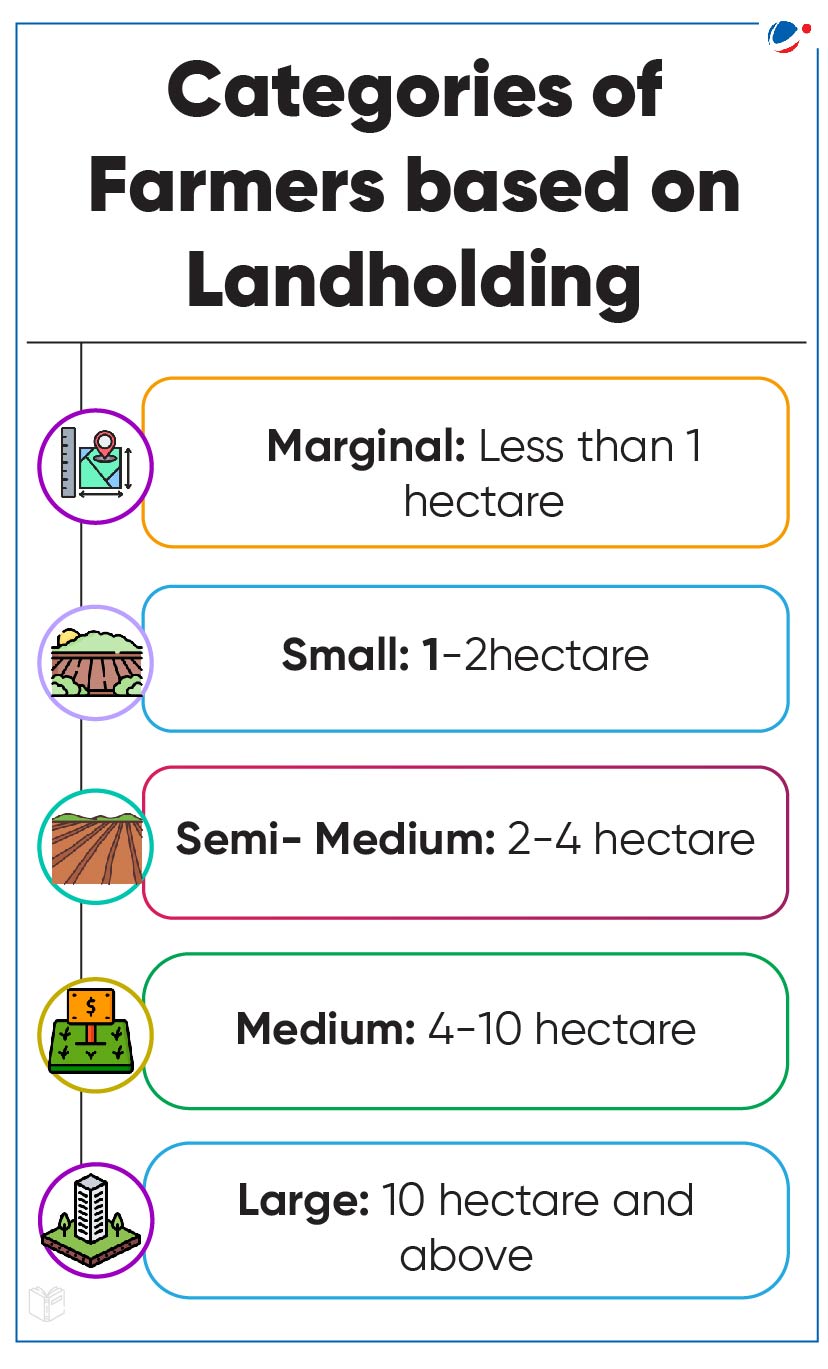
Climate Change and Marginal Farmers
‘Impact of Climate Change on Marginal Farmers’ Report was released by the Forum of Enterprises for Equitable Development (FEED) which is dedicated to advocating for marginal farmers.
Key highlights
- Vulnerability due to extreme weather: Over 1/3rd of marginal farmers had to cope with extreme weather events at least twice in five years.
- Reduction in agriculture income: Climate change may reduce annual agricultural income by 15-18% and by 20-25% in unirrigated areas (Economic Survey of 2017- 18).
- Livelihood Diversification: Over 86% of farmers altered their occupations due to climate impacts. Alternative livelihood includes temporal migration, seeking work under MGNREGA, etc.
- Hurdles in adoption of CRA practices: High up-front cost, limited knowledge about options, small land holdings and lack of physical resources are the major hurdles in adoption of Climate Resilient Agricultural (CRA) practices.
Key Recommendations
- Strengthening existing platforms like the Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA) developed by the FAO.
- Shift focus from land productivity (grains produced per hectare) to water productivity (grains produced per cubic meter of irrigation water).
- Mission mode approach on Education, Training, Orientation, and Extension Support to farmers.
- Tags :
- Climate change
- Climate Resilient Farming
- Marginal Farmers
Spring Initiative
UN-backed network Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) has launched “Spring”, a new initiative to halt or reverse nature loss by 2030.
About Spring Initiative
- Supported by a coalition of 200 investors managing a combined $15trn in assets.
- Objective: To address systemic risk of nature loss to societies and long-term portfolio value creation by enhancing corporate practices on forest loss and land degradation.
- It focuses on responsible political engagement, a vital aspect of corporate governance.
- Tags :
- SPRING INITIATIVE
- Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI)
Fund for Responding to Loss and Damage
The Board for Loss and Damage Fund decided to call it as “Fund to respond to Loss and Damage” (FrLD).
- It was decided that Philippines will be the host country for Board of the fund.
About FrLD
- It was established in 27th session of UNFCCC Conference of the Parties (COP) in Sharm el-Sheikh (Egypt) in 2022.
- Purpose: Fund will help developing countries compensate for losses and damages from natural disasters caused by climate change.
- Loss and damage refer to the negative consequences that arise from unavoidable risks of climate change, like rising sea levels, prolonged heatwaves, desertification, ocean acidification etc.
- Tags :
- Loss and Damage
- FrLD
- COP27
Air Pollution Harms Pollinators More: Study
A recent study published in Nature Communications reveals that air pollution disproportionately harms pollinators like bees and butterflies while crop-destroying pests remain largely unaffected.
Key Findings
- Scent-based communication disruption: Air pollutants alter scent trail (airborne chemical signals), disrupting bees' and wasps' ability to locate flowers, mates, or prey.
- Biological impact: Among the biological behaviours including feeding, growth, survival, and reproduction, the ability to locate food was most severely impaired.
- Ozone is most harmful pollutant: Ozone reduced beneficial insects' ability to thrive by around 34%. Nitrogen oxides also had substantial negative effects.
- Damage at low pollution levels: Changes in insect performance occur even at low levels of air pollution.
About Pollination and pollinators
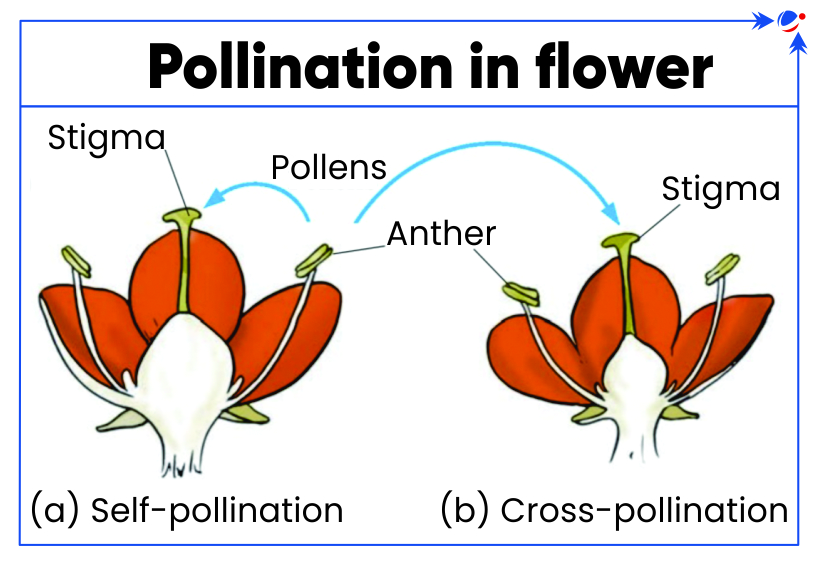
- Pollination, an essential part of plant reproduction, refers to transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. It is of two types:
- Self-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains within same flower or another flower of the same plant.
- Cross-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains to flower of a different plant of the same kind.
- Pollinators refer to agents (or facilitators) of pollination. It could be:
- Abiotic: Wind and water
- Biotic: Insects (bees, wasps, beetles, etc.), birds, and bats among others
- Tags :
- Pollinators
- Pollination
- air pollution
White Paper on Glacial Geoengineering
A group of scientists have released a landmark white paper on glacial geoengineering
- Glacial Geoengineering is the deliberate modification of the climate system around a glacier to slow the melt of the ice shelf and reduce sea level rise.
Proposed Glacial Geoengineering Strategies
- Ocean-heat transport interventions: Setting sediment berms or fibrous curtains along the seabed in the front of ice shelves to block the flow of warm circumpolar deep water.
- Basal-hydrology interventions: Slow the flow of streams that carry meltwater off the ice sheets.
- This can be done through drilling holes through glacier beds to create drainage channels, thereby diverting meltwater streams and slowing ice sheet loss.
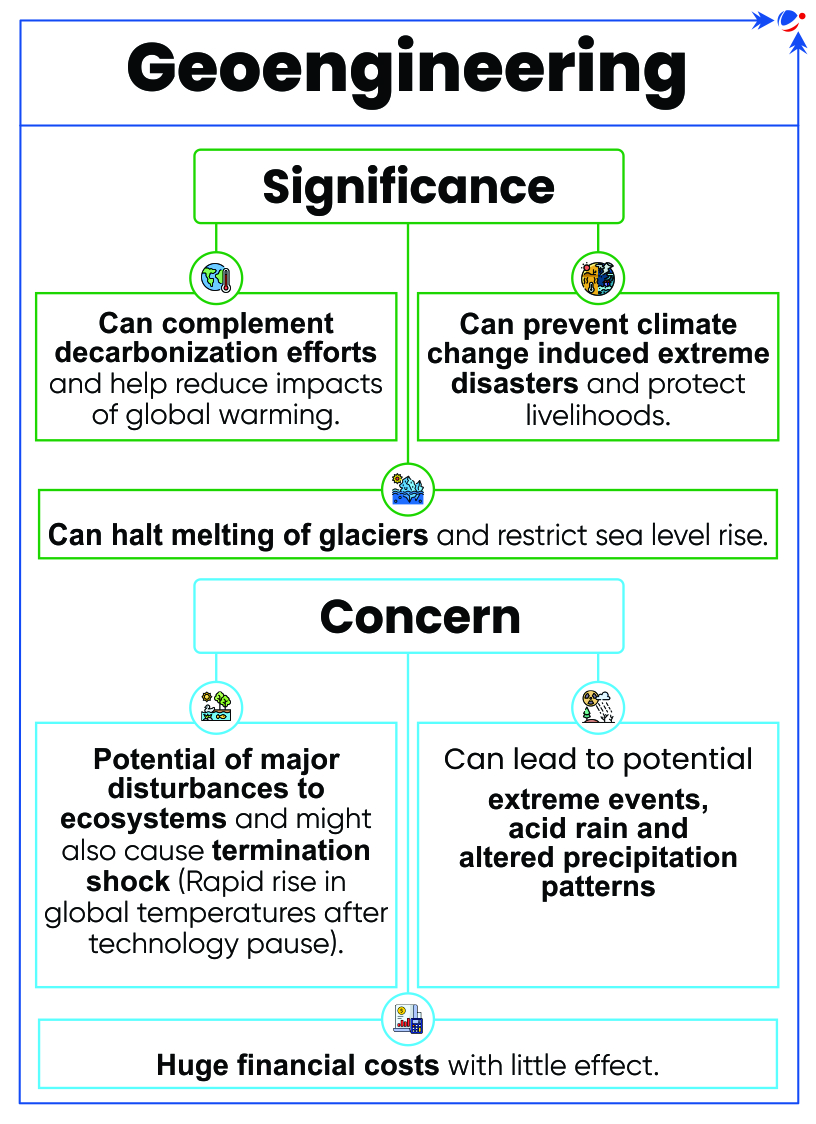
About Geoengineering
- Geoengineering is the deliberate, large-scale manipulation of Earth’s climate systems to counteract anthropogenic global warming.
- Categories of Geoengineering:
- Solar Geoengineering / Solar Radiation Management (SRM): It aims to limit the sun's radiation onto the Earth’s surface and reduce global average temperature.
- Strategies include Aerosol Injection, Marine Cloud Brightening, Albedo Improvement, Ocean Mirror etc.
- Carbon Geoengineering / Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): It aims to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere by removing it from the atmosphere.
- Strategies include Carbon Capture and Storage, Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement, Ocean Fertilization etc.
- Solar Geoengineering / Solar Radiation Management (SRM): It aims to limit the sun's radiation onto the Earth’s surface and reduce global average temperature.
- Tags :
- Glacial Geoengineering
- WHITE PAPER ON GLACIAL GEOENGINEERING
Dual Tower Solar Thermal Plant
China has unveiled the world’s first dual-tower solar thermal power plant (TPP), which boosts energy efficiency by 24%.
Features of the Solar TPP
- Tracking of Sunlight: The plant features two 200-meter tall towers, each surrounded by thousands of mirrors which automatically track the sun’s movement and achieve 94% reflection efficiency.
- Storage of excess heat: The plant utilises molten salt storage as a thermal battery, allowing it to store excess heat collected during the day for continuous power generation at night.
- Tags :
- DUAL TOWER SOLAR THERMAL PLANT
Aquilaria Malaccensis (Agarwood)
CITES eases export of agarwood from India, move to benefit lakhs of farmers.
About Agarwood:
- Aquilaria Malaccensis (agarwood) is an evergreen tree native to Northeast India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and parts of Southeast Asia, and is considered a precious aromatic plant in the region.
- Economic Utility: aromatic plant’s oil and chips both are highly valued in the market.
Protection:
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- Tags :
- CITES
- Agarwood
- AQUILARIA MALACCENSIS (AGARWOOD)
Jerdon’s Courser
Jerdon's Courser has not been visually spotted in over a decade.
About Jerdon's Courser
- Nocturnal bird found only in the Eastern Ghats.
- Exclusively endemic to Andhra Pradesh, specifically within the Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary in Kadapa, Andhra Pradesh.
- Protection Status:
- Under Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats’ (IDWH) scheme.
- Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- Tags :
- JERDON'S COURSER
- Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary
- IDWH Scheme
Wolbachia Bacteria
Recently, study has highlighted that Wolbachia bacteria had manipulated the wasp Encarsia Formosa to entirely get rid of its males.
- Encarsia Formosa wasps helps in controlling population of whiteflies, a major agricultural pest.
About Wolbachia bacteria
- Commonly found in nematodes and arthropods, especially insects
- In insects, these are present in eggs but they are absent in the sperm. Due to this, females can transmit them to their offspring whereas males can’t.
- As a result, Wolbachia have evolved ways to manipulate their insect hosts to produce more female than male progeny.
- Tra gene of Wolbachia play key role in showing this feature.
- Potential Application: Mosquitoes with Wolbachia can be used to reduce numbers of target mosquito species, for example, Ae. Aegypti mosquitoes.
- Tags :
- WOLBACHIA BACTERIA
- Tra gene
Cites Released Report on Rosewood
CITES launched “CITES Rosewoods: The Global Picture" report.
- The report details CITES-listed rosewood species’ characteristics, ecosystem roles, regeneration rates, and threats.
- Such information will help CITES parties make informed non-detriment findings (NDFs).
- NDF is a mandatory scientific analysis under CITES to ensure that exporting a specified quantity of specimens of Appendix I and II -listed species will not affect their long-term survival in the wild.
Rosewood
- About: ‘Rosewood’ also called as “palisander” encompasses a wide range of tropical hardwoods in the Fabaceae (Leguminosae) family. Rosewood in Appendix II of CITES include:
- Dalbergia latifolia (Malabar rosewood) and Dalbergia Sissoo (Shisham) are found in India and are listed as Vulnerable and Least Concern (respectively) on IUCN red list.
- African rosewood, native to West African countries, is listed as endangered on IUCN red list.
- Utility: Crafting furniture and musical instruments.
- Role in Ecosystem:
- Soil Improvement: Dalbergia species can improve degraded soil through fast decomposing leaf litter, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Some species form symbiotic associations with soil bacteria to fix atmospheric nitrogen.

- Tags :
- CITES
- Rosewood
Syntrichia Caninervis
Scientists have found a desert moss - Syntrichia Caninervis - which is able to withstand Mars-like environment conditions.
- Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta.
- Mosses are commonly found in moist-shady locations and are distributed throughout the world except in salt water.
About Syntrichia Caninervis
- It is widespread in some of Earth’s harshest locations including Antarctica and the Mojave Desert.
- It could be the first possible pioneer species for the colonization of Mars.
- Tags :
- SYNTRICHIA CANINERVIS
- desert moss
Araku Coffee
Araku coffee found mention in Prime Minister’s 'Mann ki Baat'.
About Araku Arabica Coffee
- Grows in the hilly tracks of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
- Accredited with Geographical Indication (GI) Tag in 2019.
- Takes its name from Araku Valley, situated in the Eastern Ghats (Andhra Pradesh).
- Weather of the valley with its hot days and cold nights along with the iron-rich soil allows the coffee to ripen slowly and gives it aromatic richness and taste.
- Produced by the tribals with emphasis on organic approach with use of organic manures, green manuring and organic pest management practices.
- Tags :
- GI Tag
- Araku Valley
- ARAKU COFFEE
Unming La Pass
NewSpace Research and Technologies successfully tested a 100-kg Max Take Off Weight (MTOW) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) at the Unming La pass.
About Unming La Pass:
- Located at 19,024 ft. in the Eastern Ladakh along the Ladakh Range.
- Also, it is renowned for being the highest motorable road in the world.
- Constructed by the Border Road Organization (BRO) under Project Himank.
- Geostrategic importance of Road- Improves connectivity to the Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- Also, improves local connectivity in Chisumle-Demchok sector to Leh and also boosts tourism in Ladakh.
- Other important passes in Ladakh: Khardung La, Chang La, Tanglang La, etc.
- Tags :
- Ladakh
- UNMING LA PASS




