Pump and Dump Scheme
Recently Sebi imposed a fine on some individuals for allegedly operating a ‘pump and dump’ scheme.
- It was operated by recommendations shared through Telegram channels, resulting in public shareholders purchasing stock at inflated prices.
About Pump and Dump Scheme:
- A manipulation activity involving artificially inflating a stock’s price through false and misleading information/ recommendations.
- It is done only to sell stock at an inflated price.
- Prevalent in micro-cap and small-cap sectors due to limited public information and lower trading volumes.
- Impact: Undermine confidence in financial markets, and substantial losses to investors.
- Regulation: Under SEBI’s guidelines, it is completely banned.
- Tags :
- SEBI
- PUMP AND DUMP SCHEME
SEBI Amends Infrastructure Investment Trusts (INVITS) Regulations 2024
The new norms allow for the issuance of subordinate units by privately placed InvITs only to the sponsors on acquisition of an infrastructure project.
- The move aims to bridge the difference in valuation done by the sponsor (as a seller) for an asset and that by the InvIT (as a buyer).
About InvITs
- A type of investment vehicle similar to a mutual fund that allows investors to invest in infrastructure projects like toll roads, power lines and pipelines etc.
- The sponsors (infra companies) set up the InvITs through SEBI and are recognized as borrowers under the SARFAESI act 2002.
- Parties to an InvIT include its trustee, sponsor, investment manager and project manager.
- InviTS earn income through tolls, rents, interest or dividends from their investments, which in turn is distributed to the investors as their taxable earnings.
Significance of InvITs
- Low ticket size: The investor can invest small amounts
- Liquidity: Listed on stock exchanges and can be exit at any point
- Transparency: investors are informed about where their money is invested
- Low Risk: as the trusts are regulated by SEBI
Challenges of investing in InvITs include operational risk, refinancing risk, return risk etc.
- Tags :
- InvIT
- Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)
Clearing Corporations
SEBI has formed a committee under Usha Thorat to review ownership and economic structure of clearing corporations.
Clearing Corporation (CC)
- It is an entity which handles the activity of clearing and settlement of trades in securities or other instruments that are traded on stock exchanges.
- CCs along with stock exchanges and depositories constitute Market Infrastructure Institutions.
- CCs are significant as central risk management institutions and as a first line regulator.
- Securities Contracts (Regulation) (Stock Exchanges and Clearing Corporations (SECC)) Regulations, 2018 lays down norms for ownership and governance framework of CCs.
- Tags :
- Market Infrastructure Institutions
- CLEARING CORPORATIONS
- Central Risk Management Institutions
- Usha Thorat Committee
Derivatives Trading
National Stock Exchange (NSE) chief cautioned retail investors against derivatives trading.
About Derivatives
- Definition: Derivatives are financial contracts that draw their value from an underlying asset.
- The underlying asset can be a commodity, security, currency, or index.
- Purpose: Can be used for hedging purposes or speculation.
- Types: Common types of derivatives include futures, options, and swaps.
- Derivatives Market
- In India, the derivative market is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India.
- India has two types of derivative markets:
- Exchanges-traded: Standardised contracts are traded on an exchange.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC): It is decentralised. Contracts are negotiated directly between two parties.
- Tags :
- Derivatives
- Derivatives Trading
- Futures
- Options
- Swaps
Front Running
Recently, a Mutual Fund was alleged to have indulged in Front- Running.
About Front Running
- Front Running refers to usage of non-public information to directly or indirectly buy or sell securities, or enters into options or futures contracts, in advance of a substantial order. (Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI))
- It is illegal in India.
- It undermines confidence in the financial markets and creates an uneven playing field for other investors.
- In 2022, Securities and Exchange Board of India (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996 was amended to incorporate provisions to counter front running.
- Tags :
- FRONT RUNNING
- Financial Markets
State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024
It is prepared and released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- The report’s special focus is on “Blue Transformation in Action”.
Key findings of the report
- World fisheries and aquaculture production hit a new high in 2022 at 223.2 million tonnes.
- With 8 percent of total production, India ranked second in aquatic animals production.
- For the First time, aquaculture surpassed capture fisheries as the main producer of aquatic animals.
- With 1.9 million tonnes, India ranked first in Inland fisheries production.
Role of Aquatic Foods in Climate Action
- The 2023 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Ocean Dialogue recognized the potential of aquatic foods for providing critical climate solutions.
- FAO integrates traditional knowledge for adapting to climate change in specific areas, like local species suited for evolving conditions.
Blue Transformation in Action
- FAO introduced its “Blue Transformation” vision in 2021, It aims to leverage aquatic food systems, to enhance food security, improve nutrition, etc
- Objectives:
- Sustainable aquaculture expansion to meet global demand, with equitable benefit distribution.
- Effective fisheries management for healthy stocks and fair livelihoods.
- Upgraded aquatic value chains ensuring social, economic, and environmental sustainability.
Fisheries and aquaculture in the context of Global Biodiversity Agreements
|
- Tags :
- FAO
- Blue Transformation
- Aquaculture
- State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture Report 2024
ICRIER Releases Policy Brief on Post-Harvest Losses (PHL) in India
The policy brief highlights the triple win of reducing PHL:
- benefiting farmers (enhanced income),
- enhancing food security, and
- ensuring sustainability (less resource exploitation) in agri-food systems.
Key highlights
- Production in India
- Food Grain: Increased from 74.23 million metric tonnes (MMT) in 1966-67 to 330.5 MMT in 2022-23.
- Horticulture: Increased from 96.6 MMT in 1991-92 to 355.25 MMT in 2022-23.
- India’s Storage capacity: Expanded from 108.8 MMT in 2010 to 219.4 MMT in 2021
- PHL: Globally, around 30% of food produced never reaches consumers (FAO, 2021).
- India faces higher PHL in cereals, pulses, and oilseeds than global levels.
- Annual loss of US $18.5 billion from 2020 to 2022, despite some reduction in PHL from 2012 to 2022.
Key factors behind PHL in India
- On-Farm Operations: Low farmer education and skill levels, weather conditions, and the use of defective machinery.
- Marketing Channels: En-route leakages from open lorry transport, poor quality packaging, use of iron hooks, improper storage practices, etc.
- Policy Issues: Jute Packing Material Act (1987) mandates using jute bags, which are susceptible to pests, insects, and contamination.
Way forward
- Mechanization in agriculture,
- reforming the Public Distribution System (PDS) and boosting direct cash transfer, etc.

- Tags :
- Post-Harvest Losses
- ICRIER
Container Port Performance Index (CPPI)
Nine of Indian ports have found their position among top 100 global ports in CPPI in 2023.
About CPPI (2023)
- It is developed by the World Bank and S&P Global Market Intelligence.
- The Index is a comparable assessment of performance based on vessel time in port.
- It helps to identify opportunities to improve a terminal or a port that will ultimately benefit all public and private stakeholders.
- Top-ranked container port in the CPPI 2023 is Yangshan Port (China).
- Tags :
- World Bank
- Ports
- Container Port Performance Index
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
As per data released by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), FDI inflows in 2023-24 contracted by 3.49% to $44.42 billion as compared with 2022-23.
Other Key Highlights
- Maharashtra received highest FDI followed by Gujarat and Karnataka in FY 2023-24.
- Singapore was the top source of foreign inflows followed by Mauritius and USA in FY 2023-24.
- Top 5 countries for FDI equity inflows into India during 2000-24 are Mauritius followed by Singapore, USA, Netherland, Japan.
- Computer software & Hardware, followed by Service sector and Construction Activities received highest FDI in FY 2023-24.
- Top 5 sectors receiving highest FDI equity inflow during 2000-2024 are Services Sector, Computer Software & Hardware, Trading, Telecommunications, Automobile Industry.
About FDI
- It is an investment made by a company or an individual in one country into business interests located in another country.
- DPIIT is nodal Department for formulation of FDI policy in India.
- FDI is permitted through Automatic route (Government approval not required) or Government route (approval required).
- Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds, Foreign Institutional Investment with certain conditions and Global Depository Receipts are included in FDI.
- FDI is prohibited in Lottery Business, Gambling and Betting, Chit funds, Nidhi company, Trading in Transferable Development Rights etc.
Significance of FDI
Concerns regarding FDI in India
 |
- Tags :
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
RBI Launches Various Initiatives
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has launched three initiatives to enhance public access to the central bank and facilitate regulatory approvals.
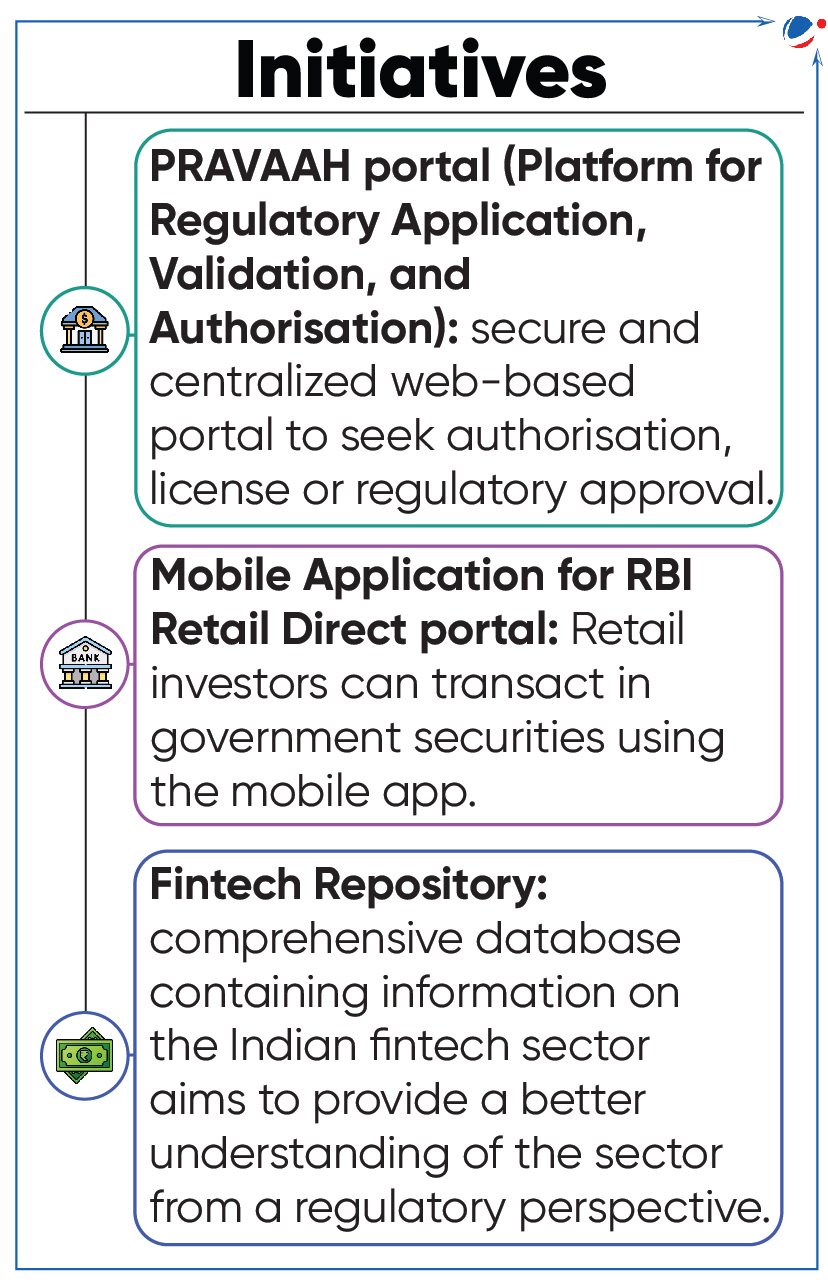
- Tags :
- Fintech Repository
- PRAVAAH Portal
- Mobile Application For RBI Retail Direct Portal



