New Ramsar Sites
Nagi and Nakti bird sanctuaries, both located in Bihar’s Jamui district, are now eecognized under the Ramsar Convention taking total Ramsar sites in India to 82.
- Both sanctuaries are man-made reservoirs (Nagi dam and Nakti dam) and feature dry deciduous forests surrounded by hills.
- Although Nagi lies in the Gangetic Plains of India, it has a landscape reminiscent of the Deccan Plateau.
- They are also recognized as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
- Major birds’ habitat
- Migratory birds: Bar-headed Goose, Greylag Goose, Northern Pintail, Red-crested Pochard, Steppe Eagle, etc.
- Resident birds: Indian Robin, Ashy-crowned Sparrow-Lark, Asian Koel, Asian Pied Starling, Bank Myna, etc.
Ramsar Convention
- An intergovernmental treaty for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
- Adopted at Ramsar (Irani) in 1971 and came into force in 1975.
- India became a party in 1982 (Maximum Ramsar sites are in Tamil Nadu followed by Uttar Pradesh).
- ‘List of wetlands of international importance’ or the Ramsar List contains wetlands which hold significant value for humanity as a whole.

- Tags :
- Nagi bird sanctuary
- Nakti bird sanctuary
Bonn Climate Change Conference Concluded
During Conference, progress was made toward adaptation indicators and better functioning international carbon market under Article 6 of the Paris Climate Deal.
- Article 6 of the Paris Climate Deal helps achieve countries’ emission-reduction goals with two main market mechanisms:
- Bilateral deals between countries and
- A new global offset market
- New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG) on climate finance & negotiations on Mitigation Work Programme (MWP) remained main issues with no progress.
New Collective Quantified Goal
- It was proposed in COP21 for setting post-2025 climate finance goal (new goal).
- In 2009 parties to UNFCCC decided to mobilise $100 billion annually by 2020 which was subsequently extended to 2025. However, developed countries failed to deliver this target fully.
- NCQG proposed to raise floor on climate finance above current $100 billion annual target while addressing key shortcomings in current climate financing mechanism.
Mitigation Work Programme
- It was established at COP26 to urgently enhance mitigation ambition and implementation to achieve 1.5°C goal of the Paris Agreement. Program in 2024 will focus on “Cities: buildings and urban systems”, including by
- Reducing operational emissions (heating, cooling);
- Designing building envelope for efficiency (retrofitting);
- Reducing embodied emissions (building materials).
- Tags :
- Paris Climate Agreement
67th Global Environment Facility (GEF) Council Meeting
67th GEF Council approved $736.4 million funding.
Funding has been mobilized for Projects from the GEF Trust Fund, Least Developed Countries Fund (LDCF), and Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF), which together are part of the GEF family of funds.
- Includes Projects like Great Green Wall (GGW), Sustainable Cities Integrated Program (SCIP) etc.
- GGW focused on restoring landscapes and ecosystems across the Sahel region of Africa.
- SCIP is a 20-country program aims to catalyze urban system transformation.
- Also includes 2 Indian Projects-
- Enhancing the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity to meet commitment to the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework targets.
- CoHABITAT – Conservation and sustainable management of wetlands forest and grassland to secure the population of migratory species along the Central Asian Flyway in India.
- These projects are implemented by the UNDP along with Indian Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change acting as the executive agency.


- Tags :
- Great Green Wall
30th Anniversary Of UNCCD
30th anniversary of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
- UNCCD is one of the three global agreements known as the Rio Conventions (1992), alongside the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
About UNCCD
- Established in 1994, UNCCD is the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management.
- Members: 196 countries and the European Union.
- Objectives
- To protect and restore land and ensure a safer, just, and more sustainable future.
- It’s committed to a bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating desertification.
- Report: Global Land Outlook.

Issue of Land Degradation and Desertification
|
- Tags :
- UNCCD
- Legally binding
Montreal Protocol
According to a study, Montreal Protocol has been effective in reducing emissions of Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS).
Key highlights of study
- Impact of Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) on Earth’s energy balance and globally averaged chlorine content of ODSin troposphere has decreased since 2021, five years earlier (2026) than expected.
- HCFCs are compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, chlorine and fluorine.
- HCFC-22, the most abundant HCFC, has declined significantly. Its Global Warming Potential (GWP) is thousands of times more than carbon dioxide (CO2).
- HCFC-22 is used as a refrigerant in air conditioners, cold storage, retail food refrigeration, etc.
- Minor decline were observed in HCFC-141b, second most abundant HCFC.
- HCFC-141b is used as a blowing agent in production of rigid polyurethane foams.
- India has achieved complete phase-out of HCFC-141b under ODS (Regulation and Control) Amendment Rules, 2014.
- This is in line with India’s commitment under Montreal Protocol for Substances that Deplete Ozone Layer.
Montreal Protocol
- Signed in 1987, it is a global treaty to eliminate production and use of ODS.
- Implemented under Vienna Convention (adopted in 1985).
- Kigali Amendment to Montreal Protocol was adopted in 2016 (and entered into force in 2019) to phase-down production and consumption of Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
- HFCs are non-ODS alternative to CFCs and HCFCs. HFC’s global-warming potential (GWP) is thousands of times more than CO2.
Ozone and Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS)
|
- Tags :
- Ozone
- Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS)
Antarctic Treaty
46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) and 26th Committee on Environmental Protection (CEP) concluded
These were hosted by the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India.
- The CEP advises the ATCM on environmental protection and conservation in Antarctica.
- Measures, Decisions and Resolutions, adopted at the ATCM, give effect to the principles of the Antarctic Treaty.
About Antarctic Treaty
- Genesis: Signed in Washington, in 1959 by 12 countries & entered into force in 1961.
- Members: 57 out of which 29 are consultative parties (participate in the decision-making).
- India has been a Consultative Party since 1983.
- Applicability: The area south of 60° South latitude.
- Key provisions
- Antarctica shall be used for peaceful purposes only.
- Facilitate international scientific cooperation in Antarctica.
- Prohibits nuclear explosions, radioactive waste disposal, and military deployments in Antarctica.
India’s initiatives for Antarctica
- India’s first Antarctic research station was Dakshin Gangotri (983). India currently operates two research stations- Maitri (1989) and Bharati (2012).
- In ATCM- 46 India announced a plan to set up an Antarctic research station, Maitri-II.
- In 2022, India enacted the Antarctic Act, reaffirming its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty.

- Tags :
- Committee on Environmental Protection (CEP)
- Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM)
Collective Intelligence (CI) Initiatives
Recently, ‘Untapped Collective Intelligence for Climate Action report’ was released by the UNDP.
- The report explores the potential of Collective Intelligence (CI) initiatives in climate adaptation and mitigation.
About CI
- It is the enhanced capacity created when people work together, often with the help of technology, to mobilize a wider range of information, ideas, and insights.
- Example- Using Artificial Intelligence, crowdsourcing, and remote sensing to tackle climate change, poverty etc.
- CI emerges when these contributions are combined to become more than the sum of their parts.
Potential of CI in Climate Action:
It can bridge:
- Data gap: Mobilising citizens to generate real-time localized data, and bringing together data sets to uncover new insight.
- Doing gap: Getting more people involved in taking climate action, and helping people monitor the follow through of institutions.
- Diversity gap: Bringing a wider range of people, including Indigenous communities and perspectives into climate processes and data collection.
It can decrease:
- Distance Gap: CI initiatives foster a two-way exchange between scientists and local communities, enhancing scientific understanding and public knowledge, as well as creating mutual trust.
- Decision-making Gap: Closing gaps between opposing views and interests (like (Climate vs. growth) to speed up required climate action.

- Tags :
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
UNESCO releases State of the Ocean Report (2024)
The report, structured around the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021-2023), offers insights into ocean-related scientific activities describing the current and future state of the ocean.
Key findings
- Warming: Ocean is now warming at twice the rate it was twenty years ago.
- Ocean temperatures have increased by an average of 1.45°C, with hotspots above 2°C in the Mediterranean, Tropical Atlantic Ocean and Southern Oceans.
- Rising Seal level rise: Mostly due to accelerated ice mass loss from the Greenland and West Antarctica ice sheets, and to a lesser degree from accelerated ocean warming.
- Acidification: Ocean absorbs around 25% of annual anthropogenic CO2. This process reduces seawater pH (ocean acidification).
- ocean acidification would increase by more than 100% by the end of the century
- Deoxygenation: Ocean oxygen content is decreasing, resulting in worsening hypoxia.
- However, it is unclear whether deoxygenation is accelerating in response to ocean heat content increase.
- Coastal blue carbon ecosystems: Mangroves, seagrasses and tidal marshes provide refuge against a warmer, more acidic ocean, and are an important store of carbon.
- However, their protection is not guaranteed and 20–35% have been lost since 1970.

- Tags :
- UNESCO
- UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021-2023)
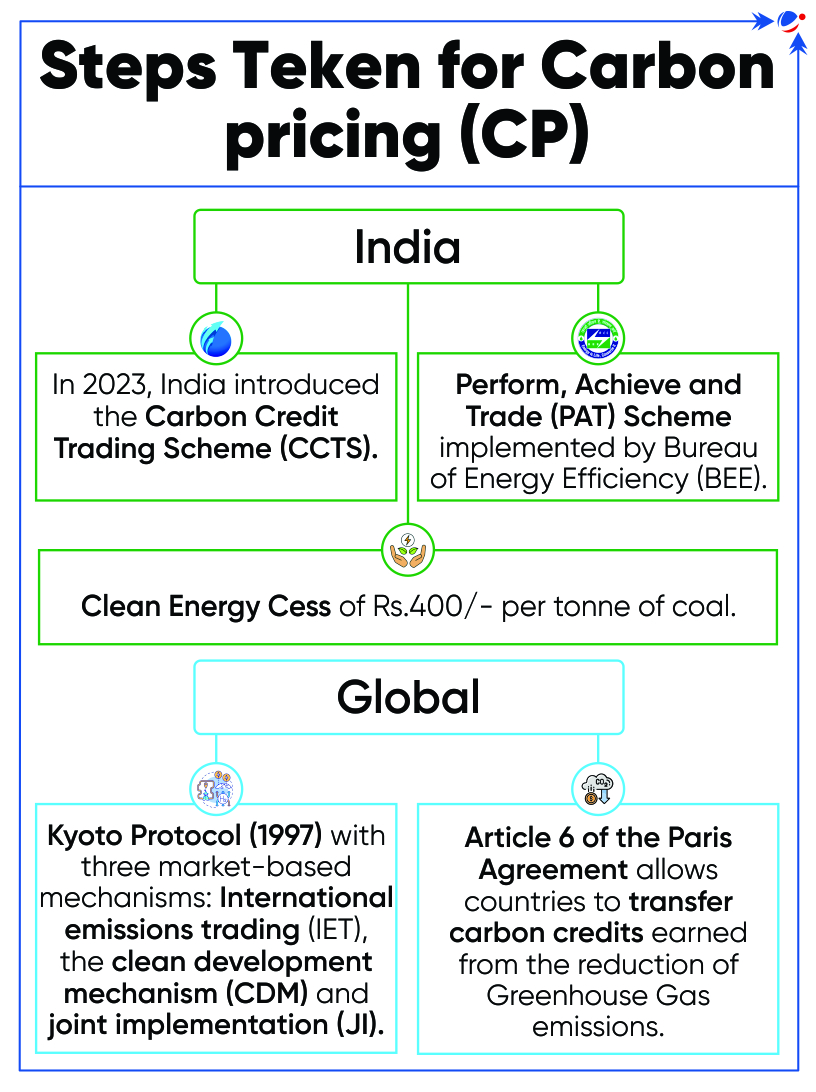
Carbon Pricing
State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2024 Report is released by the World Bank report.
Key finding of the report
- Carbon Pricing (CP) revenues in 2023 exceeded USD 100 billion for the first time.
- There are 75 global CP instruments in operation, covering around 24% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Brazil, India, and Türkiye have made notable progress towards CP implementation.
- China and India are largest host countries in terms of issuances of Carbon Credits.
- Carbon pricing (CP) is an instrument that attaches a cost to greenhouse gas emissions, typically through CO2 pricing mechanisms.
Main types of CP
- An emissions trading system (ETS): It is a system where emitters can trade emission units to meet their emission targets.
- Types of ETSs are: Cap-and-trade systems and Baseline-and-credit systems
- Carbon tax: It directly sets a price per unit of greenhouse gas emissions or carbon content.
Benefits of CP
- Place the burden of emissions damage on polluters.
- Spur investment and innovation in clean technology.
- Facilitate Paris Agreement emissions pathways for below 2°C/1.5°C warming.
- Tags :
- World Bank
- State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2024 Report
Water Credit
Packaged water maker Bisleri proposes water credits akin to carbon credits.
- Bisleri has partnered with TERI School of Advanced Studies to conduct a study and will share its findings with central government to develop a framework for water credits for beverages industry.
Water Credit
- A market-based mechanism similar to carbon credits, which incentivises water conservation and quality improvement.
- Carbon credits are generated by projects that have reduced or avoided or removed carbon emissions.
- Each credit represents one less tonne of carbon dioxide, or another greenhouse gas equivalent, (CO2e) in atmosphere.
- Individuals and entities can earn tradable credits by adopting water-saving measures.
- These credits can then be sold to others needing to offset their water usage or improve their water management practices.
Significance of Water Credits
- Addressing water stress and help in achieving SDG6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- In India, 11 out 15 major river basins will be water-stressed by 2025. (Council on Energy, Environment, and Water (CEEW))
- Promote water-saving measures and help enhance water use efficiency in agriculture, which is the largest extractor of groundwater.
- Promote and foster investment in sustainable water management practices.
Challenges in implementing water credit system
- Unlike carbon emissions, water savings require localized approach, factoring in rainfall and consumption at a watershed level.
- Spatial limitation for transactions as they are confined to hydrological boundaries.
- Preventing wealthier entities from dominating the market.
Potential approach towards water credit system
|
- Tags :
- Bisleri
- TERI
NASA’s Mission PREFIRE
NASA Launches Small Climate Satellite to measure heat lost from Earth’s poles
NASA has launched one of the two climate satellites under PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission.
- The PREFIRE Mission consists of two shoebox-size cube satellites, or CubeSats.
- The mission will measure how much heat the Arctic and Antarctica radiate into space and how this influences the planet’s climate.
- It will help scientists better understand the heat budget of the planet.
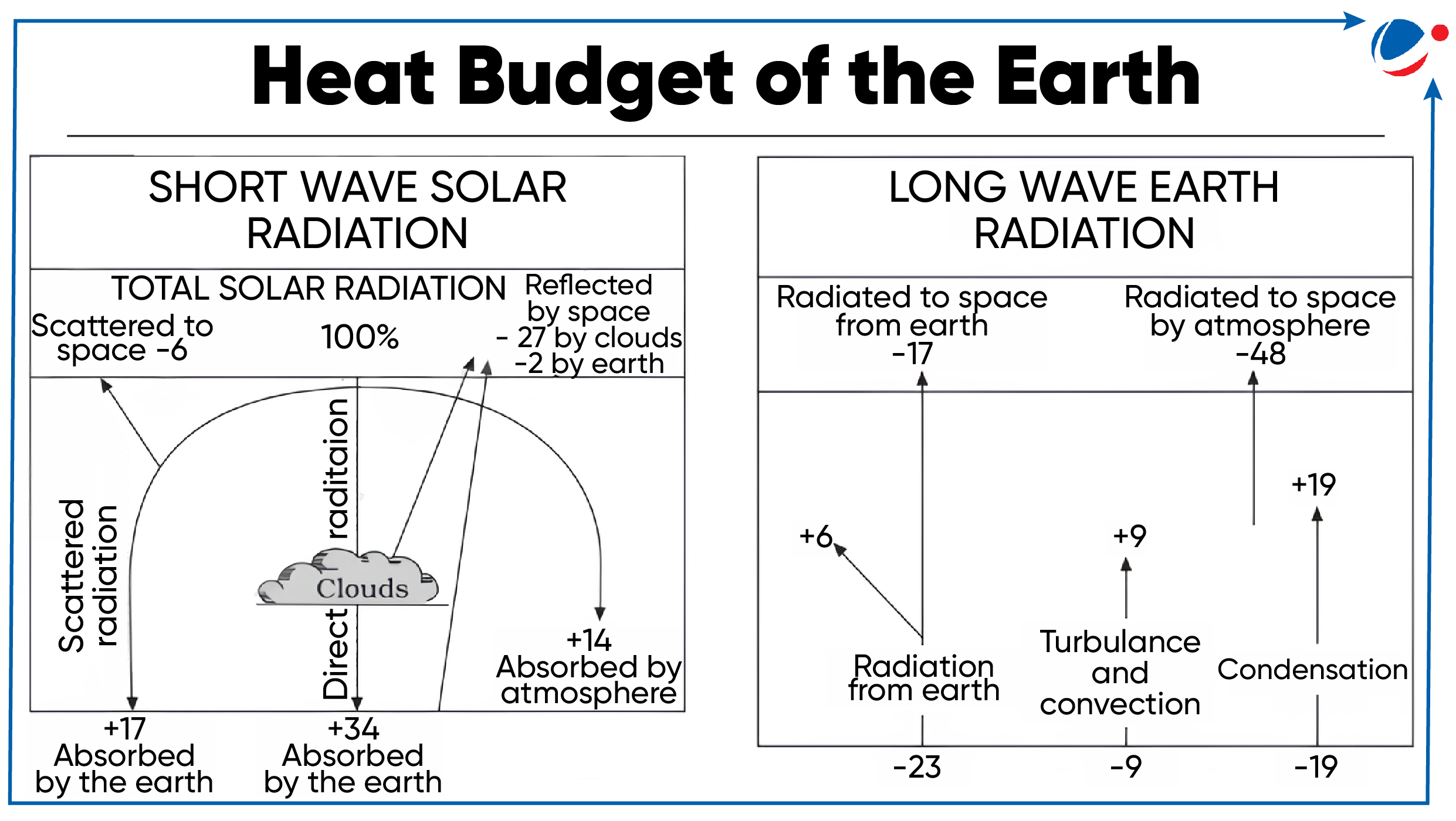
Heat Budget of the Earth
- It is the balance between the amount of heat incoming to Earth from the Sun and the amount of heat outgoing from Earth into space.
- Factors responsible for the disturbance of heat budget are Green House Gases emissions, reduction in thickness of the ozone layer, melting of glaciers etc.
Impact of imbalance of Heat budget
- Heat gets accumulated in Earth’s components like the atmosphere, land, etc which is fuelling global warming.
- Melting of ice causes a decrease in Earth’s white surface area, leading to less solar energy to be reflected (lower albedo).
- Albedo is the reflectivity of solar radiation from a surface.
- Ocean absorbs excessive heat affecting the Oceanic Circulation like Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation.
- Tags :
- Small Climate Satellite
- PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment)
Sustainable Development Report 2024
UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) released Sustainable Development Report 2024.
Published by SDSN since 2016, report reviews progress made each year on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 193 UN Member States.
- Established in 2012, SDSN works under the UN Secretary-General and promotes integrated approaches to implement SDGs and Paris Agreement, through education, research, policy analysis, and global cooperation.
Key Highlights of Report
- On average, only 16% of the SDG targets are on track to be met globally by 2030.
- SDG2 (Zero Hunger), SDG11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), SDG 15 (Life on Land) and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions) are particularly off track.
- SDG progress varies significantly across countries with Nordic countries leading, BRICS countries making significant progress and Poor & Vulnerable countries lagging far behind.
- Finland is ranked first, followed by Sweden and Denmark.
- India is ranked 109th out of 166 countries, with on track performance in Poverty reduction and Quality Education targets while decreasing progress in Sustainable Cities and Climate Action targets.
- New Index of Support to UN-based Multilateralism (UN-Mi): It ranks countries based on their engagement with the UN System.
- Barbados ranks highest, India at 139th place while USA ranks last.
Recommendations by UNSDSN
- Sustainable Development agenda should remain the core of global cooperation to 2050 and should be properly financed.
- Strengthen UN agencies along with systematic monitoring of UN-based multilateralism.
- Enhancing multilateral governance of technological risks and ensure universal access to vital technologies and R&D capacities.
- Establish UN Parliamentary Assembly and reform UN Security Council through adding India as permanent member and adoption of procedures to override a veto.
NOTE: The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2024 also details the significant challenges the world is facing in making substantial strides towards achieving the SDGs. It has been released by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).
- Tags :
- UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN)
UNESCO’S Greening Education Partnership
UNESCO launched two new tools – new Greening Curriculum Guidance (GCG) and new Green School Quality Standards (GSQS) – under Greening Education Partnership.
- New GCG: A practical manual providing, for the first time, a common understanding of what climate education should consist of and how countries can mainstream environmental topics across curricula, with detailed expected learning outcomes.
- New GSQS: It sets the minimum requirements on how to create a green school by promoting an action-oriented approach.
About Greening Education Partnership:
- It is a global initiative comprising 80 member states and supports countries to tackle the climate crisis by harnessing the critical role of education.
- Objective: To ensure all learners acquire knowledge, skills, values, attitudes and action to tackle climate change and to promote sustainable development.
Pillars of Green Education:
- Greening Schools: To ensure that all schools achieve green school accreditation and address climate change through their teaching, facilities and operations.
- Greening Curriculum: Integrate climate education into school curricula, technical and vocational education and training, workplace skills development etc.
- Greening Teacher Training and Education Systems’ Capacities: Integration of climate education in building capacity of school leaders.
- Greening Communities: Strengthen community resilience through community learning centres and learning cities.
Education and Climate Change
|

- Tags :
- UNESCO
- Greening Curriculum Guidance (GCG)
- Green School Quality Standards (GSQS)
EU’S Nature Restoration Plan (NRP)
European Union approves NRP, first of its kind.
- It is a continent-wide and comprehensive law that forms part of the EU’s European Green Deal (aims for net zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050).
Key Features
- Aim: Contains binding restoration targets for long-term recovery of nature in EU’s land and sea areas.
- It seeks to recover at least 20% of the EU’s land and sea areas by 2030, and ultimately all ecosystems in need of restoration by 2050.
- Focus areas: Covers the existing legislation (for wetlands, forests, grasslands, etc.), pollinating insects, forest ecosystem, etc.
- Implementation: Through National Restoration Plans of the EU countries.
- Tags :
- European Union
Global Soil Partnership (GSP)
GSP Assembly calls for urgent action to improve and maintain health of at least 50 percent of world’s soils by 2030 at Twelfth Plenary session (hosted by FAO).
About Global Soil Partnership
- It was established in 2012 by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) as a mechanism to develop a strong interactive partnership and enhanced collaboration and synergy of efforts between all stakeholders.
- It aims to position soils on Global Agenda, promote inclusive policies and soil governance as well as sustainable soil management.
- Tags :
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
50th Year of Crocodile Conservation Project
India launched its Crocodile Conservation Project in Odisha’s Bhitarkanika National Park in 1975 with the assistance of United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Crocodiles
- Crocodiles are largest surviving species of the vertebrate class Reptilia.
- Habitat: Except for one saltwater species, crocodiles live mainly in freshwater swamps, lakes and rivers.
- Behaviour: Nocturnal animals and are poikilothermic (regulate their body temperature only to limited degree).
- There are three main species of crocodiles in India (see table).
- Major threats: Habitat destruction, egg predation, illegal poaching, dam construction, sand mining etc.
Species | Description | Natural Habitat |
Estuarine or saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus)
|
|
|
Mugger or marsh crocodile (Crocodylus palustris)
|
|
|
Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus)
|
|
|
Bhitarkanika National Park
- Located in Odisha, it is India’s second largest mangrove ecosystem after the Sunderbans.
- It is a Ramsar site.
- It is essentially a network of creeks and canals which are inundated with waters from rivers Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra and Patasala.
- Home to largest congregation of Saltwater Crocodile along with water monitor lizard, pythons, hyenas etc.
- Tags :
- Crocodile
- Bhitarkanika National Park
Microalgae
CSIR-IICT scientists highlighted microalgae potential as a protein supplement.
About Microalgae
- Diverse group of single-cell photosynthetic organisms, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- These are groups of autotrophic microorganisms that live in marine, freshwater, and soil ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Nutrition: These are rich in nutrients and biologically active substances, such as proteins, vitamins, etc.
- Carbon cycle: They absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Food Chain: Phytoplankton, which forms the base of the food chain, includes microalgae.
- Tags :
- CSIR-IICT
Iberian Lynx (Lynx Pardinus)
According to IUCN, conservation status of Iberian lynx has improved from Endangered to Vulnerable, reflecting significant increase in its population.
About Iberian lynx
- Habitat: Medium-sized wild cat species native to Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe, including Portugal and Spain.
- Appearance: Weighs about half as much as Eurasian species, with long legs, short tail with a black tip, tufted ears and relatively small head.
- Characteristics: Solitary hunter; nocturnal or crepuscular; may temporarily become diurnal during winter; live in small, isolated meta-populations; European Rabbit accounts for 80-99% of its diet.
- Threats: Decreasing food base, Poaching, habitat loss etc.
- Conservation status: Appendix I of CITES.
- Tags :
- Vulnerable
- Appendix I of CITES
Pench Tiger Reserve
Advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) system for early detection of forest fires has been launched at Pench Tiger Reserve.
About Pench Tiger Reserve
- Location: Spread across states of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh in lower southern reaches of Satpura hills.
- Background: Status of National Park in 1975, and Tiger Reserve in 1992.
- Forest Types: South Indian Tropical Moist Deciduous, Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Teak, and Southern Dry Mixed Deciduous.
- Pench River divides it into two halves.
- Flora: Mahua, White Kulu, Salai, Saja, Bijiyasal, Dhaora, Amaltas, etc.
- Fauna: Tiger, leopard, sloth bear, Indian gaur, wild dog, wolf, etc.
- It also finds mention in Ain-i-Akbari and it is the original setting of Rudyard Kipling’s most famous work, The Jungle Book.
- Tags :
- Madhya Pradesh
Bhuvan Panchayat and NDEM 5.0
Union Minister of State for Science and Technology to launch two Geoportals – Bhuvan Panchayat 4.0 and National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM 5.0).
- National level geospatial databases for these two portals are created by ISRO.
About Bhuvan Panchayat 4.0
- It is an online geospatial data and services dissemination platform.
- Objective: Integrate and use space-based information in governance and research initiatives for spatial planning at Gram Panchayat level.
About NDEM 5.0
- It provides a comprehensive geospatial database for entire country for situational assessment and effective decision-making during disasters/ emergency situations.
- Tags :
- ISRO
- National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM 5.0)
Heat Dome
Cities across southern and western states in the USA are facing heat waves due to a weather phenomenon known as Heat Dome.
About Heat Dome
- It is a weather phenomenon where a ridge of high pressure gets stuck in the atmosphere.
- It traps hot air that expands vertically into the atmosphere and high pressure pushes it toward the ground.
- Winds usually move from high pressure but with the dome stretching far into the atmosphere, these weather systems become almost stationary.
- Tags :
- Heatwaves






