Why in the News?
India participated in the 50th Group of Seven (G7) Summit in Apulia, Italy, where India was invited as an Outreach Country.
More on the News
- Key Highlights of India's Speech:
- Technology: To Convert technology monopolies into mass usage.
- Energy: India is the first country to fulfil all the commitments made under COP before time.
- Under Mission LiFE launched "Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam" on Environment Day (5th June.)
- Global South: India has taken upon itself the responsibility to raise concerns of the countries of the Global South.
About Group of 7 (G7)Nature: The G7 is an informal grouping of advanced democracies that meets annually to coordinate global economic policy and address other transnational issues. E.g., Migration, Climate change, conflicts, etc.
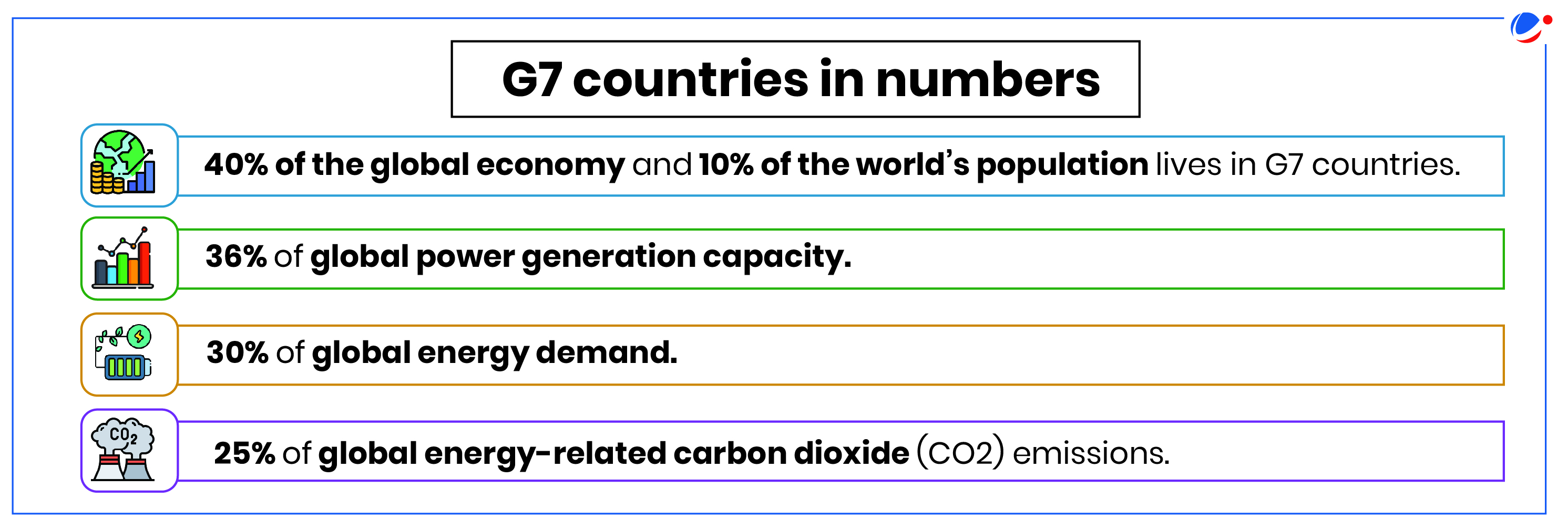  |
Major Outcomes of the Summit:
- Regional affairs:
- Ukraine-Russia war: Committed to raise the costs of Russia's war. E.g., G7 pledged $50 billion using frozen Russian assets.
- Israel-Hamas conflict: Reiterated commitment to the two-state solution and the right of countries to defend their vessels in Red Sea. E.g., Maritime operations like EU's Aspides and US-led Prosperity Guardian.
- Promote economic resilience: Through supply chain diversification (e.g., G7 PGII initiatives, IMEC, etc.), coordinated initiatives on critical minerals (e.g., Partnership for Resilient and Inclusive Supply-chain Enhancement, the Mineral Security Partnership), etc.
- Energy, climate and the environment: Aim to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by 43% this decade and 60% by 2035, compared to 2019 levels.
- Launched: The Energy for Growth in Africa to invest in sustainable development and will provide Africa with an alternative investor to China.
- Health and food security: G7 launched Apulia Food Systems to enhance food security and sustainable agriculture. Leaders also committed to support Gavi for immunization coverage.
Significance of G7 in the current Geopolitics
- Play a Central Role in Global Governance: E.g.,
- A.I Governance: Global Partnership on AI (GPAI) for A.I. governance was proposed in 44th G7 summit (2018), and later hosted by OECD.
- Also, Hiroshima AI Process (HAP) initiated at G7 summit in Hiroshima (Japan) is a significant step towards regulating AI.
- Tax governance: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) was established in 1989 by the G7 to examine and develop measures to combat money laundering.
- A.I Governance: Global Partnership on AI (GPAI) for A.I. governance was proposed in 44th G7 summit (2018), and later hosted by OECD.
- Act as a defender of the rules-based international system: E.g., Strictly defend free and open Indo-Pacific, based on the rule of law, which is inclusive, prosperous, and secure, grounded on sovereignty, territorial integrity.
- A platform to discuss and resolve prominent international crisis and disputes: E.g., Presently, Ukraine-Russia war; Israel-Hamas conflict, the Red Sea crisis, etc.
- The present Summit emerged as a platform to represent the voice of the 'Global South'
- G7 Summits have generated results: E.g., successful launch of Global Apollo Program for multinational clean energy research (2015).
- Also, the G7 has also been successfully addressing the issue of tax avoidance through the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) initiative.
- The G-7 'Club of Democracies': It has emerged as a dynamic coalition, positioned at the political epicentre of global efforts to defend democratic societies and what its leaders call the "rules-based international order."
Limitations of G7 Effectiveness
- G7 fails to reflect current global economic landscape: G7's economic dominance declined from over 60% in the 1970s to 26.4% in 2023.
- Emerging economies now represent 50.1% of global economy, increasing their demand for representation in global governance systems.
- Without broader participation: The focus of global economic governance is shifting to more inclusive, representative and democratic governance mechanisms.
- E.g., the G20, BRICS, and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, etc.
- Also, G7's representation of Global Democracy and South like India, Brazil are missing as well as formidable, emerging blocs like African Union (AU).
- G7 lacks institutional continuity: The annual leadership changes and every member tries to prioritise their own strategic concerns, thereby hindering consistent and collective action.
- Also, there are no permanent organization or staff to implement communiqués (an official statement or announcement).
- G7 unity is undermined by discord between the countries: U.S. Refused to Join G7 Climate Change Declaration in G7 meet in Canada and at the end U.S. withdrew support for any communiqué.
India and G7 | |
Significance of India's participation in G7 and as a Potential future member
| Relevance of G7 for India
|
Conclusion
U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan's description of the G7 as the "steering committee of the free world" underscores its pivotal role in shaping global policy. As democracies face complex challenges, the G7's unified approach to critical issues demonstrates its enduring relevance and influence in international affairs.




