Why in the News?
India is celebrating 25 years of Kargil War victory or success of Operation Vijay.
More on News
- Operation Vijay, was launched by Indian Army in response to the infiltration of Pakistani soldiers and militants into the Kargil district of Union Territory of Ladakh.
- Indian Airforce launched 'Operation Safed Sagar' for conducting attacks on Pakistani troops positioned on high hills. Indian Navy launched 'Operation Talwar' to check Pakistan's navy in Arabian Sea. Kargil Vijay Diwas is observed annually on July 26 to commemorate the victory of success of Operation Vijay.
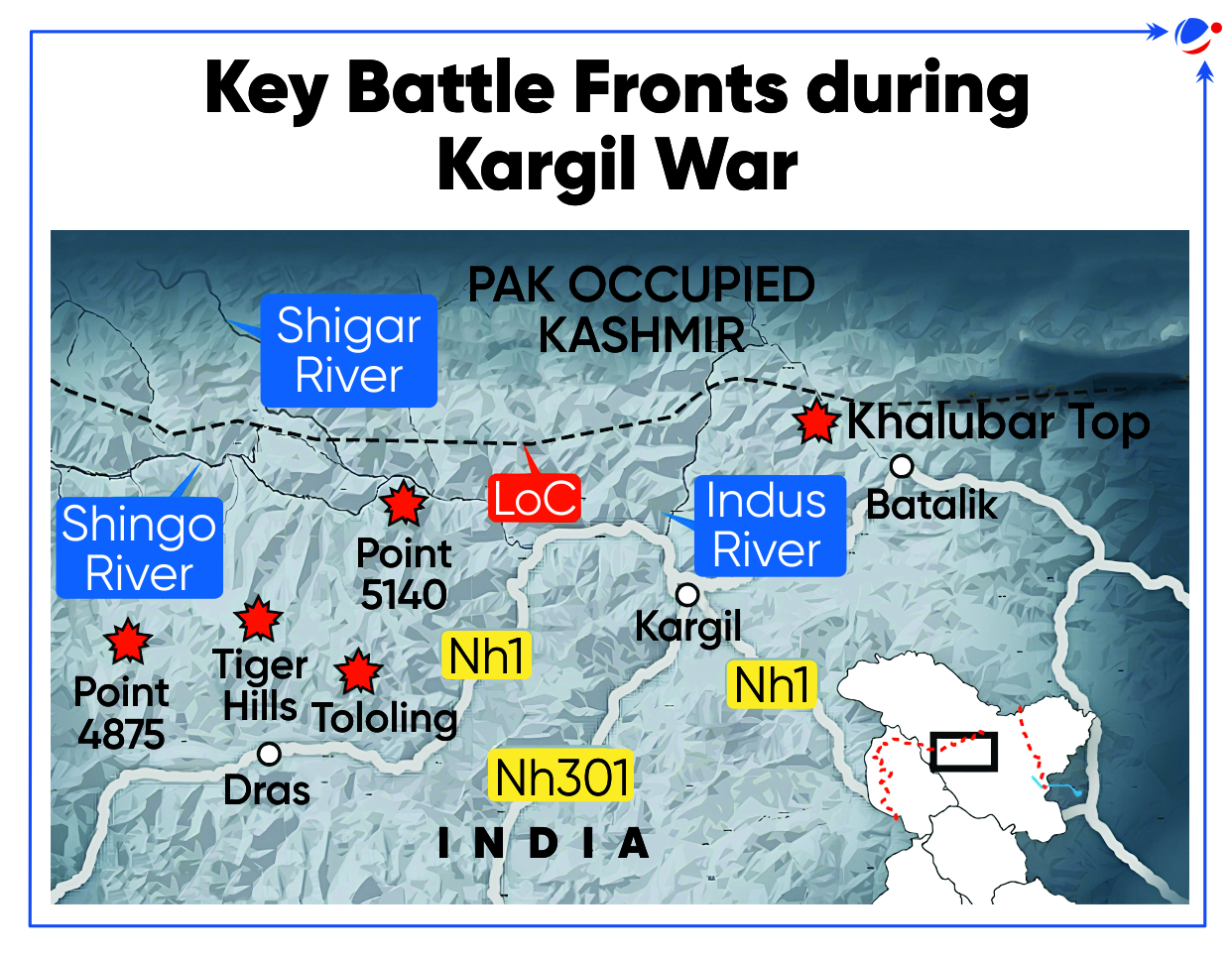
About Kargil War
- War theatre: The war was fought in the Kargil district of Union Territory of Ladakh across 170km high-altitude frontier near LoC.
- Key locations were Tololing, Tiger Hill, Batalik, Drass, Mushkoh Valley, Kaksar, Chorbat La.
- Commencement of war: The war commenced shortly after the signing of the Lahore declaration in 1999, when the Pakistan Army surreptitiously occupied the winter-vacated posts (vacated to prevent loss of soldier's life) of the Indian Army.
- In 1999, India and Pakistan signed the Lahore Declaration to reduce nuclear risks and resolve their border disputes peacefully.
Reasons for Pakistan's intrusion of India
- Politico-strategic:
- To internationalize Kashmir as a nuclear flash point requiring urgent third party intervention.
- To alter the Line of Control (LOC) and disrupt its sanctity by capturing upheld areas in Kargil.
- To achieve a better bargaining position for a possible trade- off against the positions held by India in Siachen.
- Military/Proxy War Related Motives:
- To interdict the Srinagar-Leh road by disrupting vital supplies to Leh.
- To outflank India's defences from the South and rendering its defences untenable in Turtuk and Siachen.
- To boost militancy in J&K by diverting troops from the Valley to Kargil, weakening the counter-insurgency efforts and opening new infiltration routes while also raising moral of militants.
Shortcomings in India's defense architecture that contributed to the Kargil War
In the aftermath of the Kargil War, the Indian government established the Kargil Review Committee (KRC) in July 1999. Chaired by K. Subrahmanyam, a prominent strategic affairs analyst. The KRC and its follow-up by the Group of Ministers highlighted following issues:
- Intelligence failure: Government of India did not anticipate the possibility of a war so soon after the Lahore Declaration. Therefore, intelligence failure was one of the prime causes for not anticipating Pakistan's intrusion.
- Low technology: Intrusion by Pakistan could have been detected earlier if India had half-metre resolution satellite imagery capability, appropriate Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) in addition to better Human Intelligence (HUMINT).
- Inadequate resources for defence forces: Decline in defence expenditure compromised with the defence modernisation and replacement of obsolete/ obsolescent equipment and weapons systems.
- A comprehensive security policy: No attempt was made to evolve a comprehensive security policy keeping in view the changing threat scenario because of the proxy war, nuclearisation in the sub-continent and RMA.
Suggestions made by KRC to strengthen India's defense architecture
- Strengthen National Security Council and have a full time National security adviser (NSA)
- Enhance satellite imagery capability and induct unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV's)
- Create an organization focused on electronic and communication intelligence (like the National Security Agency in US)
- Create an integrated defence intelligence agency (DIA)
- give more powers and prominence to the Joint Intelligence Committee (JIC)
- Reduce the age profile in the army and find ways to decrease the pension bill.
- Establish a committee to study all the issues related in order to have an effective border management policy
- Publish war histories and declassify official documents to establish the facts
- Create synergy between military and the media
- Create civil-military liaison mechanisms at various levels, from Command HQ to operational formations on ground to smoothen relationships.
Major initiatives taken for strengthening India's defence architecture
Specification | Reforms taken |
Intelligence
|
|
National security management and apex decision-making |
|
Defence Modernisation |
|
Border Management |
|
Conclusion
Since Kargil War, the character and conduct of warfare have changed with the growing use of terror and other irregular methods of fighting by non-state actors. Equally important have been the technological advancements in the cyber and space domains. Therefore, Indian armed forces must be prepared for future conflicts with a changed character as the war could be more violent and unpredictable.



