Why in news?
India’s processed food exports have grown by 150% in the last nine years making agricultural exports touch a value of about $53 billion.
What is Food processing?
- Food processing is the set of methods and techniques which are used to transform raw ingredients into finished and semi-finished products.
- According to Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI), if any raw product of agriculture, animal husbandry or fisheries is transformed in such a way that
- its original physical properties undergo a change,
- the transformed product is edible and
- has commercial value, then it comes within the domain of Food processing Industry (FPI) .
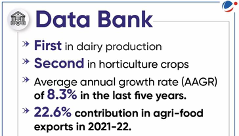
Benefits of food processing exports
- Reduction in waste as processing helps in extension of shelf life.
- Nutritional benefits include addition of particular vitamins through fortification methods tailored to specific dietary needs.
- It can address the malnutrition, under nutrition among children as well as overall population.
- Enhanced Employment: by generation of additional job in various segments of logistics, trading etc.
- Rural development: Increased export and demand of processed food worldwide can benefit farmers by improving their incomes leading to rural development, poverty reduction etc.
- Adoption of new and emerging technologies for processing improves efficiency in this sunrise sector
- Exports can lead to Foreign exchange earnings improving India's trade balance and economic growth.
Challenges persisting in Food Processing Industry
- Lack of cutting-edge infrastructure. Many businesses operate in the small and medium enterprises sector, which often lacks the resources to upgrade to the latest technology.
- Logistical challenges such as inadequate storage and transport facility, inefficient global supply chains also leads to wastage and inadequate processing of food materials.
- Lack of access to credit and financing creates entry barriers make it difficult for small businesses to enter the market and compete with larger and better established companies.
- Inadequate quality control & testing infrastructure leads to issues such as pest infestations, presence of chemical residues.
- Global Standards are often not met due to which our products are banned by the importing country affecting India’s export leading to loss of income for exporters, farmers and processors.
Institutional Measures
|
Way forward
- Changing the trend from sustenance to market-oriented by increasing focus on large-scale food processing rather than exporting only raw materials.
- Promoting better Interaction between farmers and processors and the market demand like buying directly from farmer producer organisations (FPOs).
- Strengthening institutional framework to develop manpower and bringing improvement in R&D capabilities.
- Enhance export competitiveness by developing Efficient Quality control, and Food safety Assurance of processed food products
- facilities to move up the value chain and meet international standards like sanitary and phyto sanitary measures.
- Evolving the supply chain model by adoption of cooperative model, diversification of agricultural exports, timely delivery of goods etc.
Initiatives taken by Government
|



