Why in the news?
As per various reports there has been a surge in demand of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) from India and India is becoming a growing market for the same.
What is ADAS?
- ADAS are a set of electronic systems which are integrated into vehicles to enhance driver safety, improve vehicle performance, and provide convenience.
- This is made possible with use of sensors, cameras, radar, and other advanced technologies to monitor the vehicle's surroundings and detect potential hazards.
- There are different levels of ADAS in the market as per the customers’ demand.
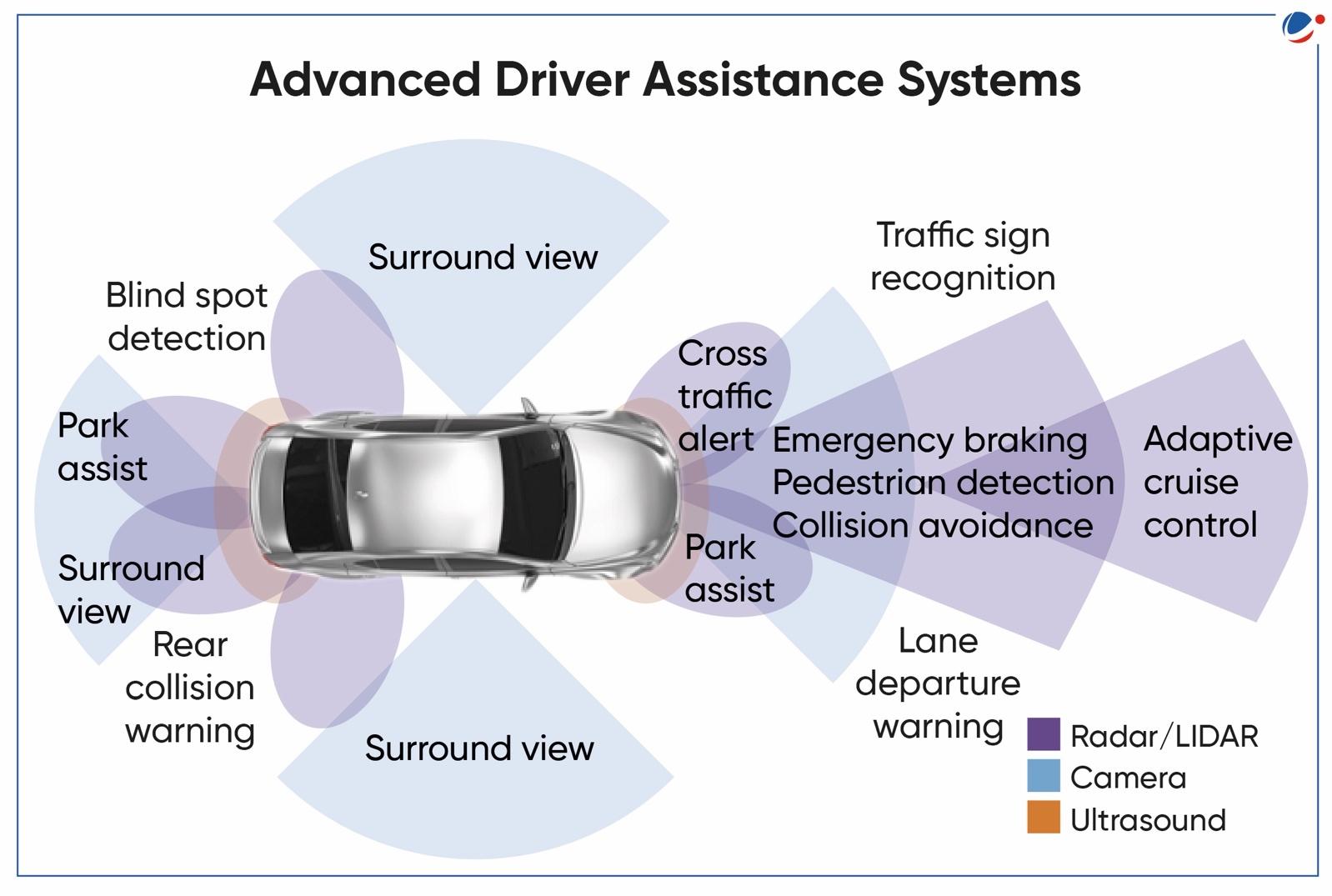
Equipment used in ADAS
|
Types of ADAS
There are two types of ADAS:
- Active ADAS: These systems actively intervene and assist in critical driving situations and can even perform automatic corrective actions
- E.g. collision avoidance systems, lane keep assist systems, and automatic emergency braking.
- Passive ADAS: These systems are mainly limited to provide information and alerts to the driver without directly intervening in the driving process.
- E.g. blind spot monitoring systems, lane departure warning and traffic sign recognition.
Different levels of Autonomous Driving
|
Benefits of ADAS
- Improve Overall Road Safety: ADAS can reduce the number of fatalities by providing assistance in emergency braking, and avoiding collisions in events of fog etc.
- Improved Traffic Management: It can optimise traffic flow, minimise congestion, and enhance the overall efficiency of road networks.
- Increased Comfort and Convenience: Features such as adaptive cruise control and automated parking can make drivers less stressful.
- Environmental Impact: ADAS can help in reducing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions through optimization in driving patterns.
Reasons behind increasing demand of ADAS in India
- Progressive democratisation of autonomous driving tools with car manufacturers offering advanced driver assistance systems in their mid-segment range.
- Increasing demand for safer vehicles among Indian consumers as people are increasingly becoming safety-conscious and are willing to stretch their budget to buy safer cars.
- Government’s push for increased road safety through Education, Engineering (both of roads and vehicles), Enforcement and Emergency Care
- Availability of more affordable ADAS technology with time.
Challenges in adoption of ADAS
- Non-Standardised Road Infrastructure India's diverse road conditions, from good highways to poorly constructed rural roads, pose challenges due to inconsistent road markings.
- Indian roads have a mix of pedestrians, cyclists, and other non-motorized vehicles making ADAS systems adaptation more complex.
- Affordability issues: ADAS is prevalent in premium and luxury cars due to its high cost. Making these features affordable for the majority of Indian consumers remains a challenge.
- Connectivity and Data: ADAS systems require real-time data updates and reliable connectivity, which might be an issue in remote or poorly networked areas of India.
- Cyber Threats It includes flaws in hardware and software which may lead to attempt of hacking, malware, and unauthorized system access.
- These attacks may deceive or undermine the functionality of systems and pose risks to passengers and drivers’ safety.
- Error and Malfunctions may be caused due to hardware or software faults, sensor failures, calibration mistakes, or improper data processing or outside influences like bad weather.
- These flaws could result in the ADAS system making poor decisions or failing to recognize dangers, which could cause accidents
- Human Factors may present obstacles for the safe and efficient use of the system, including attention, overreliance, complacency, and incorrect interpretation of ADAS.
- Too heavy reliance on ADAS may lead to complacency or distraction and raise the possibility of accidents.
- Supply Chain Security Issues related to non-proper safeguarding of the components and processes may create vulnerabilities and threaten the system's operation and safety.
- Consumer Trust is essential for successful adoption of the technology. If consumers believe them to be risky, they might be reluctant to trust them.
Steps to be taken
- Government Regulations , focussed at establishing clear regulations and standards for ADAS implementation, incentivizing manufacturers to produce vehicles with ADAS features, and providing financial support.
- Building of Consumer Trust by persistent investment in research and development and open and consistent communication from manufacturers and authorities about the technology’s potential and constraints.
- Defence against ADAS attacks are essential to ensure the safety and security of the people inside the vehicle
- Software updates and patches, secure coding techniques, encryption of critical data, and network segmentation are a few defence mechanisms.
- Driver Behavior: The success of ADAS systems depends on responsible driving behavior, which may require significant efforts in driver education and awareness campaigns.



