Why in the news?
Telangana signs agreement with World Economic Forum for setting up Centre for Industrial Revolution (C4IR) in Hyderabad.
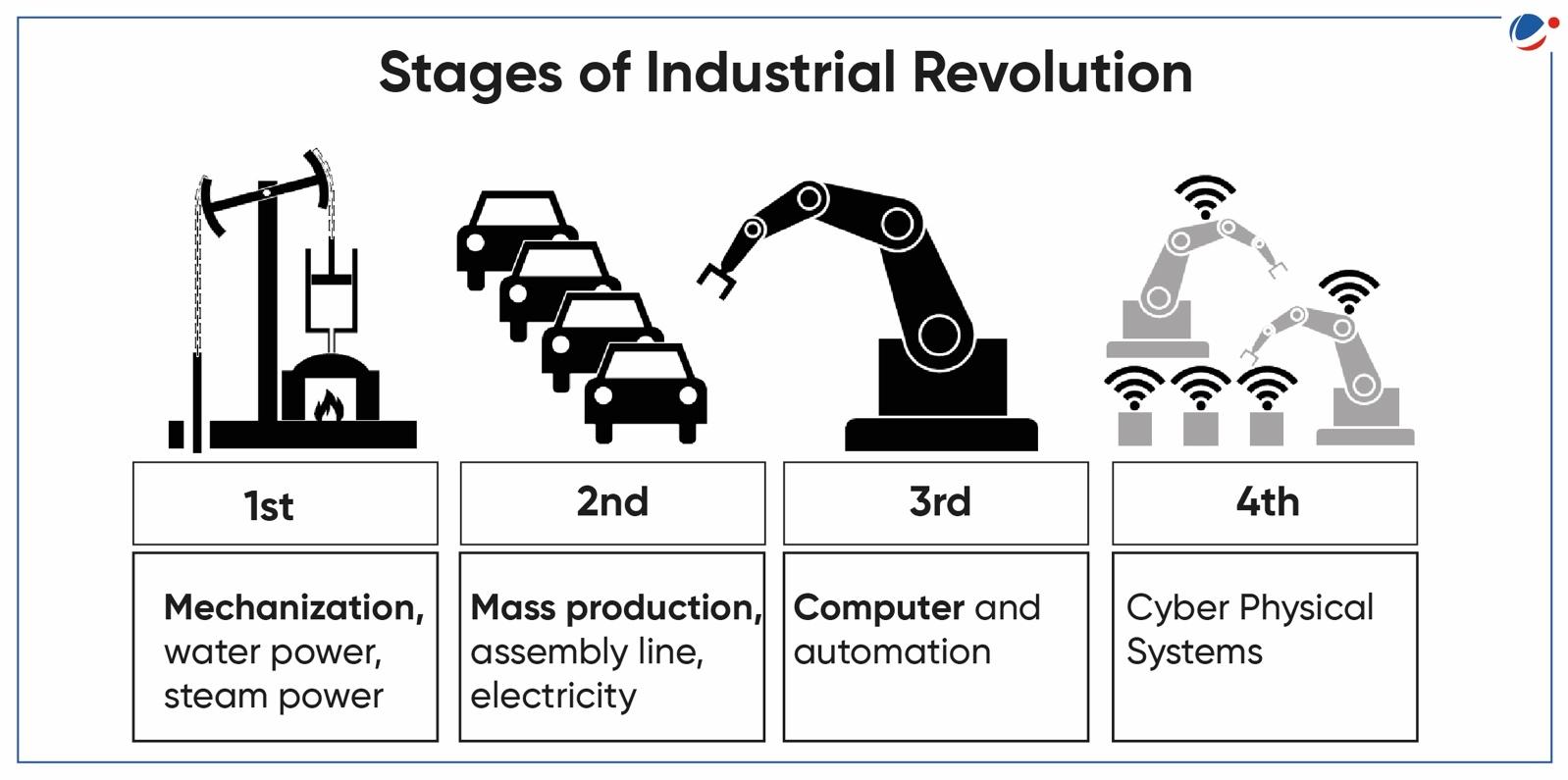
Fourth Industrial revolution (4IR)
- The term was coined by Klaus Schwab, founder of the World Economic Forum (WEF) in 2016.
- 4IR means the digital transformation of the manufacturing industry by new technologies such as artificial intelligence, additive manufacturing, augmented/virtual reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- It is also used to refer to concept of “smart factories”–which are fully connected cyber-physical systems that merge the physical and digital aspects.
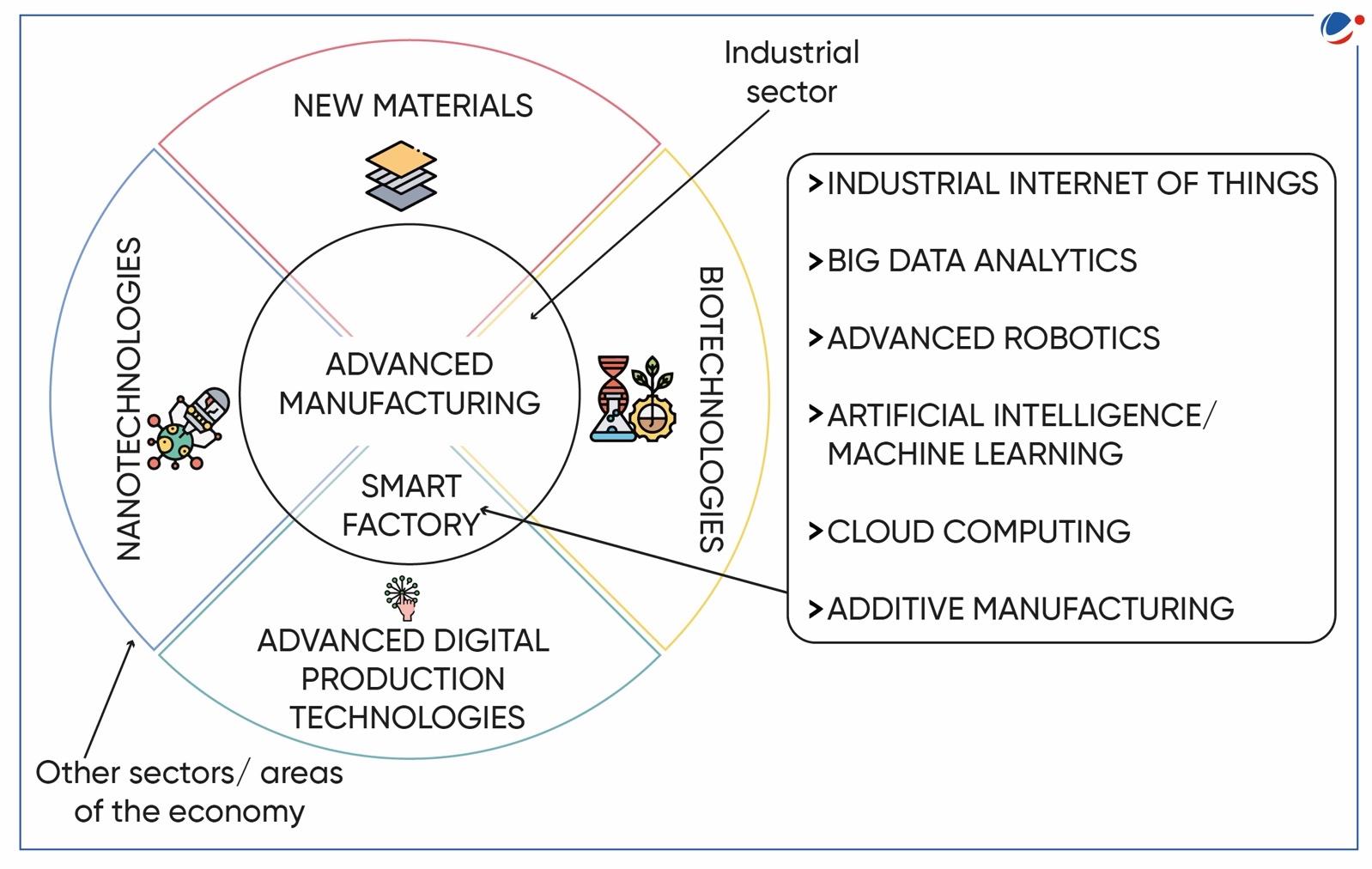
Benefits of 4IR for India
- Better digital infrastructure and massive Productivity boom due to:
- Digital communication: connecting billions of people and things opening new ways of interaction
- Digital energy: combining smart power grids dynamically matching energy generation and demand.
- Digital health: remotely enabling connected health care from anywhere.
- Global manufacturing hub India can develop itself as a global manufacturing hub by harnessing factors like demography, demand and decisive governance in the field of 3D printing, machine learning, data analytics and IoT.
- Creation of Future Workforce India can use advanced technologies and processes for skilling, re-skilling and up-skilling and emerge as largest providers of skilled workforce in the world
- Resilient and efficient supply chain: successfully scaling 4IR technology makes supply chains more efficient reduction in factory waste and increased productivity.
- Spill-over effects: acceleration in the digitalization of industries will create opportunities across nearly every segment of the economy, from health care to transport, energy etc.
- Easier accessibility of products and services for businesses, consumers, and stakeholders all along the value chain.
Challenges for India in harnessing advantages of Fourth Industrial revolution
- Economic Challenges:
- Exacerbating Inequality with low-skill low-pay and high-skill high-pay giving rise to social tensions.
- Fear of mass unemployment: Increased deployment of capital-intensive equipment in manufacturing activities may disrupt labour markets.
- It may harm economies like India by cutting their cheap labour advantage.
- Further, the net displacement of workers by machines might exacerbate the gap between returns to capital and returns to labour.
- Environmental Impacts due to increased digital environment footprint.
- Cyber challenges include loss of privacy, fast spread of fake news. Fear of corporate takeover as it may be difficult to regulate big tech companies.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce for future Industry demand which requires specialized skilling based on Internet of things, artificial intelligence, 3D printing.
- Ethical issues: Discontent can also be fueled by the pervasiveness of digital technologies.
- It can create and propagate unrealistic expectations as to what constitutes success for an individual or a group.
- It may also offer opportunities for extreme ideas and ideologies to spread.
- Privacy Concerns: Tracking and sharing of information is likely to intensify the debates about fundamental issues such as loss of control over one’s data.
Measures India has taken
- The Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (India) is collaboration between the WEF and the Government of Maharashtra, coordinated by the National Institute for Transforming India (NITI) Ayog.
- Artificial Intelligence for Agriculture Innovation (AI4AI) initiative is supporting India’s agricultural transformation.
- Lives of small landholders and women farmers can be improved by using AI.
- ~7,000 chilli growing farmers in Khammam district (Telangana) are using digital solutions to transform value chains.
- Urban transformation: India Hub for Urban Transformation in partnership with Smart City Mission is using emerging technologies for future sustainable cities.
- Education 4.0 in partnership with UNICEF, is creating roadmap for foundation literacy and numeracy, school to work transition etc.
- FIRST Cancer Care on the lines of FIRST Healthcare (Fourth Industrial Revolution for Sustainable Transformation of Healthcare) has been developed in Meghalaya.
- >700,000 residents of East Khasi Hills in Meghalaya will be impacted through the initiative.
- Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) - Udyog Bharat 4.0 is an initiative of Ministry of Heavy Industry to enhance competitiveness in capital goods sector by raising awareness about Industry 4.0 through demonstration centres.
Conclusion
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is about more than technology-driven change. It is an opportunity to help everyone create an inclusive, human-centered future. However exponential and disruptive nature of technology demands long-term decision making to ensure that they are governed in a way that maximizes societal benefit whilst minimizing potential misuse or harm.



