SQUARE KILOMETRE ARRAY OBSERVATORY (SKAO) PROJECT
- Union Cabinet approves Rs 1,250 cr for India's participation in Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO) Project.
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy, headquartered in United Kingdom.
- SKAO will consist of one global observatory, operating two telescopes, across three sites.
- Two SKA telescopes will be at radio-quiet sites in South Africa and Australia.
- They will operate as one large unit.
- They are expected to be operational by 2029.
- SKAO will consist of one global observatory, operating two telescopes, across three sites.
- Objectives of SKAO:
- Understand about the birth of Universe.
- Detect Gravitational Waves.
- A gravitational wave is an invisible ripple in space.
- Understand the evolution of Galaxies, Dark matter and Cosmic Magnetism.
- India joined SKAO in 2012 as an Associate Member and has actively participated in the pre-construction phase of the SKA telescopes.
- In 2022, the National Centre for Radio Astronomy, Pune and SKAO signed cooperation agreement.
- Giant Metre wave Radio Telescope (GMRT) is playing role in SKAO.
- Significance for India: Will allow Indian astronomers direct access to the best radio astronomy facility in the world in the future.
- Also, it will drive growth of technologies several key areas, ranging from antennas and electronics to data and software, including areas like artificial intelligence.
- Tags :
- intergovernmental organisation
- SKAO
- GMRT
OSIRIS-APEX
- OSIRIS REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification and Security-Regolith Explorer) is embarking on a new mission as OSIRIS-APEX (Apophis Explorer)
- Recently, OSIRIS REx delivered a sample from asteroid Bennu.
- OSIRIS-APEX
- It will study Apophis when it will be closest to Planet Earth i.e. 20000 miles.
- Apophis is an S-type asteroid made of silicate materials and nickel-iron.
- The mission aims to observe the physical changes in asteroid Apophis induced by Earth’s gravitational pull.
- Space Agency: NASA
- It will study Apophis when it will be closest to Planet Earth i.e. 20000 miles.
- Tags :
- NASA
- Bennu
- OSIRIS-REx
PEREGRINE MISSION 1 (PEREGRINE LUNAR LANDER)
- NASA launched Peregrine Lunar Lander to explore Moon’s Bay of Stickiness.
- Mission is part of Nasa's Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, which partners with commercial entities to deliver payloads to Moon.
- Scientific goals of mission include:
- To analyze lunar exosphere.
- Assess thermal properties and hydrogen content of lunar regolith.
- Study magnetic fields etc.
- Bay of Stickiness (also known as Sinus Viscositatis region), an area on moon, lies adjacent to Gruitheisen Domes near Oceanus Procellarum, or Ocean of Storms.
- Tags :
- NASA
- Lunar lander
- Moon
SMART LANDER FOR INVESTIGATING MOON (SLIM)
- Japanese spacecraft SLIM landed on the moon, making Japan the fifth country to reach the lunar surface.
- The other four countries are India, United States, Russia, and China.
- About SLIM
- It successfully demonstrated pinpoint technology for landing.
- This technology enables landing within 100 m of a target.
- Because of achieving this feat, it is also referred as Moon Sniper.
- Objective: Acceleration of the study of the Moon and planets using lighter exploration systems.
- Agency: Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
- It successfully demonstrated pinpoint technology for landing.
- Tags :
- JAXA
- Lunar lander
- Moon
GSAT-20
- India to use SpaceX Falcon-9 Rocket to Launch Communications Satellite GSAT-20 in 2024
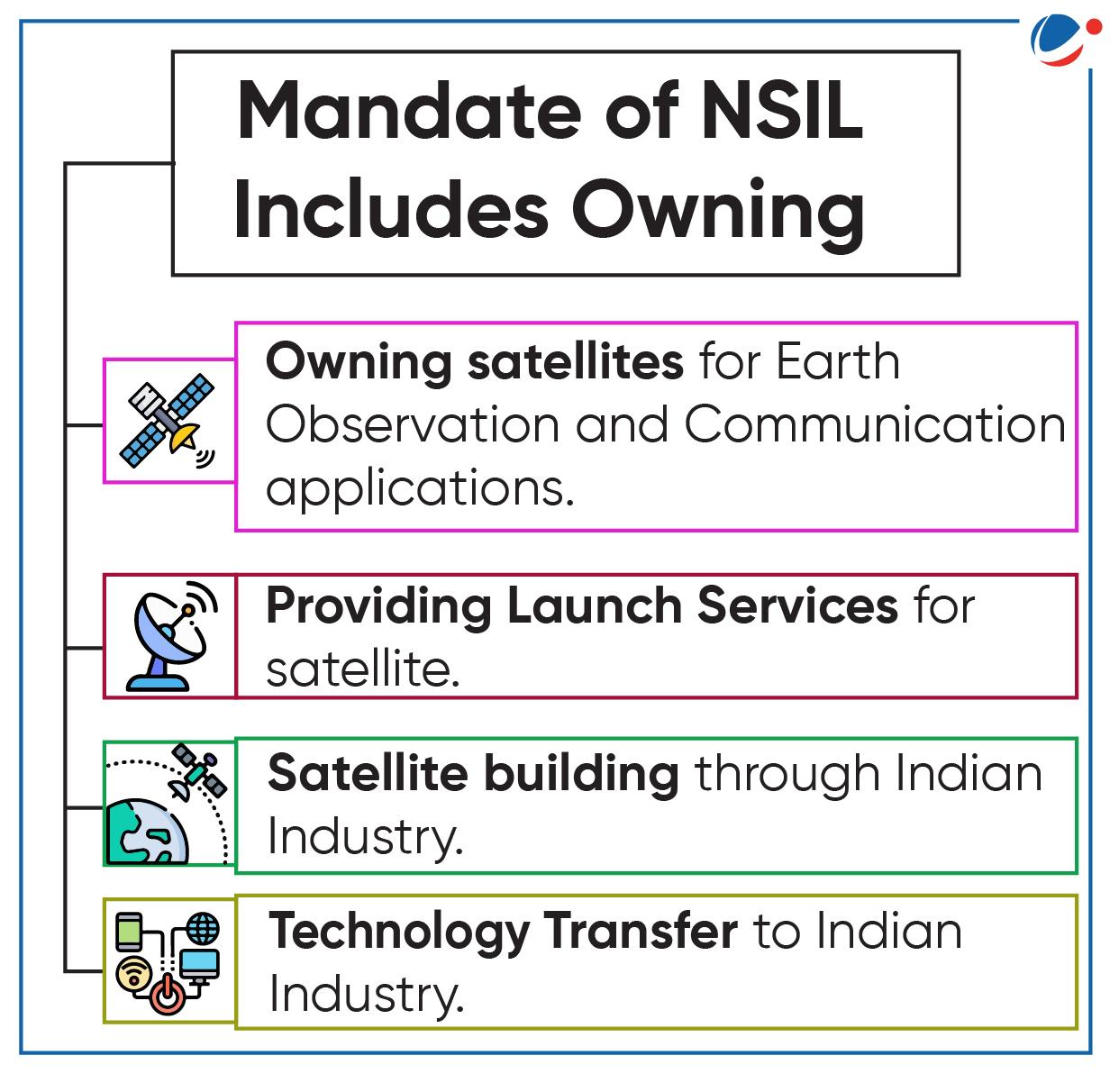
- For the first time, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will launch a communication satellite on a SpaceX rocket.
- About GSAT -20 (Renamed as GSAT-N2)
- GSAT-20 is a high- throughput Ka-band Satellite which will be fully owned, operated and funded by NSIL.
- The satellite, weighing 4700 kg, has been specifically designed to meet the demanding service needs of remote and unconnected regions.
- It is much heavier than launch capacity of ISRO’s most powerful rocket; LVM-3 (which can launch spacecraft weighing up to 4000 kg into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit).
- GSAT-20 will be the second “demand driven” satellite launch enabled by NSIL.
- Previously, NSIL successfully undertook its 1st Demand-driven satellite mission, GSAT-24, with TataPlay purchasing its capacity for Direct-To-Home broadcasting.
- According to India's 2020 space sector reforms, NSIL is required to build, launch, own, and operate satellites in a "Demand-driven mode."
- In the "Demand-driven" mode, when a satellite is launched, it is known in advance who the end customers will be.
- Previously, the mode was more "supply-driven," where capacity was leased after the satellite launch.
NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
- NSIL (incorporated in March 2019) is commercial arm of ISRO.
- It is a Central Public Sector Enterprise under the Department of Space.
- Presently, NSIL owns and operates 11 communication satellites in orbit.
- Tags :
- New Space India Limited (NSIL)
- GSAT-N2
FEAST (FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES)
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), ISRO developed FEAST, a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software.
- FEA is a computerized method for predicting how a product reacts to real-world forces.
- FEAST will be used to perform FEA of various types of structures including rockets, aircraft, satellites, buildings, etc.
- So far, users have mostly depended on expensive software versions from foreign firms for this function.
- VSSC, Thiruvananthapuram (Kerala), is the lead centre of ISRO responsible for the design and development of launch vehicle technology.
- Tags :
- ISRO
KILONOVA EXPLOSION
- A team of researchers have developed a method to model the kilonova explosion.
- About Kilonova Explosion:
- A kilonova is a bright blast of electromagnetic radiation that happens when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a stellar-mass black hole collide and merge.
- A neutron star is formed when a star having a mass more than 1.44 times that of the Sun (as per Chandrasekhar limit) blows off its gaseous envelope in a supernova explosion.
- They are among the densest objects in the cosmos.
- Tags :
- Space
- Neutron Star
CHAMELEON TROJAN
- Cyber security researchers have issued a warning about this new malware.
- Chameleon Trojan attaches itself to legitimate Android apps to avoid detection and runs code in the background.
- It uses 'Accessibility service' on Android devices to disable biometric authentication methods like fingerprint and face unlock to steal the phone’s PIN.
- It uses stolen PIN to unlock the device and steal more sensitive information like credit card passwords, login credentials, etc.
- Tags :
- Cyber Security
- Malware
DIRECT-TO-CELL
- SpaceX, an American company, launched the first batch of Starlink satellites with “Direct-to-Cell” capabilities.
- Direct-to-Cell satellites have an advanced eNodeB modem onboard that acts like a cellphone tower in space.
- Current communication system is based on the land based tower for transferring signals.
- It allows Starlink to deliver direct satellite broadband connectivity on smartphones anywhere on Earth.
- It will also connect Internet of Things (IoT) devices with common LTE (Long-Term Evolution) standards.
- IoT refers to a network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software and network connectivity that allows them to collect and share data.
- Tags :
- SpaceX
- Starlink
REVISED PHARMA MANUFACTURING RULES
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) notified revised pharma manufacturing rules.
- Rules will ensure good manufacturing practices (GMP) and requirements of premises, plant, and equipment for pharmaceutical products.
- Revised rules are notified under Schedule M of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945 and will be called Drugs (Amendment) Rules, 2023.
- Schedule M prescribes GMP for pharmaceutical products and includes requirements of facilities and their maintenance, personnel, manufacture, control and safety testing, storage and transport of material, written procedures and records, traceability, etc.
- Key highlights of the revised rules
- Include new categories of drugs: pharmaceutical products containing hazardous substances such as sex hormones, steroids, cytotoxic substances; biological products; radiopharmaceuticals; phytopharmaceuticals; and investigational pharmaceutical products for clinical trials for humans.
- Implementation: 6 and 12 months for large manufacturers (over Rs 250 crore turnover) and MSMEs (less than Rs 250 crore turnover) respectively.
- Provision for informing the licensing authority about drug recall (presently no such mechanism for informing).
- Other changes introduced: A pharmaceutical quality system, quality risk management, a computerised storage system for all drug products etc.
About GMP
- GMP ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled according to set quality standards.
- WHO has established detailed guidelines for GMP.
- In India, GMP system was first incorporated in 1988 in Schedule M of Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, and were revised in 2018, bringing them on par with WHO standards.
- Tags :
- Pharmaceutical Sector
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW)
- Good Manufacturing Practices
HAVISURE: INDIGENOUSLY DEVELOPED HEPATITIS A VACCINE
- Havisure-India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine launched.
- Havisure was developed by Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
- Havisure is a two-dose vaccine wherein first dose is administered at above 12 months of age and second dose is given at least after 6 months of the first dose.
- It is also recommended for individuals who are at risk of exposure or travel to the regions with high hepatitis A prevalence.
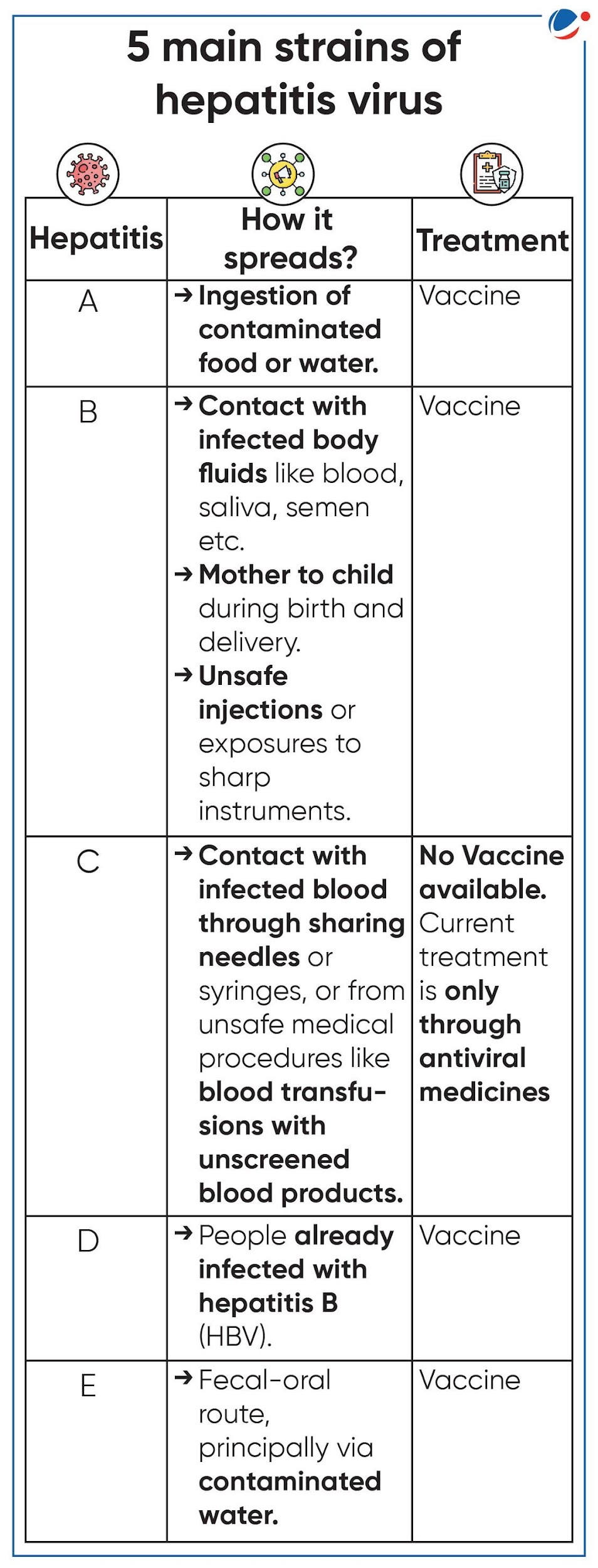
- Hepatitis is an inflammation of liver that is caused by a variety of infectious viruses and non-infectious agents.
- There are five main strains of hepatitis virus i.e. A, B, C, D and E.
- Initiatives taken to prevent Hepatitis
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program 2019 to eliminate Hepatitis C in India by 2030.
- Mission Indradhanush 2014 provides vaccination against Hepatitis B along with 7 other infections.
- World Hepatitis Day (28 July every year).
- Tags :
- Hepatitis
- Virus
‘SMART 2.0’ FOR AYURVEDA TEACHING PROFESSIONALS
- Two prominent institutions under Ministry of Ayush namely National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM) and Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS) have launched 'SMART 2.0'.
- SMART 2.0 (Scope for Mainstreaming Ayurveda Research in Teaching Professionals) Program
- It aimed to promote robust clinical studies in priority areas of Ayurveda with Ayurveda academic institutions/ hospitals across the country through mutual collaboration.
- Earlier launched SMART 1.0 aimed to boost scientific research in priority healthcare research areas through Ayurveda colleges and hospitals.
- Tags :
- Ayurveda
- Ministry of AYUSH
WHO’S INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DISEASES 11 (ICD-11)
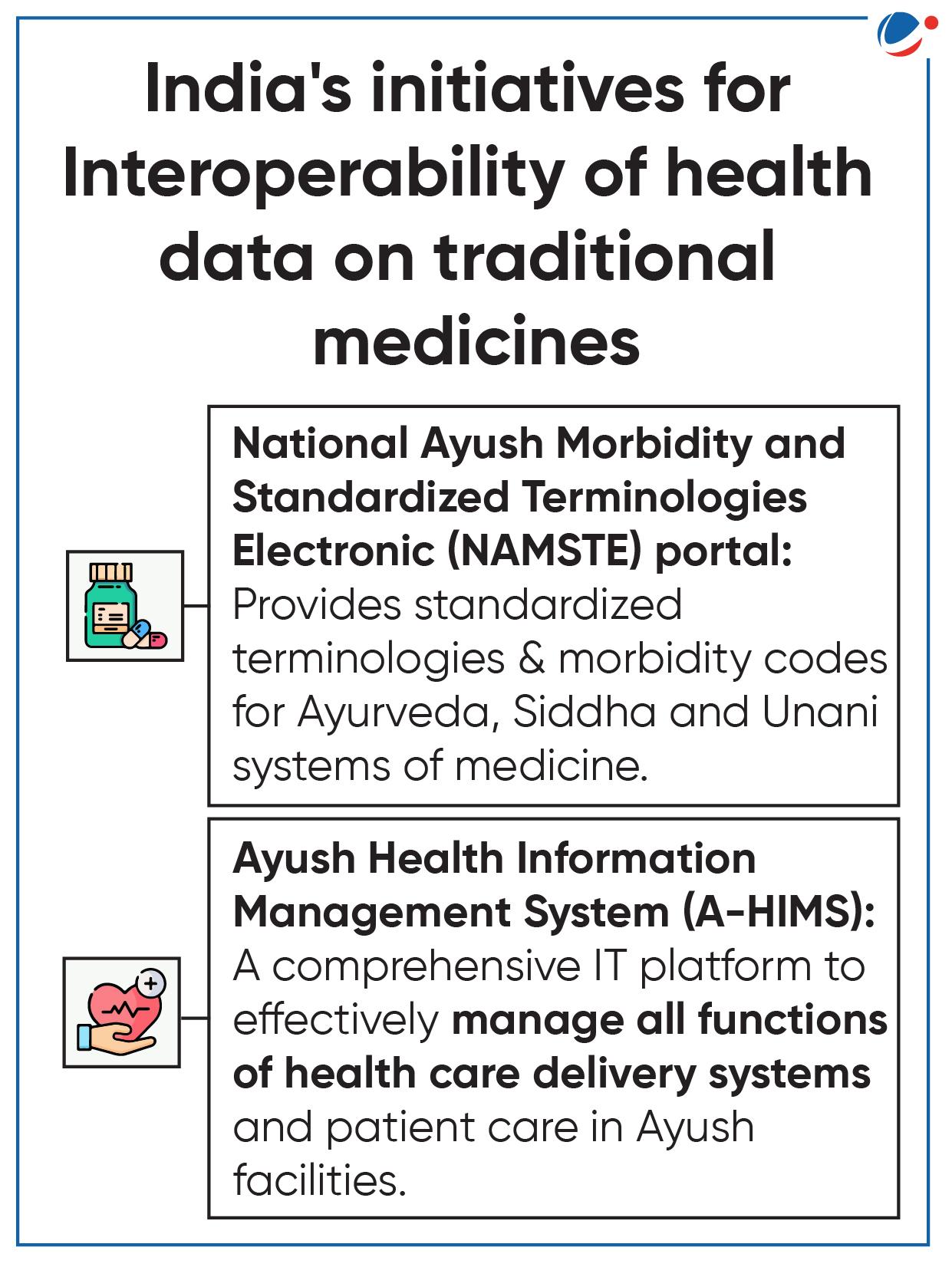
- WHO’s International Classification of Diseases 11 (ICD-11) now introduced Module 2 (ICD 11 TM 2).
- Module 2 of the supplementary chapter on traditional medicine conditions under ICD 11 is dedicated to Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani (ASU) data and terminology.
- It encompasses more than 500 codes. Infectious diseases like Malaria and lifestyle diseases like chronic insomnia are also included.
- ICD is the international standard for systematic recording, reporting, analysis, interpretation, and comparison of mortality and morbidity data.
- It also includes a dedicated chapter on traditional medicine.
- Previously, ICD-11 included Module-1 which covers traditional medicine conditions originating in ancient China, which is now commonly used in Japan, Korea etc.
- ICD-11 came into effect in January 2022.
- Significance of ICD-11
- Provides a list of diagnostics categories to collect and report on traditional medicine conditions in an internationally comparable manner.
- Link traditional medicine practices with global conventional medicine’s norms and standard development.
- Enable integration of traditional medicine into insurance coverage and reimbursement systems, in line with WHO objectives relating to universal health coverage.
- Tags :
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Traditional Medicine
- ICD-11
WHO REPORT ON PREVALENCE OF TOBACCO USE
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global report on Trends in prevalence of Tobacco use 2000–2030 released.
- India is world's second biggest tobacco producer after China.
- Globally, there are 1.25 billion adult tobacco users.
- Nearly 267 million adults (15 years and above) in India are users of tobacco.
- Major tobacco producing states: Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, West Bengal, Telangana, and Bihar.
- Tobacco is a drought-tolerant, hardy and short-duration crop which can be grown on soils where other crops cannot be cultivated profitably.
- Key findings of report
- Decline in tobacco use with about 1 in 5 adults worldwide consuming tobacco in 2022 compared to 1 in 3 in 2000.
- At least 37 million adolescents aged 13–15 years are current users of some form of tobacco – 25 million boys and 12 million girls.
- Impact of Tobacco use
- Kills more than 8 million people each year due to risk of heart disease, lung disorders, cancer etc., including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.
- As per WHO, smoking costs world's economies more than US$ 1 trillion annually in healthcare expenditure and lost productivity.
- Deforestation due to its cultivation.
- India’s initiatives to control Tobacco use: National Tobacco Control Programme, Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes Act, 2019, Cigarette and Other Tobacco Products Act 2003, National Tobacco Quit Line Services etc.
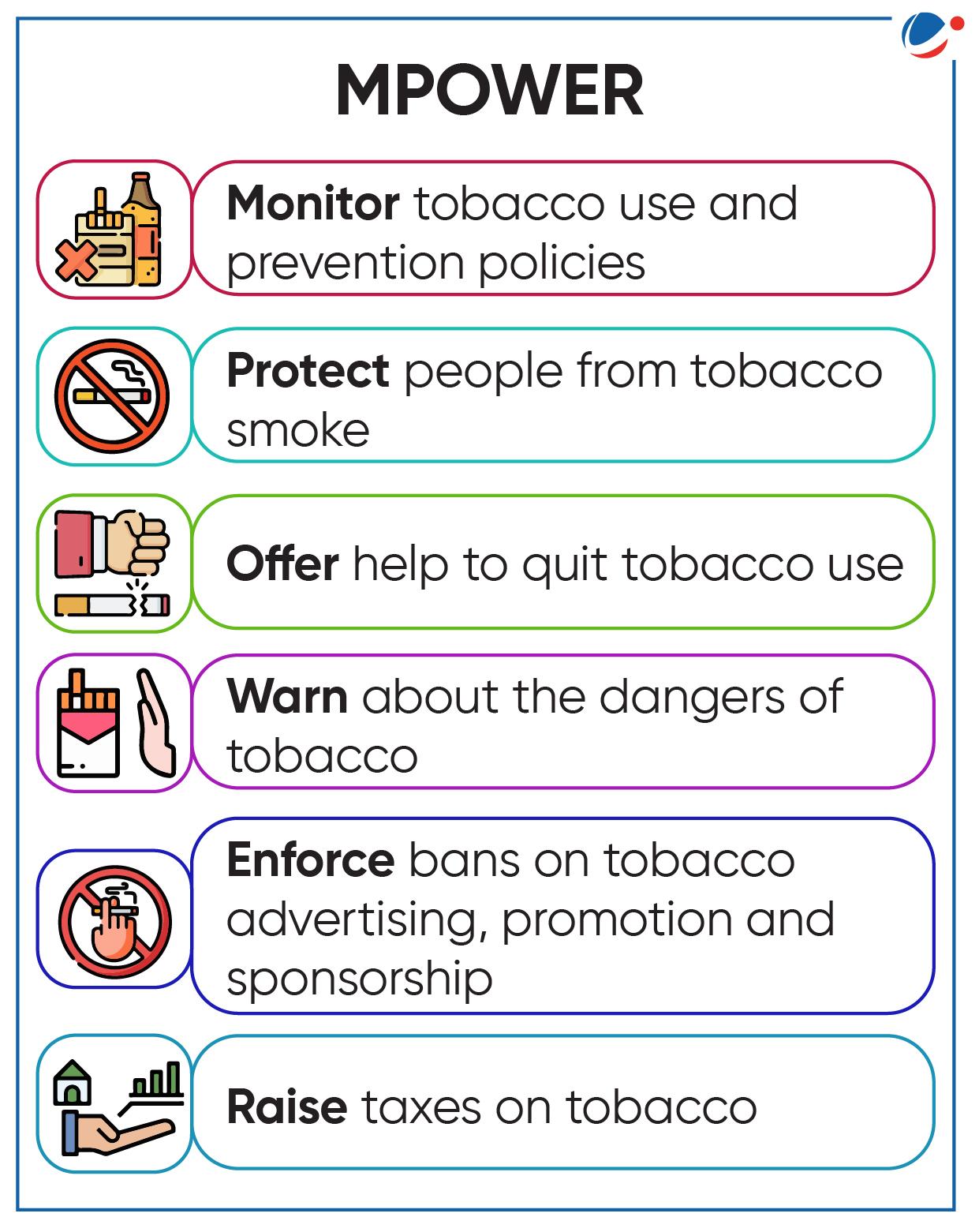
Global Initiatives to control tobacco use
 |
- Tags :
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Tobacco
- MPOWER
DISEASE X
- World Economic Forum is set to begin session on novel ‘Disease X’.
- About ‘Disease X’
- It is a theoretical term and "X" refers to "unexpected”.
- WHO introduced Disease X in 2018 to represent an unknown pathogen that could cause a serious international epidemic.
- WHO has placed Disease X alongside other high-priority diseases such as Ebola and Zika virus in its awareness campaigns.
- Tags :
- World Economic Forum (WEF)
BIO-IMAGING BANK (BIB)
- Mumbai’s Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), has established a ‘Bio-Imaging Bank’ for cancer.
- Through it, the hospital is utilizing deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to craft a cancer-specific tailored algorithm that aids in early-stage cancer detection.
- BIB aims at creating a robust repository encompassing radiology and pathology images.
- It will be linked with clinical information, treatment specifics date etc.
- This will be also used for training, validation, and rigorous testing of AI algorithms for early detection of cancer.
- Tags :
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Cancer
- Deep Learning
NEW TREATMENT REGIMEN FOR LEPROSY
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare announced new treatment regimen for Leprosy.
- About Leprosy (Hansen’s disease)
- Cause: It is a chronic infectious disease which is caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae.
- Affects: Skin, peripheral nerves, mucosa of upper respiratory tract, and eyes.
- Transmission mode: Droplets, from the nose and mouth, due to close contact with untreated cases.
- Treatment: Curable with multidrug therapy.
- Classification: into two types for treatment purposes,
- Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases have fewer bacteria visible and show no signs of advanced disease in biopsies.
- Multibacillary (MB) patients have visible bacteria and may show signs of more advanced disease in biopsies
- About new treatment regimen announced
- Ministry has decided to introduce a three-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases of leprosy in place of a two-drug regimen for six months.
- Multi-drug therapy (MDT), as recommended by WHO, consists of three drugs - dapsone, rifampicin and clofazimine.
- Recent Steps Taken
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) & Roadmap for Leprosy (2023-27) to achieve zero transmission of leprosy by 2027.
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme a centrally sponsored scheme under National Health Mission.
- Nikusth 2.0 Portal, an integrated portal for leprosy case management.
Status of leprosy in India
- India has achieved elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at National level in 2005.
- Prevalence Rate at national level has decreased to 0.45 per 10,000 population in 2021-22 as compared to 0.69 per 10,000 population in 2014-15.
- Tags :
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW)
- Leprosy
- Hansen's disease
BUBBLE BABY SYNDROME (BBS)
- A two-month old girl, diagnosed with BBS, became the youngest to receive bone marrow transplant from a voluntary donor.
- BBS, also known medically as Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), is a rare genetic disorder affecting the immune system.
- A baby with SCID completely lacks a functional immune system and is extremely vulnerable to severe and life-threatening infections.
- Babies born with SCID lack white blood cells, including lymphocytes (T-cells and B-cells), which fight infections.
- Most common treatment is a stem cell transplant (bone marrow transplant).
- Tags :
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
- Genetic Disorder
STEEL SLAG ROAD TECHNOLOGY (SSRT)
- JSW Steel has constructed 1 km long four lane steel slag road section on NH-66 (Mumbai-Goa).
- Earlier, Border Roads Organization has also constructed a steel slag road in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This project falls under the initiative of the Waste to Wealth and Clean India Campaign
- Steel Slag Road Technology
- The slag is generated from a steel furnace burning in the form of molten flux material as an impurity.
- Steel slag is a non-metallic, glassy material consisting of calcium, magnesium, manganese, and aluminium silicates and oxides in various combinations.
- During the road construction, steel slag is processed to remove impurities and metal content.
- These processed steel slag aggregates exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to natural aggregates.
- The road includes bituminous and cement concrete steel slag sections on both the right-hand and left-hand carriageways.
- Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Steel slag roads offer approximately 30% cost savings compared to traditional road construction.
- Durability: Steel slag's robust properties ensure roads built with it surpass the lifespan of conventional roads.
- Abundant Availability: India, as the world's second-largest steel producer, has abundant access to steel slag, facilitating widespread use in infrastructure projects.
- Environmental Friendliness: The innovative process significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a greener approach in road construction.
- SDG 9 Contribution: Embracing steel slag roads contributes to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 9, promoting resilient infrastructure and sustainable industrialization.
- Temperature Resilience: With a melting point over 200 degrees Celsius, steel slag is resistant to temperature variations, suitable for diverse climates.
- Tags :
- Steel Industry
- waste to wealth
ANEEL (ADVANCED NUCLEAR ENERGY FOR ENRICHED LIFE)
- An American company has developed a fuel ANEEL (named after India’s scientist, Dr Anil Kakodkar).
- ANEEL is a mix Thorium and Uranium of a certain level of enrichment, called HALEU (High Assay Low Enriched Uranium).
- HALEU has an enrichment level of 5-20%, whereas most current reactors are enriched up to 5%.
- Potential Benefits
- ANEEL can be used in the existing Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactors (PHWRs) of India’s nuclear fleet.
- Reduction in nuclear waste etc.
- Tags :
- Nuclear Energy
- Thorium
- Uranium



