Why in the news?
In a bid to boost e-mobility, India plans to transform the Golden Quadrilateral into a network of electric vehicles (EV) ready highways using induction charging technology.
What is Induction/Wireless charging?
Induction Charging (IC) also known as wireless charging is method of charging in which electromagnetic fields are used to transfer energy between two coils without the need of a physical connection.
Processes Involved/Working
- The transmission of electricity generally takes place by either of the two methods:
- By electric fields using capacitive coupling between metal electrodes (capacitive charging) or
- By magnetic fields using inductive coupling between coils of wire (inductive charging).
- The most extensively utilised wireless technology is inductive charging.
- The operating principle is similar to that of a transformer and is based on the laws of magnetic induction.
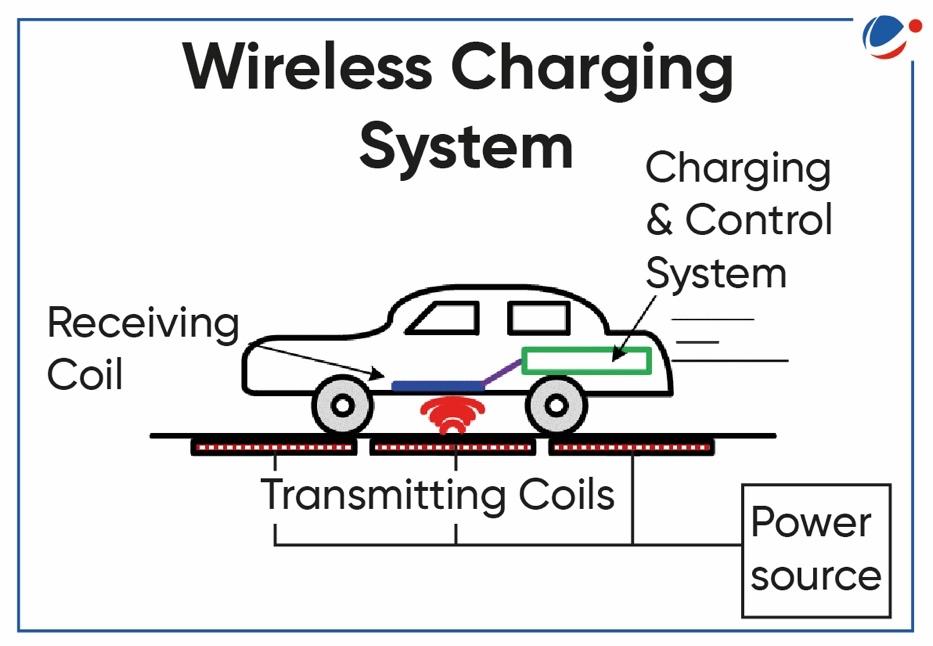
- One coil is in the charging station and the other is in in the EV and the energy is transferred from transmitting coils to the receiving coils.
- A primary circuit, called a transmitter, generates a time-varying magnetic field.
- A secondary circuit receives this field, called the receiver, which is connected to the device to be powered.
- To start charging, drivers only need to park their EV above the charging pad.
Types of Inductive charging
IC is mainly classified into three types:
- Static or stationary charging (used at homes, office)
- In this method of charging, the EV does not move while being charged. It is used when EV is parked for a long time.
- Used at homes, workplaces, public parking, garages etc.
- Quasi-dynamic or opportunistic charging
- This process permits an EV to get charged while traveling at low speeds and during momentary pauses.
- Used at intersections, traffic signals, bus stops etc.
- Dynamic EV Charging (Roads and Highways)
- In this method, owners can charge their EVs continuously as they go. It allows owners to drive long distances without having to stop for charging or risk running out of power
- Used for long distances, inter-city trips, highways, expressways with restricted accessibility to stops etc.
Benefits of Induction charging
- Reduces time and efforts: The technology enables EV owners to simply park their vehicles over a charging pad, reducing the time and effort required to plug in and charge.
- Convenience: It eliminates the need to handle charging cables, making the process more user-friendly and less time-consuming.
- Reduced Maintenance: With no physical connectors, there’s less wear and tear on charging equipment, leading to lower maintenance costs in the long run.
- All-Weather Charging: As there are no exposed electrical connections, wireless charging is suitable for all weather conditions, ensuring uninterrupted charging experiences.
- Help in meeting CO2 emission reduction targets by accelerating the adoption of e-mobility and supporting the deployment of e-buses.
- Supports the development of autonomous driving technology: Wireless charging is well suited for autonomous electric vehicles, as it allows for seamless charging without human intervention
Challenges in adoption of the technology
Although, wireless EV charging offers various benefits, there are some challenges which need to be overcome before its widespread adoption and implementation. These are:
- High costs: Wireless charging systems are currently more expensive than conventional charging stations.
- Efficiency: Wireless charging systems typically experience lower efficiency than traditional wired charging due to energy losses during induction. This could lead to longer charging times and higher energy consumption.
- Interoperability issues: Additional efforts are needed to bring in fully scale interoperable operation among various kinds of transmitter and receiver pad designs with the roads
- In addition, the method of pad integration with both the vehicle and road is an open question that requires extensive engineering effort.
- Durability: As these charging systems will be implemented outdoor for general use, so they need to be robust to withstand the harsh environmental and extreme operating conditions.
- Safety Concerns associated with shielding designs, heat produced in metallic objects next to the system.
- Also, living object detection method is required to prevent pets and animals accessing the hot region during operation.
- Technologies concerns: It is necessary to achieve the development of the sensor systems and controllers that are used to detect EVs on the highways to charge batteries without errors to increase total system efficiency.
Way Forward
- Proper research is required to assess impacts on health caused due to long-term exposure to weak electric and magnetic fields,
- Mechanisms to detect living and foreign objects in the proximity of induction charging systems needs to be built.
- Collaboration between government agencies, automakers, and tech companies will be crucial to drive innovation, reduce costs, and improve efficiency, making wireless charging a viable solution for India’s EV landscape.



