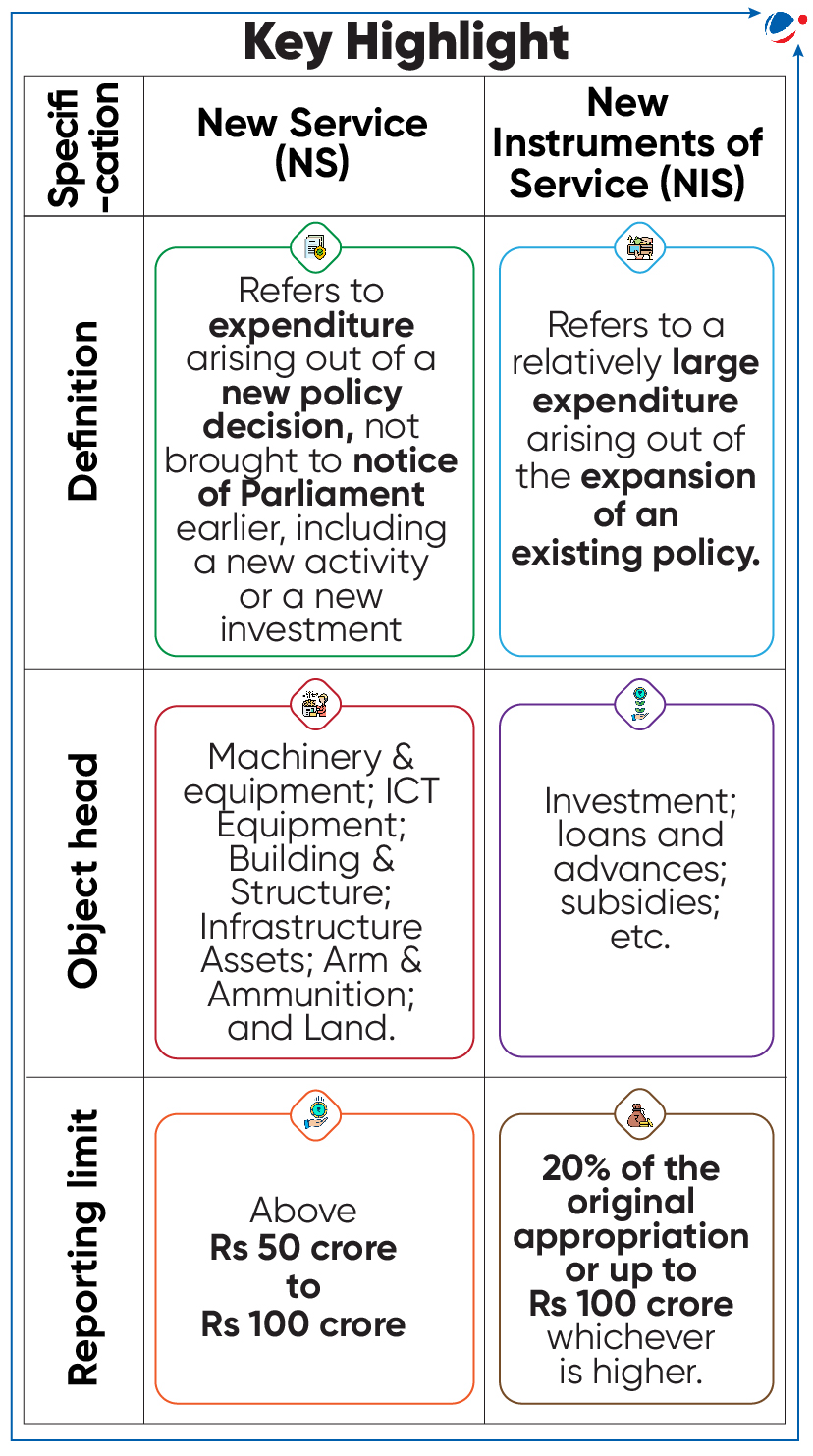
HIGHER FINANCIAL LIMITS FOR NS AND NIS
- Public Accounts Committee (PAC) approved revision of financial limits for ‘New Service (NS)’ and ‘New Instruments of Service (NIS)’.
- The report approved a proposal by the Ministry of Finance to raise financial limits for NS and NIS (it was last revised in 2006).
- This limit is applied whenever expenditure provisions are augmented through appropriation of funds from the savings available within the same sections of Grants/Appropriation.
- Expenditure beyond financial limits can be done through supplementary proposals (from ministries/ departments) for which parliamentary approval is necessary.
- Rationale for revision
- Economic growth: Due to expansion in GDP growth (6-7% on YoY basis), budget size is also expected to grow.
- Delays in project execution: Low financial limits for NS/NIS expenditure prompted a rise in supplementary proposals.
- Enhanced monitoring: Defining NS/NIS uniformly at standardised Object Head would enable effective scrutiny by CAG.
- Tags :
- Public Accounts Committee
RASHTRIYA UDYAMITA VIKAS PARIYOJANA (RUVP)
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship launched RUVP under Skill India Mission.
- About RUVP:
- Tailored specifically for beneficiaries of PM SVANidhi (Street Vendors AtmaNirbhar Nidhi) scheme.
- Offers individuals with comprehensive entrepreneurship training (over a period of 22 weeks) combining theoretical knowledge with practical exposure through experiential learning.
- Focuses on reskilling and upskilling employees to enhance their competitiveness and adaptability.
- It will be piloted initially in selected districts, with focus on ensuring 40% women participation.
- Training will be conducted through offline, online and hybrid modes, with certificates awarded upon completion.
- Tags :
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
- Skill India Mission
STARTUPSHALA
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) launched ‘StartupShala’ - Startup India’s flagship accelerator program.
- Launched in 2016, Startup India is a flagship initiative of DPIIT to support entrepreneurs and build a robust startup ecosystem in India.
- About StartupShala
- Sector-specific initiative for existing entrepreneurs to provide them access to knowledge, network, funds, and guidance required to scale up.
- Three-month long accelerator program.
- 2 Cohorts - Clean Technology and Deep Technology.
- 20 startups will be selected from each cohort.
- Tags :
- DPIIT
- Startup India
EASE OF DOING BUSINESS REFORMS
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) Operationalises Central Processing Centre to facilitate Ease of Doing Business (EoDB).
- CPC is established for centralised processing of regulatory compliance forms filed under Companies Act and Limited Liability Partnership Act.
- It will process applications in time bound and faceless manner on lines of Central Registration Centre (CRC) and Centralized Processing for Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE).
- CRC provides services for speedy incorporation of companies whereas C-PACE provides centralised processing of applications for voluntary closure of companies.
- It will process applications in time bound and faceless manner on lines of Central Registration Centre (CRC) and Centralized Processing for Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE).
- EoDB refers to simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of setting-up, operating, and closure of businesses in a particular territory.
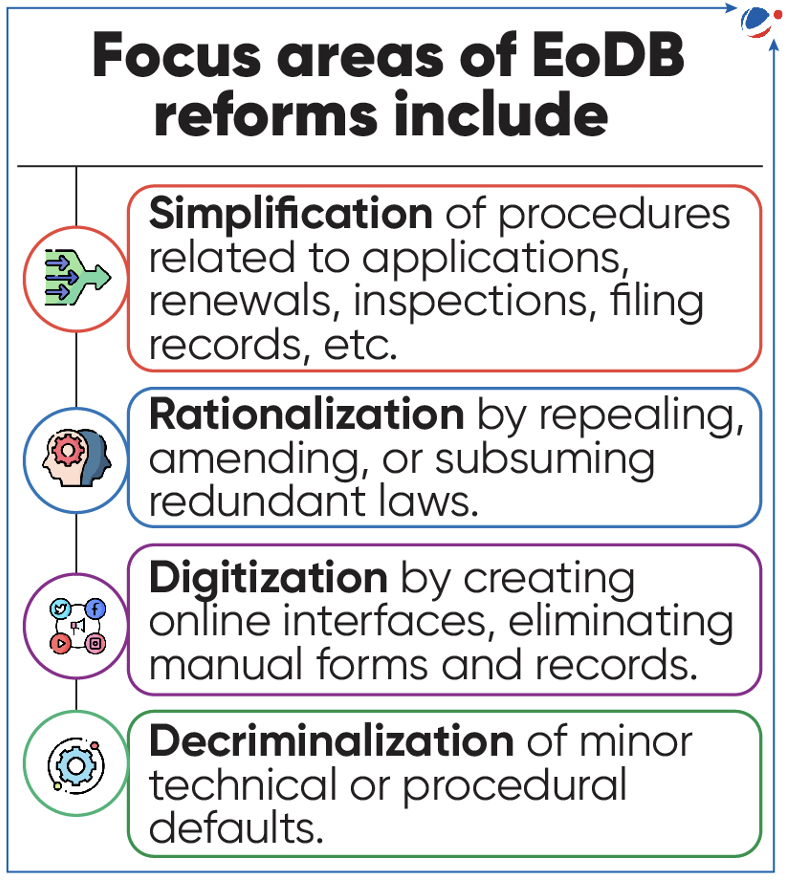
- Significance of EoDB reforms
- Economic growth: Through improved resource allocation, enhanced competitiveness to boost innovation, etc.
- Foreign investment: Through reduced bureaucratic hurdles, improved transparency to reduce perceived risks for investors, etc.
- Social development: By promoting inclusivity and providing opportunities for marginalized communities to participate in economic activities.
Initiatives taken for EoDB reforms
|
- Tags :
- EoDB
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs
REPORT ON FRAMEWORK FOR INSOLVENCY MEDIATION
- Expert committee was constituted by Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) with T.K. Vishwanathan as Chairperson to examine the scope of using mediation in various processes under the IBC 2016.
- Currently, there are no specific provisions for mediation of insolvency and bankruptcy disputes under IBC.
- Mediation is use of a neutral third party to facilitate the negotiated settlement of a dispute between two or more parties.
- Typically, it is initiated by mutual consent of the parties, or pre-agreed contract, or court reference or law-mandated requirement.
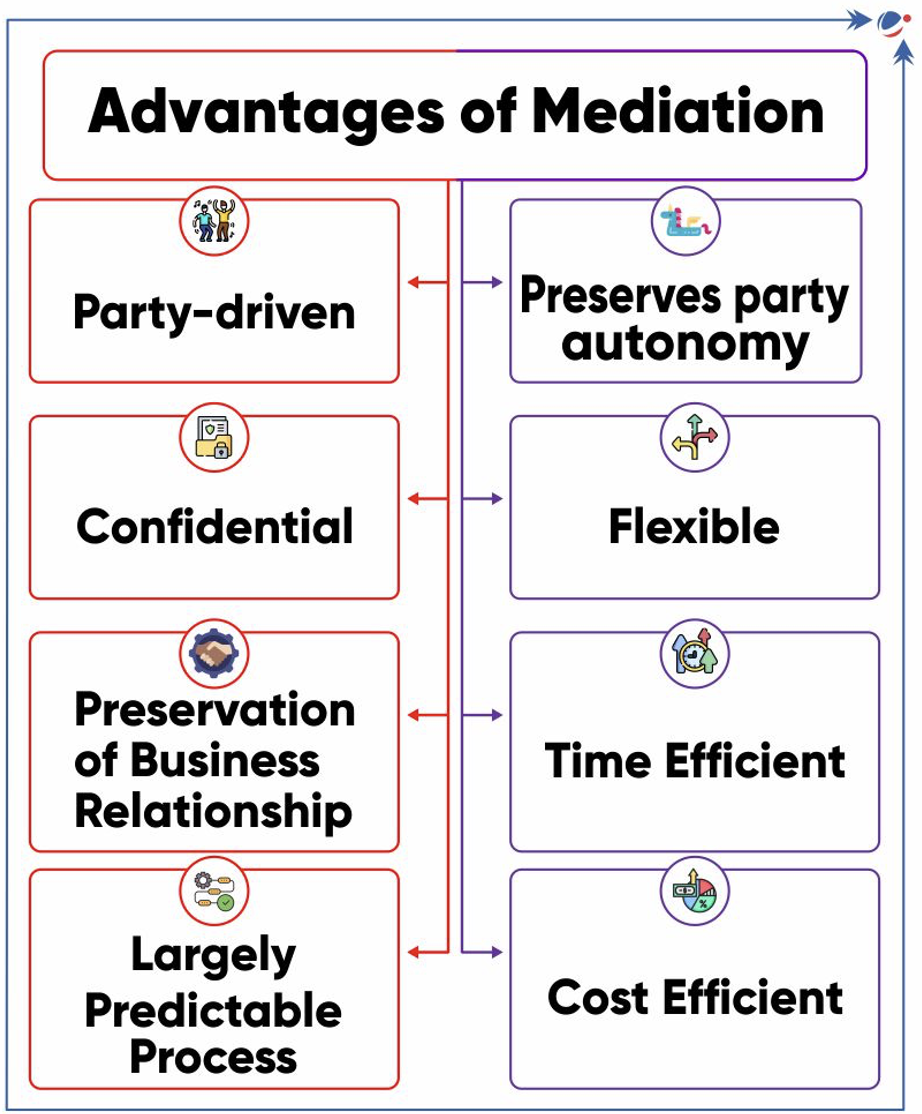
- Mediation framework in India
- The Mediation Act, 2023 aims to facilitate mediation, especially institutional mediation.
- Provisions in other legislations: Civil Procedure Code, 1908, Companies Act, 2013, Commercial Courts Act, 2015 and Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- India is signatory to the Singapore Convention on Mediation.
- Recommendations of the Committee
- Phased introduction of voluntary mediation as a dispute resolution mechanism under IBC.
- Centre may by rules prescribe structure of insolvency mediation framework with specifying categories of mediable disputes.
- IBBI to specify procedures for conduct of mediations and their enforcement.
- Costs for the mediation to be borne equally between parties or as mutually agreed.
- Tags :
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)
- Mediation
SECURITIES APPELLATE TRIBUNAL (SAT)
- Absence of a full bench is affecting functioning of the SAT leading to delays and disruptions.
- About Securities Appellate Tribunal
- It is a statutory body established under the provisions of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992.
- It hears and disposes appeals against orders passed by
- SEBI
- Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA)
- Insurance Regulatory Development Authority of India (IRDAI)
- The Presiding Officer and Judicial Members are appointed by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India or his/her nominee while Technical members are appointed on recommendation of a Search-cum-Selection Committee.
- Tags :
- Statutory Body
- Securities Appellate Tribunal
UNIFIED PAYMENT INTERFACE (UPI)
- Prime Minister of India jointly inaugurated UPI services with Mauritius and Sri Lanka and also RuPay card services in Mauritius.
- This will boost digital transformation, promote tourism and strengthen bilateral economies ties with both countries.
- About UPI:
- It powers multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application (of any participating bank), merging several banking features e.g., transfer of funds, etc.
- Developed by National Payments Corporation of India, an initiative of RBI and Indian Banks’ Association under provisions of Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Tags :
- UPI
- National Payments Corporation of India
CODEX COMMITTEE ON SPICES AND CULINARY HERBS (CCSCH)
- 7th Session of the Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH) Held at Kochi.
- In this session, quality standards for 5 spices, namely small cardamom, turmeric, juniper berry, allpice and star anise were finalised.
- CCSCH has forwarded these 5 standards to Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) recommending for adoption as full-fledged Codex standards.
- For first time ever in CCSCH, strategy of grouping of spices was successfully implemented.
- About CCSCH
- Establishment: CCSCH was established as one of the Commodity Committees under CAC in 2013.
- Host: India hosts CCSCH since the beginning and Spices Board India (Ministry of Commerce and Industry) serves as the Secretariat organization.
- Term of reference :
- To elaborate worldwide standards for spices and culinary herbs in their dried and dehydrated state.
- Consult with international organizations in the standards development process to avoid duplication.
- Codex Standards
- About: These are international food texts, i.e. standards, codes of practice, codes of hygienic practice, guidelines and other recommendations.
- Nature: Codex texts are voluntary and do not have binding effect on national food legislation.
- Codex and WTO: WTO Agreements on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS Agreement) and on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT Agreement) encouraged WTO members to harmonise national regulations with international standards.

- Tags :
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH)
- Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC)
- WTO Agreements
REPORT ON TRANSFORMING FAIR PRICE SHOPS
- Standing Committee on Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution submits report on ‘Transforming Fair Price Shops (FPSs)’.
- As per the National Food Security Act, 2013, FPS refers to shops licensed to distribute essential commodities to ration card holders under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Such license is issued by an order under section 3 of Essential Commodities Act (ECA), 1955.
- ECA provide for regulating control of production, supply, distribution, and trade of certain commodities in the general public interest.
- Launched in 1997 TPDS provides for lower subsidised food prices for Below Poverty Line (BPL) families than those for Above Poverty Line (APL) beneficiaries
- Such license is issued by an order under section 3 of Essential Commodities Act (ECA), 1955.
- Key issues with FPS: Leakages and diversion of food-grains, financial non-viability of FPS, etc.
- Recommendations for transforming FPS
- Increase sales of non-PDS commodities such as Khadi & Ayush products from MSMEs
- Form a monitoring cell to track the progress of model FPS in all states.
- Improve working of Vigilance Committees (VCs) established under NFSA.
- VCs are established by State Governments at the State, District, Block and FPS levels to ensure transparency and accountability of the functionaries in TPDS.
- Ensure all ePoS machines are connected to and synchronized with weighing machines for effective delivery of ration.

- Tags :
- National Food Security Act, 2013
- Fair Price Shops (FPSs)
- Essential Commodities Act (ECA)
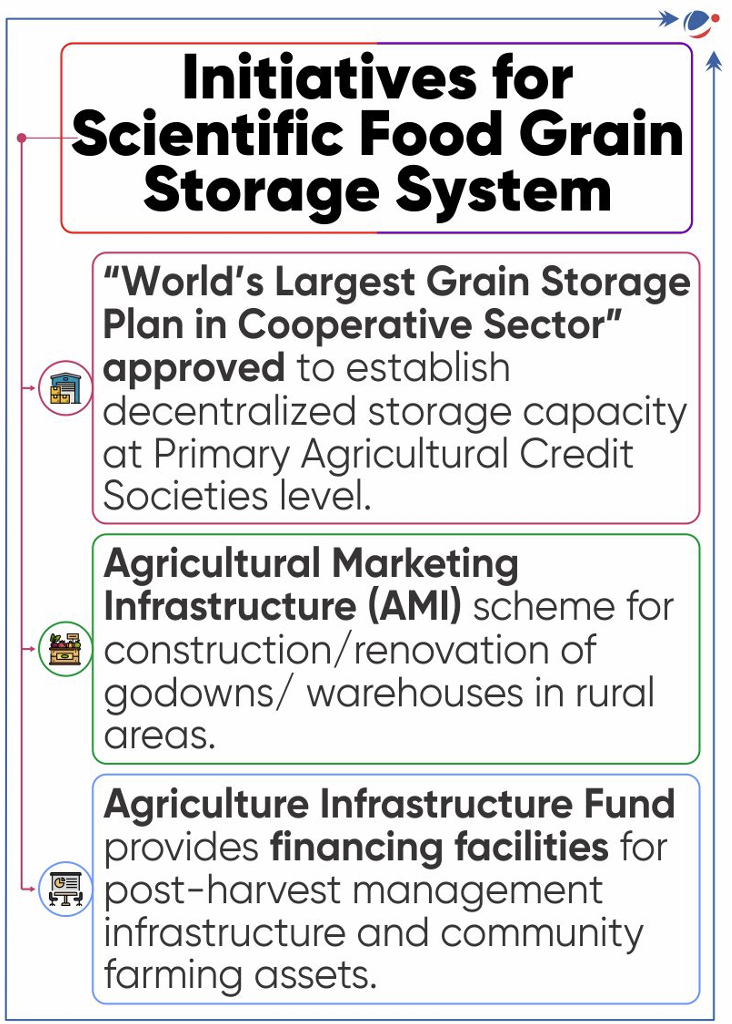
INDIA’S FOOD GRAIN STORAGE SYSTEM
- MeitY transfers the technology for Smart Food Grain Storage System (SAFEETY) to the industry.
- Technology for SAFEETY was developed by the Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research (SAMEER).
- SAMEER is an autonomous R&D institution under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It features conveyorized loading & unloading of grain bags having RFID for traceability, online weight and moisture measurement with radio frequency-based removal of moisture from grain.
- Need for Scientific Food Grain Storage System
- Low production capacity: India accounts for 18% of the global population but only 11% of the arable land.
- Inadequate storage capacity: India's foodgrain storage capacity is only 145 MMT, covering 47% of the total production at 311 MMT.
- Food security: FCI has grains beyond its buffer capacity which also requires a robust network of foodgrain storage facilities.
- Economic viability of farming: Robust storage will reduce wastage, keep farm produce less volatile to market fluctuations and boost foodgrain exports.
- Tags :
- Smart Food Grain Storage System (SAFEETY)
- Scientific Food Grain Storage System
CABINET APPROVES ADDITIONAL ACTIVITIES IN NLM
- Cabinet approves inclusion of additional activities in National Livestock Mission (NLM).
- Key changes
- Additional coverage: Eligible entrepreneur will get capital subsidy and state government will be assisted for breed conservation of horse donkey, mule, camel.
- Enhancing Fodder supply:
- Eligible entrepreneurs will get capital subsidy for seed processing Infrastructure.
- State government will be assisted for fodder cultivation in the non —forest land, waste land/range land/non-arable, etc.
- Simplification of Livestock Insurance programme:
- Premium for the farmers has been reduced to 15% as against the current beneficiary share of 20%,30%, 40% and 50%.
- Remaining premium will be shared by the Centre and the State.
- Number of animals to be insured has also been increased to 10 cattle unit instead of 5 cattle unit for cattle sheep and goat.
- About NLM
- Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying
- Type: Both Centrally Sponsored and Central sector
- Key objectives
- Entrepreneurship development in small ruminant, poultry and piggery sector & Fodder sector.
- Increase of per-animal productivity through breed improvement.
- Increased meat, egg, goat milk, wool and fodder production.
- Jurisdiction: Implemented all over India from 2021-22.

- Tags :
- National Livestock Mission (NLM).
- Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying
INITIATIVES UNDER PMFBY
- Union Government launched 3 new initiatives under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY).
- PMFBY is comprehensive crop insurance from pre-sowing to post-harvest period.
- Krishi Rakshak Portal and Helpline (KRPH) 14447: To provide multilingual support, transparent communication and real-time grievance resolution.
- Learning Management System (LMS) to train stakeholders in efficient crop insurance and agricultural credit.
- SARTHI Portal: To extend coverage to health, life, home, shop, agriculture implements, motor, and parametric products.
- SARATHI is a digital insurance platform launched in collaboration with UNDP India.
- Tags :
- SARTHI Portal
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
ANNUAL SURVEY OF INDUSTRIES (ASI)
- Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- ASI is the principal source of Industrial Statistics in India.
- It is conducted under the Collection of Statistics (COS) Act, 2008.
- It covers all factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948.
- Also, covers unit under the Bidi and Cigar Workers (Conditions of Employment) Act 1966 etc.
- However, defence establishments, oil storage and distribution depots, etc. are not covered under it.
- Key Highlights
- In terms of Gross Value Addition, Gujarat remained at the top, followed by Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh
- The top five states in terms of employment are Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana.
- Manufacturing sector showed resilience even after the disruption caused by the pandemic.
- Main driver of resilient included Manufacture of Basic metal, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Pharmaceutical Products, Motor vehicles, etc.
- About Manufacturing Sector
- Contributes around 17% in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- India aims to increase share to 25% by 2025.
- There is huge potential exporting manufactured goods.
- Key Deriving factors: Huge domestic demand, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), etc.
- Contributes around 17% in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Challenges faced by Sector: Lack of Credit Availability, Low productivity in comparison to other counties like China, Vietnam etc., Informal or unorganised sector, Lack of skilled labour, Infrastructure bottlenecks etc.

- Tags :
- Manufacturing Sector
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
SANGAM: DIGITAL TWIN INITIATIVE
- Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has unveiled the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative.
- This initiative is a Proof of Concept focused on revolutionizing the planning & design of infrastructure.
- It aims at combining the prowess of Digital Twin and Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, 5G, 6G, and next-gen computational technologies.
- It brings all stakeholders on one platform to demonstrate practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions.
- It is to be conducted in one of the major cities of India in two stages i.e. Exploration stage and Demonstration stage.
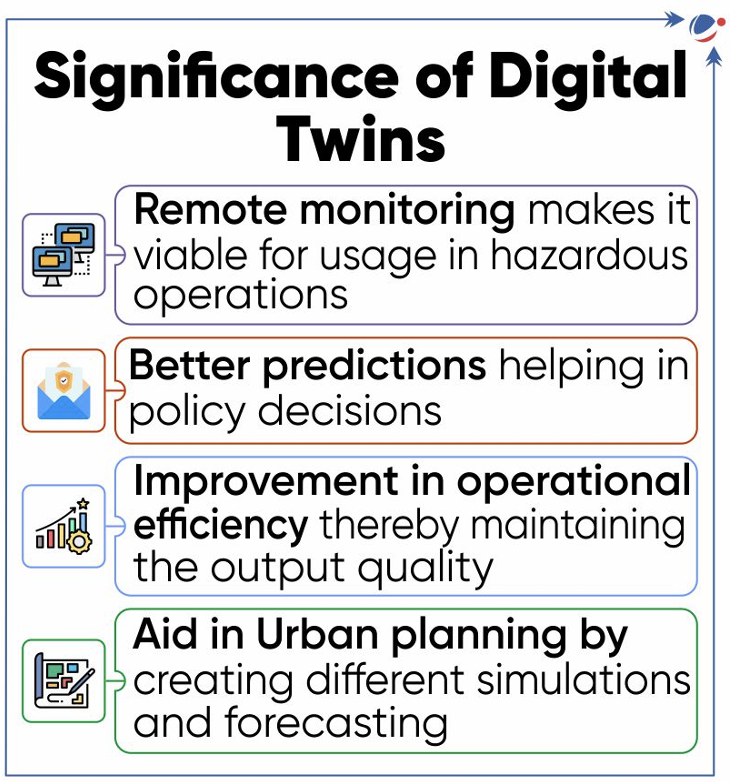
- Digital Twin is a virtual model designed to accurately reflect a real-world physical object.
- It spans the object's lifecycle and uses real-time data sent from sensors to simulate the behavior and monitor operations, thus helping decision making.
- Digital twins differ from simulations in its large scale and two-way flow of information.
- Digital twins are already being used in power generation equipment, large physical structures, manufacturing operations, healthcare services and automotive industry.
Related news Recently, a private company has created digital twin of Hyderabad’s 16th century Qutub Shahi tombs using drone scanners.
|
- Tags :
- Digital Twin
- Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
DIGITAL CREATOR ECONOMY
- Union Government Announces Inaugural Edition of National Creators Award.
- Award aims to celebrate diverse voices and talents shaping India’s growth and cultural narrative, driving positive social change, etc., in India’s Digital Creator Economy.
- Digital Creator Economy refers to a segment of the economy driven by individuals who create content, products, or services and monetize them through various digital platforms.
- About Awards
- Features wide array of categories recognizing excellence and impact across various domains, including storytelling, social change advocacy, environmental sustainability, education, etc.
- Selection Process: Combination of jury and public votes.
- Spearheaded by: MyGov India.
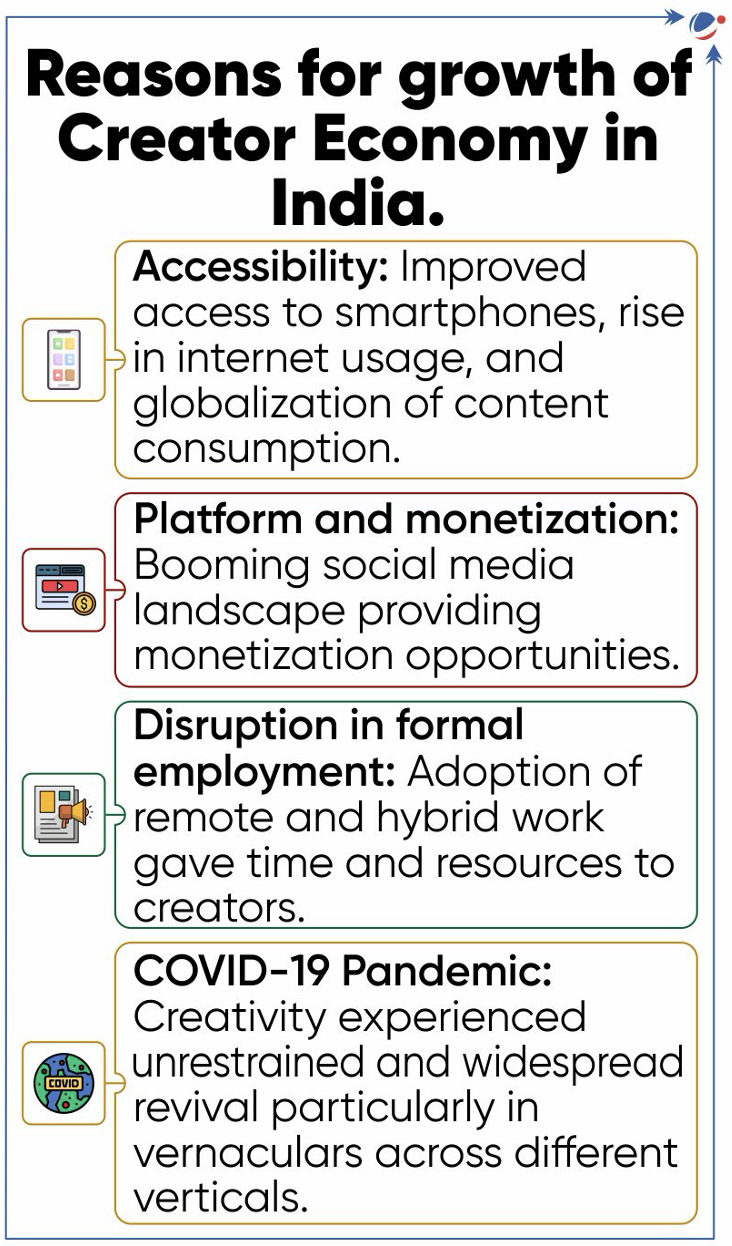
- Current state of Indian creator Economy
- ~80 million Creators and Knowledge Professionals in India.
- ~150000 Professional content creators in India who are able to monetize their services effectively.
- Opportunities of Creator economy
- For individuals: Diversification of income streams, creative expression, flexible work model, reach to global audience, etc.
- For businesses: Cost-effective and organic marketing, community building, etc.
- For society and economy: Cultural expression, social mobilization, skill development and entrepreneurial mindset, etc.
- Challenges: Authenticity and integrity concerns, mental health and burnout due to excessive competition, gatekeeping and algorithmic biases of platforms, etc.
- Tags :
- National Creators Award
- Creator Economy
INPUT SERVICE DISTRIBUTION (ISD)
- Interim budget has proposed to mandatorily register for ISD for companies with branches in multiple cities to claim input tax credit.
- Input Tax Credit is the tax that a business pays on a purchase and that it can use to reduce its tax liability when it makes a sale.
- ISD is a mechanism (office) that allows billing of common input services to one location of the company and permitting it to distribute it to its branches with separate GST registration.
- This recent move is expected to reduce disputes significantly.
- Tags :
- ISD
THREE NEW MAJOR RAILWAY CORRIDORS ANNOUNCED
- PM GatiShakti to be utilized for three new major railway corridors announced under Interim Budget 2024-25.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High traffic density corridors
- Significance of the three Corridors
- Increase logistics efficiency and reduction of cost of logistics related to rail movement.
- Decongestion of high density rail routes
- Facilitate modal shift from road to rail and to coastal shipping
- Reduction of carbon footprint in logistics.
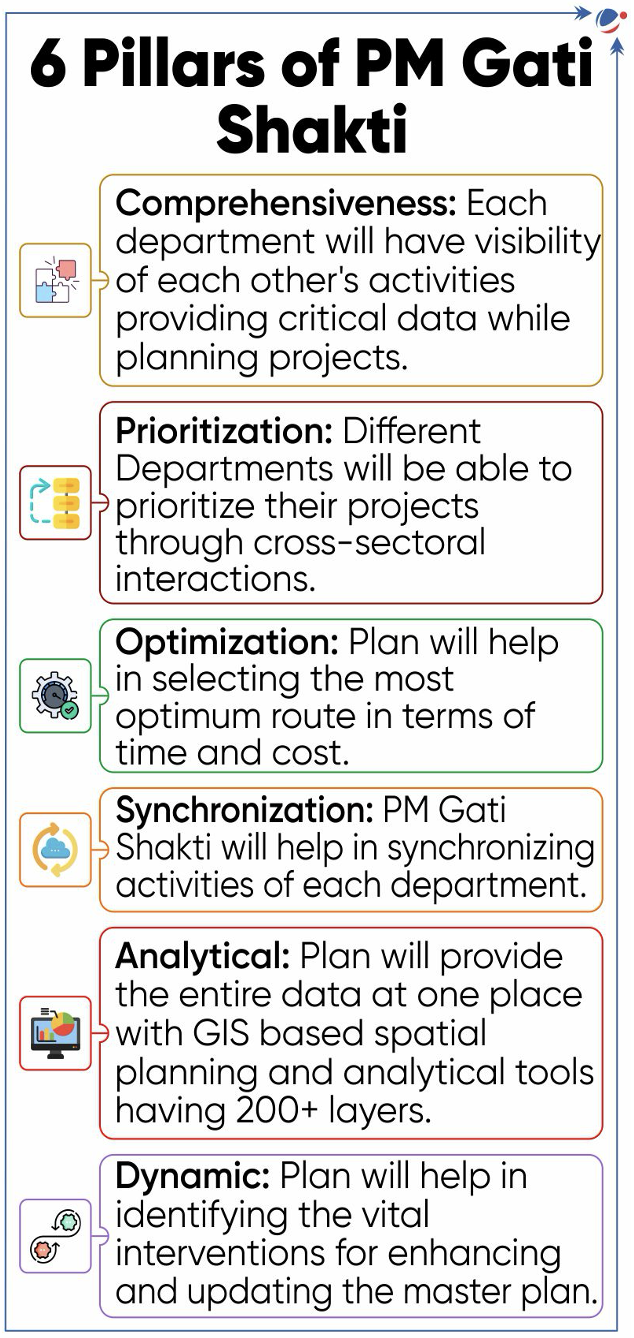
- About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launched in 2021 for providing multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- Provides a comprehensive database of the trunk & utility infrastructure, ongoing & future projects of various Infrastructure and Economic Ministries/Departments of Central Government and States/UTs.
- This data is integrated with the GIS-enabled PM Gati Shakti platform, thereby and monitoring of the Next Generation infrastructure projects on a single portal.
- Goal of achieving self-reliance and a $5 trillion economy by 2025.
- Focusses on economic growth driven by 7 engines namely: Railways, Roads, Ports, Waterways, Airports, Mass Transport, and Logistics Infrastructure.
- It incorporates various infrastructure schemes like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, UDAN, etc.
- Tags :
- PM GatiShakti
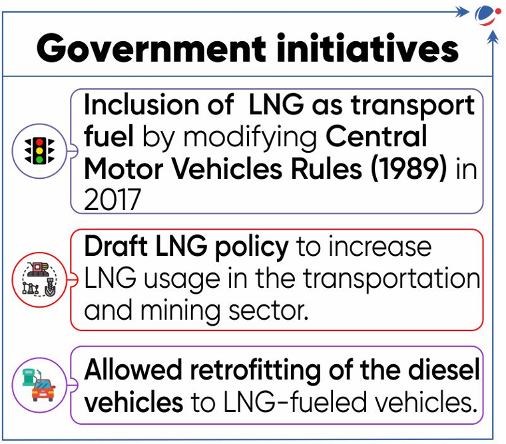
NITI AAYOG REPORT ON LNG AS A TRANSPORTATION FUEL
- NITI Aayog launched LNG as a Transportation Fuel in Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicle (M&HCV).
- It is the outcome of NITI Ayog and the Embassy of Netherlands bilateral cooperation for energy transition and decarbonizing agenda.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a clear, colourless, non-toxic liquid that forms when natural gas is cooled to the liquid state, at about -162 degrees Celsius for shipping and storage.
- Need of LNG push for M&HCV:
- Achieving the target of Net Zero by 2070 through CO2 emission reduction.
- Reducing oil import dependency.
- India's rapidly expanding trucking market (expected to more than quadruple in 2050 from 2022)
- Contribute to a Gas-based economy (achieving a share of natural gas in the primary energy mix to 15% by 2030).
- Challenges in the adoption of LNG: high initial cost compared to traditional diesel trucks, lack of availability of LNG retail outlets, hesitancy in the market, etc.
- Recommendations in the report
- Demand aggregator for deployment of LNG-based vehicles aiming at cost reduction with higher order volumes.
- Fiscal Incentives like bringing LNG under GST, revised depreciation schedules, toll fee exemption, production-linked incentives.
- Non-fiscal incentives like preferential right of way, "ECO" labels, priority lane access, Fuel cards, etc.
- Tags :
- NITI Aayog
ERRATA
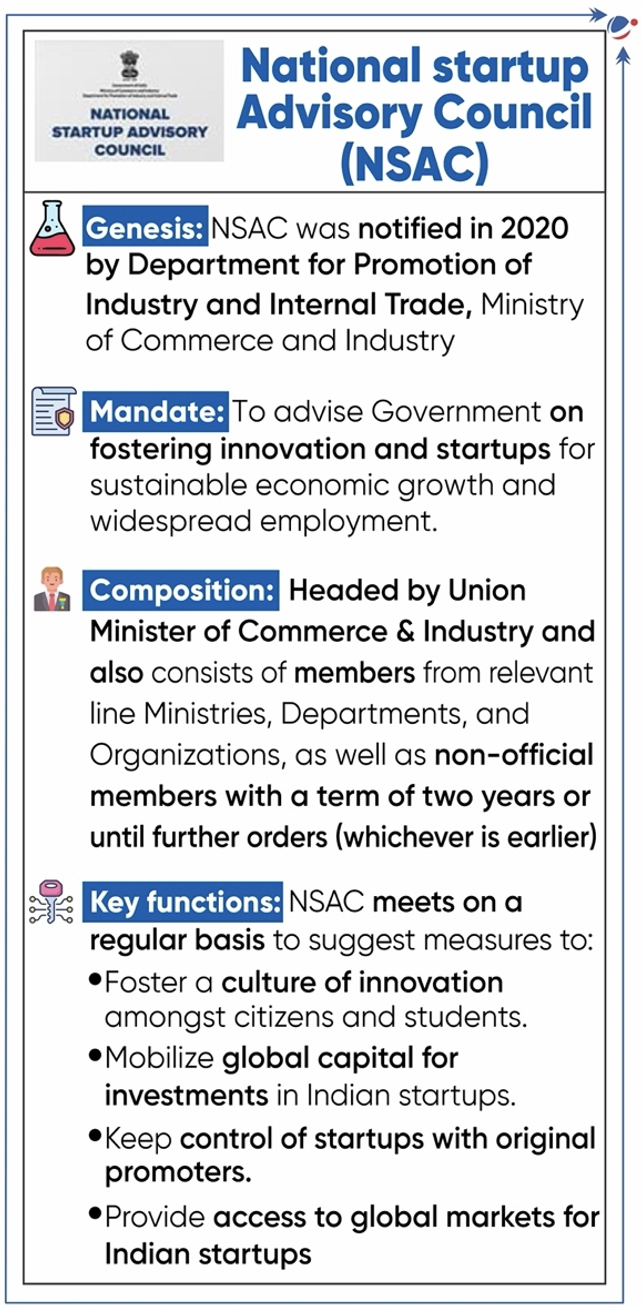
- In December 2023 Monthly Magazine in Article 3.9.1 National Startup Advisory Council, due to a design error, incorrect spelling and logo was used in the infographic. Please find attached updated infographic.
- Tags :
- National Startup Advisory Council



