Why in the News?
The eminent physicist S.N.Bose was remembered on his 50th death anniversary.
About S.N.Bose (1894-1974)  Early life
Rewards and Recognitions
|
Scientific Contributions of S.N Bose
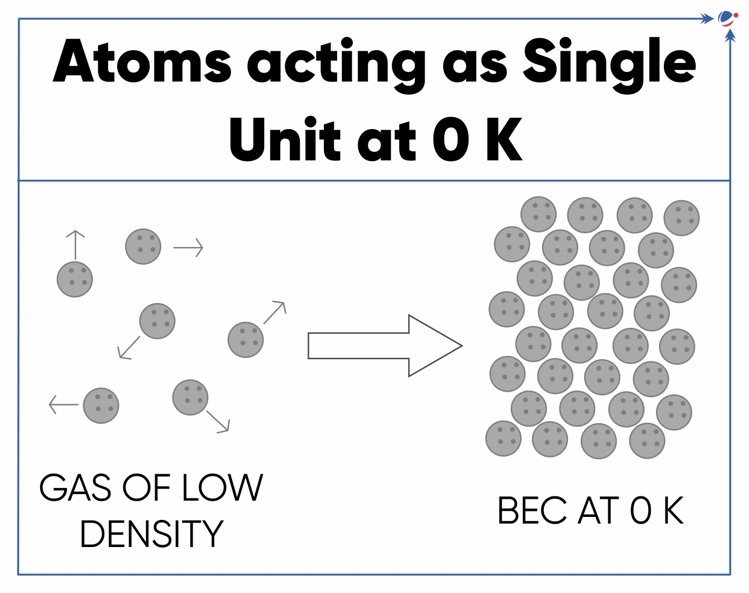
- Bose-Einstein Condensates (BEC): It is a quantum phenomenon predicted by Bose and Einstein (1925). It is a state of matter created when particles are cooled to near absolute zero (-273.15 degrees Celsius/0 Kelvin).
- All the atoms become a single entity at this point, and possess quantum properties, wherein each particle together functions as a wave of matter
- Referred to as the 'fifth state of matter', it was proved experimentally by Weimann, Cornell and Ketterle for which they received Nobel prize in 2001.
- Properties of BEC include:
- Super fluidity: BEC has zero viscosity and can flow without resistance.
- Super conductivity: The zero resistance leads to optimal conductivity.
- Coherence: All particles in the BEC are in the same quantum state behaving as a single entity.
- Macroscopic Occupation: In a BEC, a number of particles occupy a same quantum state, leading to a macroscopic wave function.
- Bose-Einstein Statistics: Earlier proposed as a statistical procedure for counting possible states of a quantum system composed of identical particles with integer spin for light quanta in 1924 by Bose.
- The statistics was extended to gas molecules by Einstein.
- Particles which obey Bose-Einstein Statistics principle are referred as “Bosons”.
- Bosons are particles with integer spin and include photons (light), gluons (particles that act as force carriers in the nucleus), the Higgs boson, and the W and Z bosons.
- X-ray diffraction cameras: Designed and constructed by him for rotation and powder photography.



