Why in the News?
The Climate and Clean Air Coalition's (CCAC) annual meeting, the Climate and Clean Air Conference, recently took place in Nairobi, Kenya.
More on the news
- The conference was held on the margins of the Sixth Session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA-6).
- Objectives of the conference: Highlighting ways to further scale up implementation of the Global Methane Pledge, Clean Air Flagship and Kigali Amendment.

Key outcomes of the CCAC Conference 2024
- Launch of Clean Air Flagship: To save lives and slow climate change by boosting cooperation and reducing pollutant emissions.
- The programme is aimed at supporting governments to achieve cleaner air as quickly as possible, consistent with improved WHO air quality interim targets.
- ‘Used Heavy Duty Vehicles (HDVs) and the Environment’ Report: Launched by the UNEP & the CCAC, outlines a roadmap for reducing sector’s emissions through standardizing, monitoring, and greening strategies.
- CCAC Technology and Economic Assessment Panel: To help close the gap between technologies and finance by focusing on how to overcome barriers to scale up climate finance.
- Launched a major cost of inaction study that supports economic case to act on short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) to limit hazardous global warming and climate disasters.
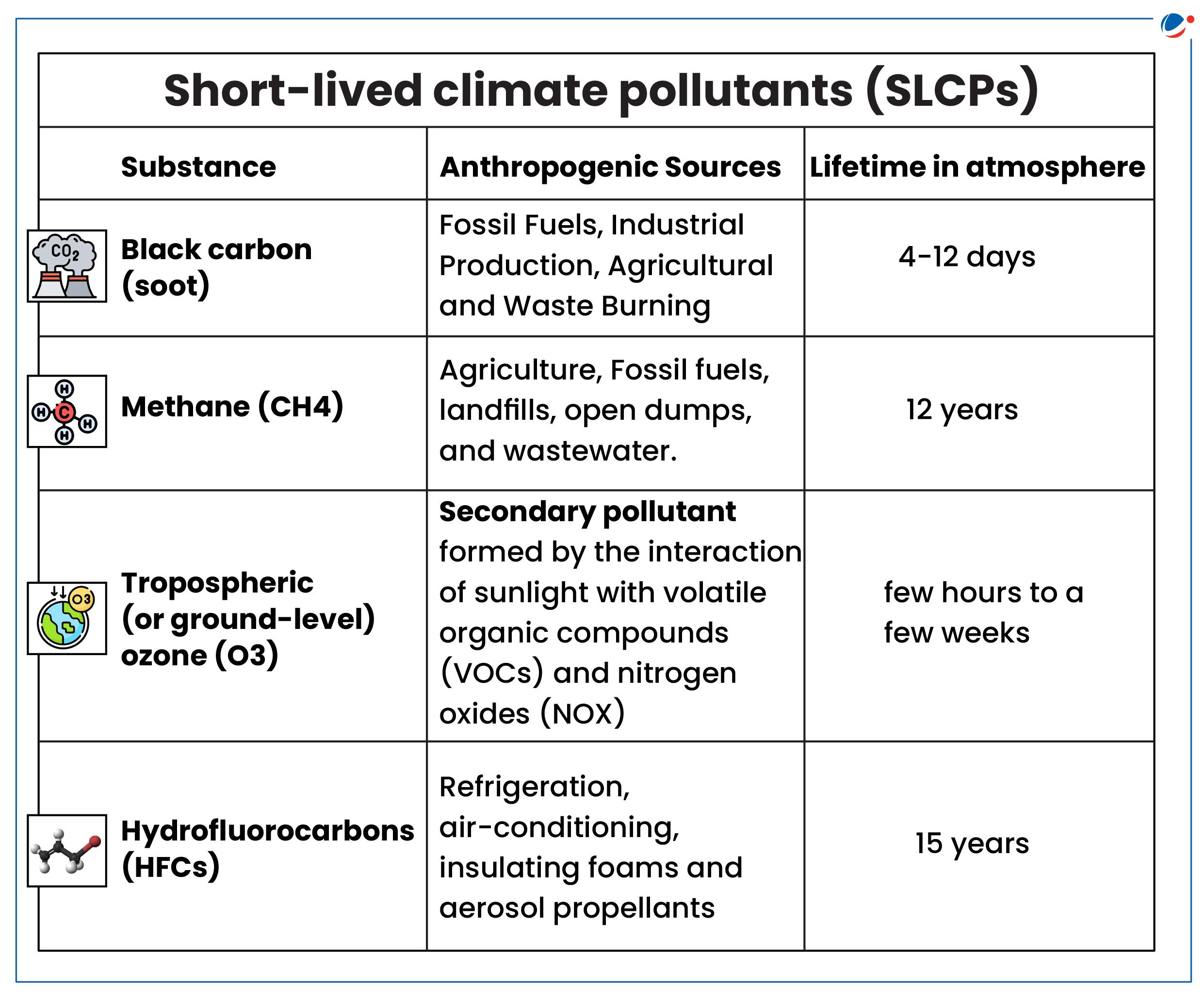
What are short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs)?
- They are powerful climate forcers that remain in the atmosphere for a much shorter period of time than carbon dioxide, yet their potential to warm the atmosphere can be many times greater.
Impact of SLCPs
- Global warming: SLCPs are the second largest contributor to human-caused climate warming after carbon dioxide, contributing up to 45% of global warming to date.
- On Human Health:
- Exposure to ground-level ozone can cause inflammation of the lungs, asthma and allergies.
- Black carbon is a primary contributor to both indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- On weather patterns: Tropospheric ozone influences cloud formation, thereby changing regional weather and, in particular, rainfall patterns.
- Accelerated ice melt: When deposited on ice or snowfields, black carbon reduces the albedo of these surfaces and leads to accelerated melting rates and atmospheric warming.
- On Agriculture: Tropospheric ozone harms vegetation by damaging leaves, reducing photosynthesis, impairing plant reproduction and growth, reducing plants’ uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) and decreasing crop yields.
Sector-wise solutions to reduce SLCPs
- Agriculture
- Promote farm-scale anaerobic digestion to control methane emissions from livestock
- Eliminate open burning in agriculture through regulation and farmer education to reduce black carbon.
- Fossil fuels
- Carry out pre-mining de-gasification and recovery and oxidation of methane from ventilation air from coal mines.
- Improve flaring efficiency in oil and gas production to reduce black Carbon.
- Waste
- Separate and treat biodegradable municipal waste, and turn it into compost or bioenergy to mitigate methane.
- Improve and extend municipal waste collection services and ban open burning of municipal waste to reduce black carbon.
- Household energy: Replace traditional cooking with clean-burning modern fuel and cookstove technology, such as solar, biogas, electricity to reduce black carbon.
- Transport: Adopt ultra-low sulphur diesel and minimum Euro 6/VI emission standards to mitigate black carbon.



