FUNCTIONING OF THE 17TH LOK SABHA
- PRS Legislative Research released Vital Stats on Functioning of the 17th Lok Sabha.
- The 17th Lok Sabha (LS) held its sessions between June 2019 and February 2024. During this period,
- It held 274 sittings and passed 179 Bills.
- Question Hour functioned for 60% of scheduled time in LS and 52% in Rajya Sabha.
- Question hour was cancelled in monsoon session of 2020, due to pandemic.
- Other Key Highlights of the report:
- Fewest sittings amongst all full-term Lok Sabhas with 206 instances of suspension of Members of Parliament.
- Average annual sitting days down to 55 from 135 in the first LS.
- For the first time, LS did not elect Deputy Speaker for entire duration.
- Article 93 of Constitution requires that LS elect a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker ‘as soon as may be’.
- Only 16% bills referred to committees for detailed scrutiny with passage of majority of bills without recorded voting.
- 35% of bills passed with less than an hour of discussion.
- Time spent on budget discussions has reduced with about 80% of the budget voted without discussion.
- Fewest sittings amongst all full-term Lok Sabhas with 206 instances of suspension of Members of Parliament.
- Tags :
- 17th Lok Sabha
- Lok Sabha
- Article 93
ANNUAL NESDA REPORT
- Annual National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) Way Forward Report, 2023.
- Report released by Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) highlights initiatives taken towards enhancing e-Service delivery.
- e-Service Delivery involves delivery of public/ other services such as receipt of forms and applications, issue/ grant of license, receipt or payment of money, etc., through electronic mode.
- Key Highlights of the report
- Jammu and Kashmir provides maximum (1117) number of e-Services, across States/UTs.
- 76% Mandatory e-services are available, an increase from 48% under NeSDA 2019.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Kerala, Assam and Odisha provide 100% of their services through their identified Single Unified Service Delivery Portal.
- Tourism sector achieved highest saturation for provision of all mandatory e-services in 23 out of 36 States/UTs.
- Significance of e-Service Delivery
- For Citizens: Empowerment and participation, improved access to services by removal of intermediaries, etc.
- For Governments: Informed data-driven decision making, resource optimization and cost efficiency by reducing inclusion and exclusion errors, etc.
- Challenges: Digital divide, lack of standardization and interoperability, issue of change management due to bureaucratic inertia, concerns related to cyber-security, etc.
- Tags :
- e-Service Delivery
- NeSDA
PREVENTION OF DAMAGE TO PUBLIC PROPERTY
- 22nd Law Commission (LC) submits 284th Report titled Prevention of Damage to Public Property.
- Commission took suo motu cognizance to prepare the report on account of rising incidents of vandalism and consequent loss to the state exchequer.
- Also, it highlighted the issue of wilful obstruction of public place or way.
- It said that only some States have provisions for dealing with obstructions on public pathways.
- Key Recommendations:
- Amendment in the PDPP Act, 1984, it should include
- One of the conditions for bail should be the deposit of an amount equivalent to the estimate value of the property damaged.
- Enact comprehensive law dealing with wilful obstruction.
- Also, related provision can be included in BNS.
- Amendment in the PDPP Act, 1984, it should include
- Constitutional and Legal Provisions for Protection
- Fundamental Right under Article 19 implicitly contains the Right to protest.
- However, demonstration which creates nuisance and disturbances are not covered under it.
- Fundamental Duties, Article 51 A (duty of every citizen to safeguard public property and to abjure violence).
- Prevention of Damage to Public Property (PDPP), Act 1984 contains provisions dealing with mischiefs resulting in damage of public property.
- Sections 425 to 440 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) deal with it.
- Fundamental Right under Article 19 implicitly contains the Right to protest.
Several sections of Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) (which will replace IPC) deal with it.
Related Supreme Court Judgement
|
- Tags :
- Law Commission
- Public Property
PORTALS FOR A ‘MODERNIZED MEDIA LANDSCAPE’
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting launched 4 new media-related portals to streamline media-related services under its umbrella.
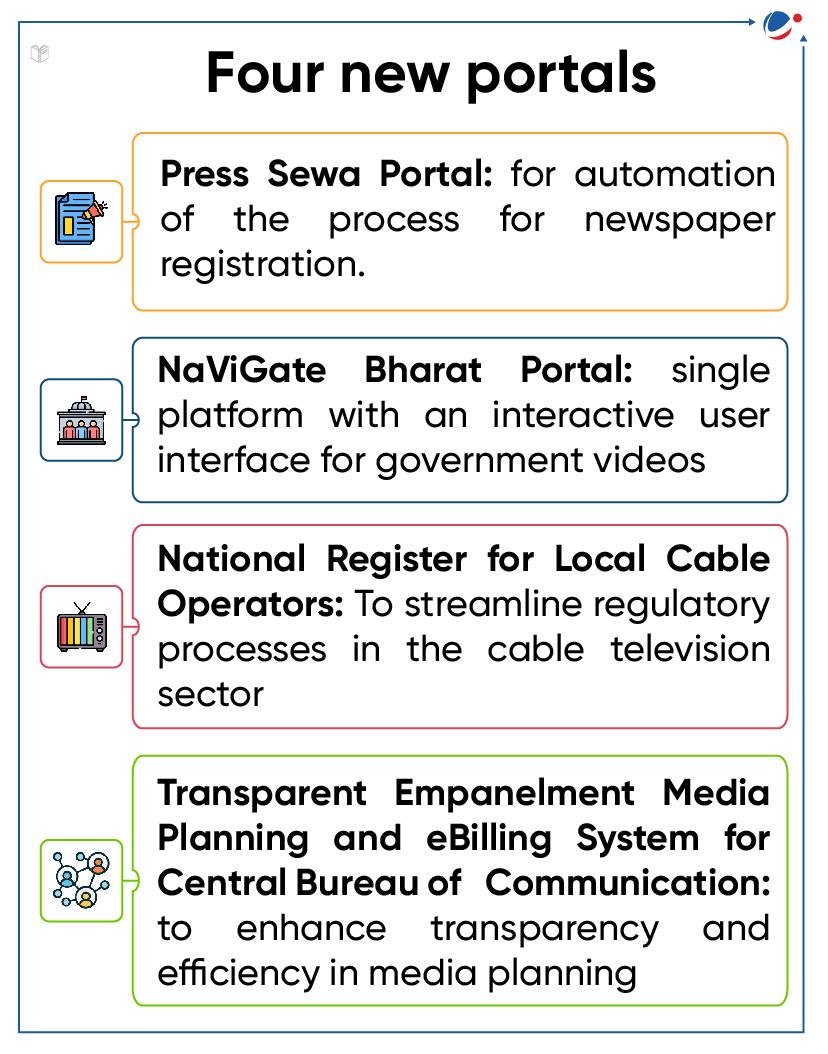
- Tags :
- Portals for a ‘Modernized Media Landscape’
- Media
- Portal
CORRUPTION PERCEPTIONS INDEX (CPI), 2023
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023.
- India was ranked 85 in 2022.
- About CPI
- Released by: Transparency International
- Ranks countries and territories by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- In 2023, Denmark ranked first, followed by Finland, New Zealand, and Norway.
- Tags :
- Rank
- Corruption
PANDARAM LANDS
- Lakshadweep administration continues to number trees on Pandaram lands.
- Laccadive Minicoy and Amini Islands Land Revenue and Tenancy Regulation, 1965 defines Pandaram lands as
- land in which Government has, a proprietary right immediately before the commencement of this Regulation and
- includes any land in which government may acquire such rights under this Regulation or under any other law.
- Land other than pandaram land over which a person has proprietary rights under the customary law of the Islands are defined as "jenmam land" under the 1965 regulation.
- Tags :
- Lakshadweep
- Land rights
AADHAAR CARD
- Employees' Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has removed Aadhaar from list of acceptable documents for proof of Date of Birth (DoB).
- Aadhaar is considered a proof of identity but not of citizenship or DoB.
- About Aadhaar:
- 12-digit random number issued by Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI).
- UIDAI is a statutory authority established under the Aadhaar Act, 2016.
- It contains Demographic (Name, Gender, DoB, Address) & Biometric (Fingerprints, Iris scans and Facial Photograph) data.
- Eligibility: Any resident of India of any age and gender.
- 12-digit random number issued by Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI).
- Tags :
- Aadhaar
- UIDAI



