NITI AAYOG LAUNCHES GROW REPORT AND PORTAL
- NITI Aayog unveiled the Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW) report.
- Report emphasizes potential of converting wastelands into productive agroforestry zones.
- It employed remote sensing and GIS techniques to evaluate the suitability of agroforestry practices across all districts of India and introduced an Agroforestry Suitability Index (ASI) for national-level prioritization.
- NITI Aayog also launched “GROW-Suitability Mapping” portal on Bhuvan (a geoportal of ISRO) for ensuring universal access to state and district-level data.
- Wastelands are lands which are unproductive, unfit for cultivation, grazing and other economic uses.
- According to Wasteland Atlas of India 2019, wastelands constitute 16.96% of geographical area of India in 2015-16.
- Agroforestry is a collective name for land-use systems where trees are managed together with crops and/or animal production systems in agricultural settings.
- Presently, agroforestry covers 8.65% of India's total geographical area.
- Three main types:
- Agrisilvicultural systems are a combination of crops and trees.
- Silvopastoral systems combine forestry and grazing of domesticated animals on pastures or on-farm.
- Agrosylvopastoral systems where trees, animals and crops can be integrated.
- Significance of Agroforestry
- Mitigating climate change through microclimate moderation and carbon sequestration
- Enhancing productivity, soil fertility and conserving soil
- Optimizing use of arable land.

- Tags :
- Agroforestry
- Wasteland
- NITI Aayog
TERAI ARC LANDSCAPE (TAL)
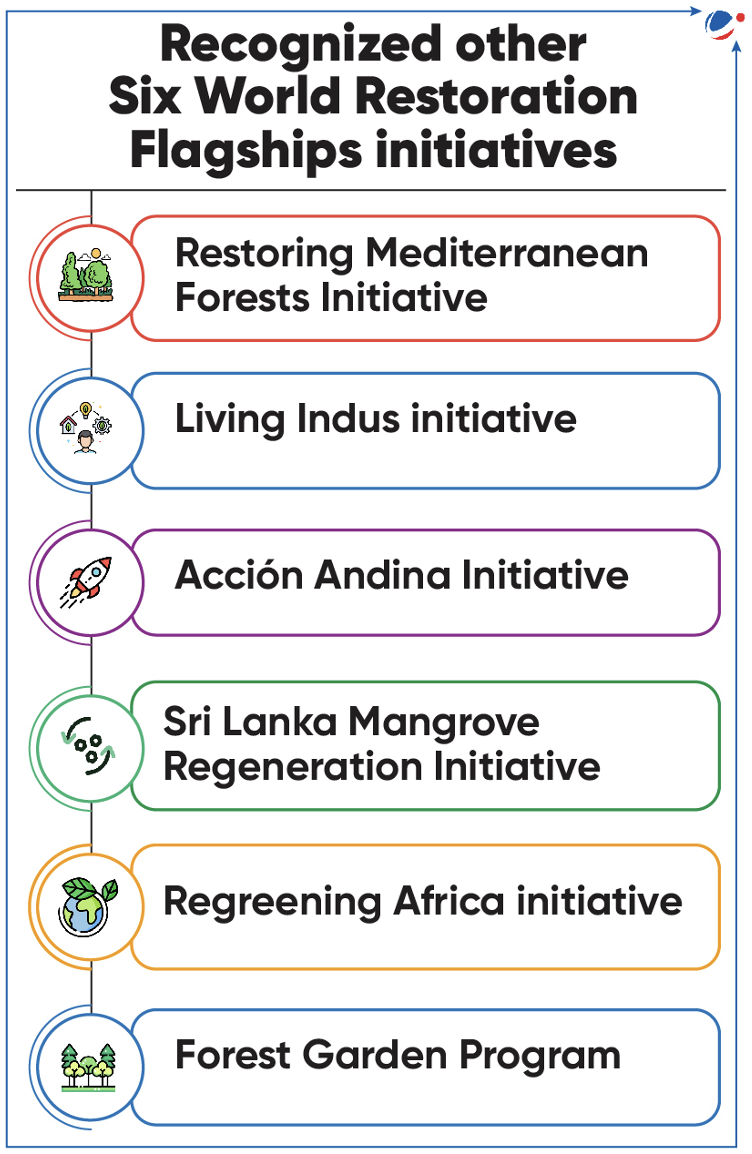
- Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) recognized as the United Nation World Restoration Flagship.
- Along with TAL, 6 other initiatives have been recognised (refer to infographics).
- Recognized initiatives will be eligible for technical and financial UN support.
- In 2022, Namami Gange initiative has been also recognized under it.
- About Terai Arc Landscape (TAL)
- A Trans-boundary biodiversity hotspot, launched in 2001.
- TAL is Critical habitats for tigers, rhinos, elephants, etc.
- Aims to conserve ecosystems of the Terai and Churia hills.
- Covers several protected areas such as Corbett Tiger Reserve, Rajaji National Park etc.
- Extend over 900 km from the Bagmati River (Nepal) in the east to the Yamuna River (India) in the west.
- Stretching across 5.10 million hectares and over seven million people depend on the Landscape.
- A Trans-boundary biodiversity hotspot, launched in 2001.
- About World Restoration Flagship (commenced in 2022)
- Recognized under the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021-30).
- Led by UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) and other partner organisation.
- Objective: Prevent, halt, and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.
- Selection Criteria: On the basis of Geographic and probability of success criteria.
- Progress is monitored through the Framework for Ecosystem Restoration Monitoring.
- Tags :
- United Nation World Restoration Flagship
- Terai
GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT FACILITY (GEF) COUNCIL MEETING
- First Global Environment Facility (GEF) Council meeting of Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF) held in United States.
- GBFF aims to scale up financing for implementation of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
- Ratified by 186 countries and launched in 2023 at Seventh GEF Assembly in Vancouver, Canada.
- Decisions of GBFF Council are to be taken by consensus.
- World Bank invited to serve as Trustee of GBFF.
- Key highlights of meeting
- GEF’s member government have agreed to invest $1.1 billion for international action on biodiversity, climate change, nature renewal, and pollution control.
- They endorsed $203 million for 21 climate change adaptation projects funded by Least Developed Countries Fund and Special Climate Change Fund.
- Spain announced 10 million euros to GBFF, adding to contributions announced by Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, and Japan.
- GBFF Resource Allocation Policy and Project Cycle Policy were approvedto allocate donor funds based on availability.
- About KMGBF
- Adopted at COP15 (held in Montreal) to UN Convention on Biological Diversity.
- KMGBF has set 23 targets to be achieved by 2030 which include 30% conservation of land and sea, 50% reduction of invasive species, raising at least $200 billion per year etc.

- Tags :
- Global Environment Facility (GEF)
- Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF)
- Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
SPECIES THREAT ABATEMENT AND RESTORATION (STAR) METRIC
- STAR metric, developed by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in partnership with other organizations and experts, has been expanded for use in marine areas.
- It was first unveiled in 2021 for use in terrestrial areas.
- The STAR metric utilizes existing data from IUCN Red List of Threatened Species to quantify extinction risks and threats faced by species.
- STAR assesses the potential of specific actions at specific locations to contribute to international conservation targets.
- STAR estimates the contribution of two kinds of action – threat abatement and habitat restoration.
- Tags :
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- Red List
CONSERVATION RESERVE
- Telangana’s State Board for Wildlife (SBWL) approved the corridor area between Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kawal Tiger Reserve (Telangana) as a conservation reserve.
- SBWL is established under the Wildlife (Protection) Amendment (WPA) Act, 2002, headed by Chief Minister or Administrator in case of UT.
- About Conservation Reserve:
- A protected area under the ‘Wildlife (Protection) Act (WPA), 1972’ (added through the WPA Act of 2002).
- Acts as buffer zone to or connectors and migration corridors between national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and protected areas.
- Declared by the State Government, after consulting with the central government and the local communities.
- It is administered with the help of the Conservation Reserve Management Committee.
- Tags :
- Kawal Tiger Reserve
- Wildlife (Protection) Amendment (WPA) Act, 2002
- Wildlife (Protection) Act (WPA), 1972
- Tadoba-Andheri
ENERGY CHARTER TREATY
- The UK to leave 'Outdated' Fossil Fuel Friendly Treaty ie. The Energy Charter Treaty.
- About The Energy Charter Treaty
- It provides a multilateral framework for energy cooperation that is unique under international law.
- It entered into legal force in April 1998.
- It is designed to promote energy security through the operation of more open and competitive energy markets while respecting the principles of sustainable development and sovereignty over energy resources.
- Currently, there are 53 Signatories and Contracting Parties to the Treaty.
- Tags :
- UK
BRUMATION
- During the winter months, American alligators go into a state of brumation, a type of hibernation.
- Hibernation is a period of inactivity that allows animals to survive when food is scarce and the weather is harsh.
- About Brumation:
- Period of dormancy exhibited by reptiles and amphibians in colder months.
- Reptiles are ectothermic (their body temperature is dependent on their environment), hence require brumation.
- In it, reptiles may retreat to underground burrows or other sheltered areas.
- Other types of hibernation:
- Diapause: a state of arrested growth or reproduction of many hibernating or estivating arthropods
- Aestivation: Summer dormancy in invertebrates and fish
- Torpor: Short-term physiological state of decreased activity
- Tags :
- hibernation
WHITE RHINOS
- World’s first white rhinoceros In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) pregnancy could save subspecies.
- Scientists has announced the first successful embryo transfer in white rhinoceros using IVF method that could save Critically endangered northern white rhino subspecies from extinction.
- Other biotechnologies to protect species
- Bio-banks store biological samples (cell, tissues etc.) for research and as backup resource to preserve genetic diversity.
- Biosynthesis creates substitutes for animal-derived products like safer fungicides from printed DNA to protect endangered species.
- Gene drive can be harnessed to eliminate invasive species like rats with high efficiency and minimal harm to native wildlife.
- About Rhino
- Five species of rhino: 2 African (White Rhino, Black Rhino) and 3 Asian [Greater One Horned Rhino (Indian rhino), Sumatran Rhino, and Javan Rhino].
- Threat: Habitat loss, poaching for horn, climate change etc.
Difference between White Rhino and Indian Rhino
Features | White Rhino (African Rhino)  | Indian Rhino (Asian Rhino)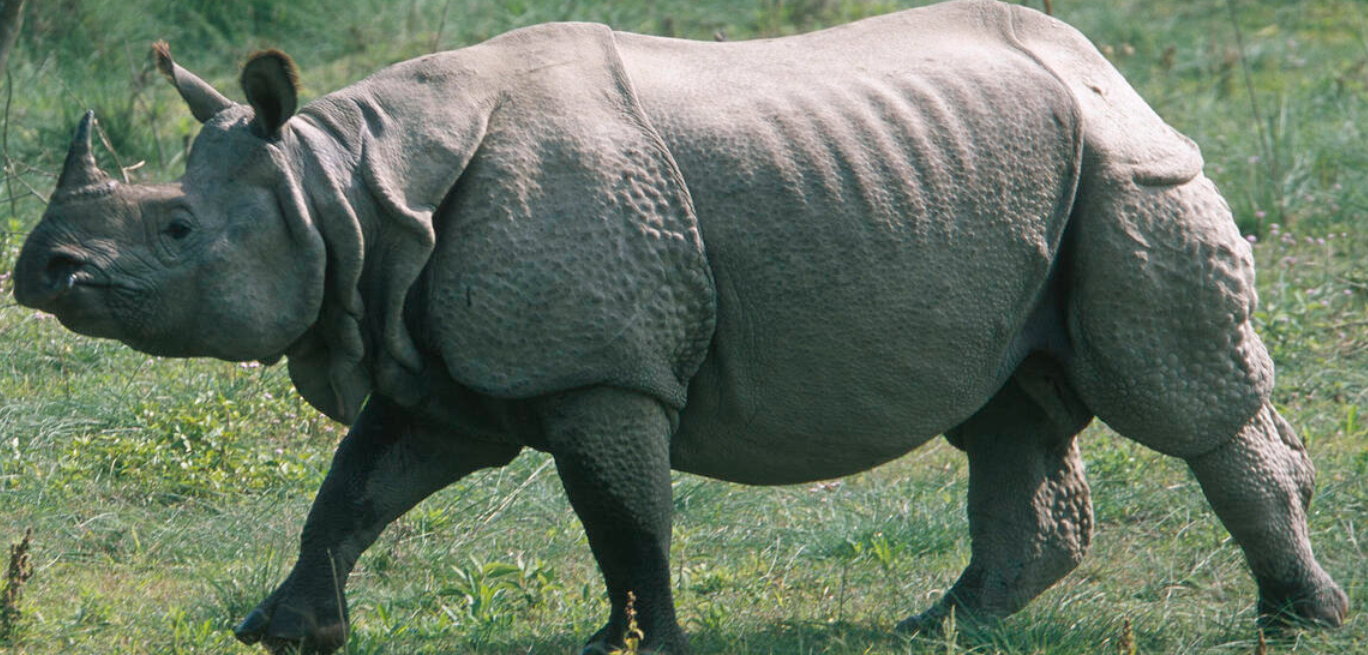  |
Size | Second-largest land mammals after elephants | Largest of all Asian rhino species |
Appearance | Barrel-shaped with a flat back 2 Horns Wallow in mud | Knobby skin that appears to be armor-plated One Horn Good swimmers |
Habitat | Long and short grass savannah areas in grasslands | Tropical and Subtropical Grasslands, Savannahs, and Shrub-lands |
Distribution | Namibia, Uganda, Rwanda etc. | India (Assam, West Bengal and Utter Pradesh), Nepal etc. |
Conservation status | Near threatened (IUCN) (Southern white rhino subspecies is Near threatened) | Vulnerable (IUCN) Schedule I (Wildlife Protection Act, 1972) |
Note: Northern White, black, Javan, and Sumatran rhinos—are categorized as critically endangered under IUCN’s red list. | ||
- Tags :
- Schedule I WPA
- RHINOS
- Critically endangered
INDIAN SKIMMERS
- India and Bangladesh submit a joint proposal to list Indian skimmers (also known as Indian scissors bill) under the Convention on Migratory Species.
- About Indian Skimmer
- Indian skimmer is found in the coastal estuaries of western and eastern India. It occurs primarily on larger, sandy, lowland rivers, around lakes and adjacent marshes, estuaries and coasts.
- It breeds colonially on large, exposed sand-bars and islands.
- It feeds on surface-dwelling fish, small crustaceans and insect larvae.
- Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Not listed
- WPA, 1972: Schedule I
- Tags :
- Schedule I WPA
- endangered
- Convention on Migratory Species
- Endangered
NEEM TREE (AZADIRACHTA INDICA A. JUSS)
- The Neem Summit has been organized by collaboration with lCAR-Central Agroforestry Research Institute.
- About Neem Tree
- Native to Indian sub-continent.
- Climate: Grow in arid, semi-arid, wet tropical and sub-tropical climates and is tolerant to high temperature up to 49 °C.
- Type: Evergreen tree (deciduous in drier areas).
- Benefits:
- Has a medicinal property.
- Act as very efficient, natural air filters trapping dust particles, absorbing gaseous pollutants.
- Other- Pesticides, mosquito repellents, fertilizers (neem coated urea), etc.
- Tags :
- Neem Summit
- lCAR-Central Agroforestry Research Institute
HYPERLOCAL WEATHER FORECASTING
Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare have initiated the Weather Information Network and Data System (WINDS) to generate long-term, hyper-local weather data.
About WINDS
- It set up a robust mechanism to integrate weather data, pooled from different weather observation systems in the country, into a single national level WINDS portal.
- Under this programme, more than 2 lakhs ground stations will be installed,
- which can help in enhancing weather data utilisation and thus in improving weather predictions and decision making.
About Hyperlocal Weather Forecasting
- Hyperlocal weather forecasting provides granular and localized weather predictions,
- It enables farmers to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting based on real-time weather data specific to their location.
- This approach utilizes advanced technology, such as high-resolution weather models, weather sensors, and data analytics.
Why is hyperlocal weather forecasting required in India?
- Monsoon Variability: Tropical climates are more unpredictable and thereby more difficult to predict, as opposed to US and UK which have more systematic weather systems
- Disaster Preparedness and Response: Predicting rain, cyclones, heatwaves and drought accurately are critical to informed decision making on disaster management.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Where urban areas experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding areas. This localized heating complicates temperature forecasting and require localized forecasting.
- Tags :
- WINDS
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
- Monsoon
FLOOD MANAGEMENT AND BORDER AREAS PROGRAMME (FMBAP)
- Union Cabinet approves continuation of Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)
- FMBAP continuation has been approved for period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- It was initially launched during Eleventh Five Year Plan (2007–2012).
- FMBAP aims to supplement the efforts of the State Governments to protect human life, land and property from flood fury by providing technical guidance and financial assistance.
- Also, promotes bilateral co-operation in the field of water resources with neighboring countries.
Key Features of Scheme
- Type: Centrally sponsored Scheme
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Sub-components:
- Flood Management Programme (FMP)
- Covers critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- Funding Pattern: 90%:10% between Centre and 8 North-Easter States and Hilly States (For rest state 60%:40 %).
- 427 projects have been completed under it which have benefitted 4.99 mha of land and provided protection to 53.57 million people.
- River Management and Border Areas (RMBA):
- Covers flood control and anti-erosion works on common border rivers with neighbouring countries.
- Hydrological observations and flood forecasting.
- Investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers.
- Funding Pattern: 100% central assistance.
- Flood Management Programme (FMP)
- Tags :
- Ministry of Jal Shakti
ATMOSPHERIC RIVER
- California (the USA) has been hit by two back-to-back Atmospheric River storms.
- Atmospheric Rivers
- Atmospheric Rivers indicate narrow, elongated corridors of concentrated moisture transport associated with extra-tropical cyclones.
- Typically located within low-level jet, an area of strong winds in lower levels of atmosphere, ahead of cold front in an extra-tropical cyclone.
- These are largest transport mechanisms of freshwater on Earth.
- Strong landfall by interacting with topography, can deposit significant amounts of precipitation in short periods of time leading to flooding and mudslides.
- Tags :
- extra-tropical cyclones
ATLANTIC MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION (AMOC)
- Researchers developed an early warning indicator for the breakdown of the AMOC.
- AMOC has been labeled as one of the tipping elements in the climate system.
- About AMOC
- The AMOC circulates water from north to south and back in a long cycle within the Atlantic Ocean.
- This circulation brings warmth to various parts of the globe and also carries nutrients necessary to sustain ocean life.
- It is driven by differences in temperature and salt content.
- It is being eroded by faster than expected melt-off of Greenland’s glaciers and Arctic ice sheets.
- Implications of AMOC collapse: Rise in Atlantic Sea levels; Flipping of wet and dry seasons in the Amazon; More erratic fluctuations in temperatures; warmer southern hemisphere.
- The AMOC circulates water from north to south and back in a long cycle within the Atlantic Ocean.
- Tags :
- AMOC
RIP CURRENTS
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and ISRO to monitor and issue operational forecast alerts of rip currents.
- About Rip Currents
- A strong flow of water running from a beach back to open ocean, sea, or lake.
- They can be as narrow as 10 or 20 feet in width though they may be up to ten times wider.
- Prevalent along East, Gulf, and West coasts of U.S., as well as along shores of Great Lakes.
- They do not pull people under water rather they pull people away from shore.
- Tags :
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS)



